versionarte 0.7.2  versionarte: ^0.7.2 copied to clipboard
versionarte: ^0.7.2 copied to clipboard
Remotely manage your Flutter app's versioning and availability.
versionarte #
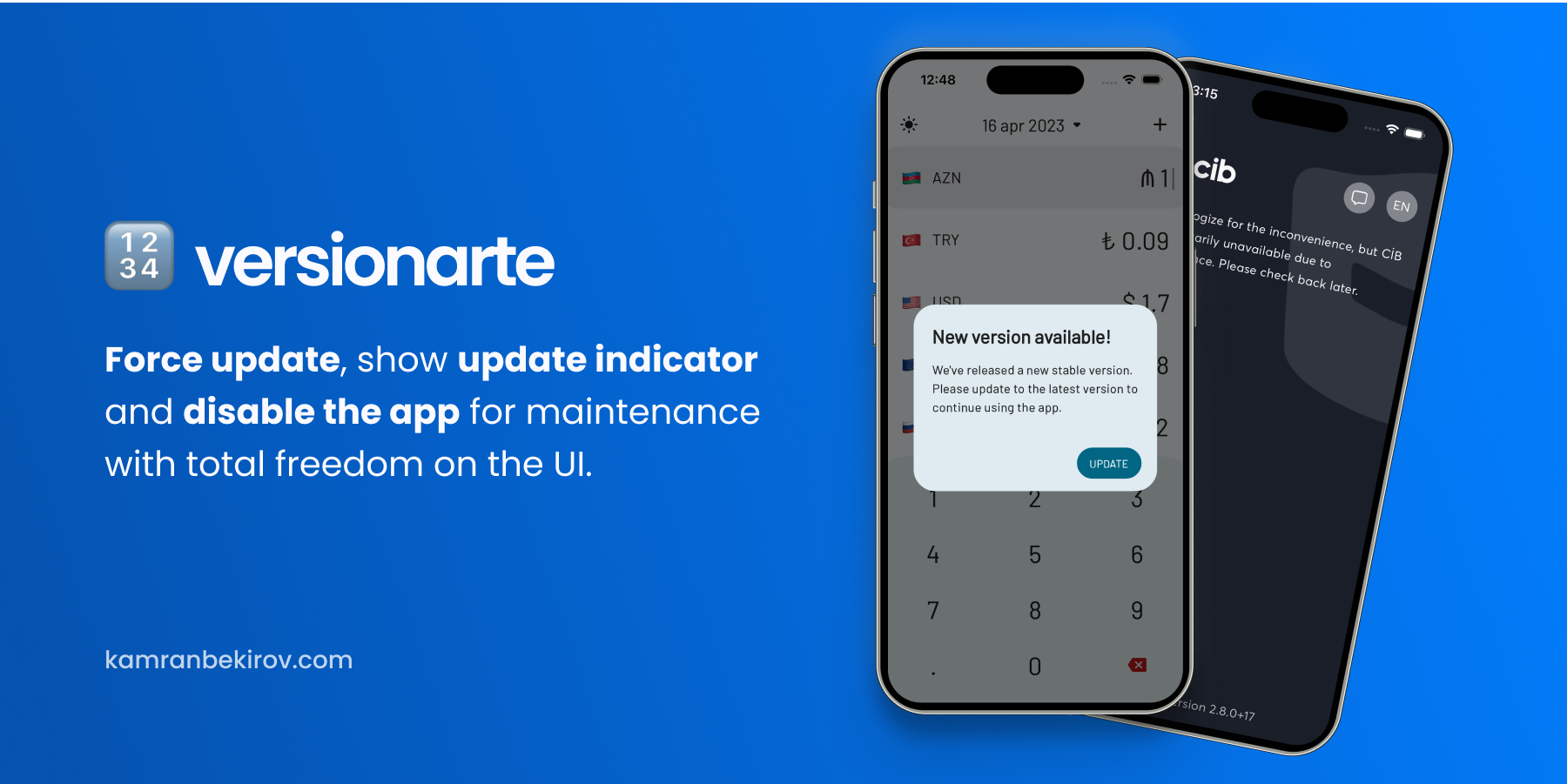
Versionarte allows you to remotely manage your Flutter app's versioning and availability, with a variety of heplful, and in some cases life-saving features:
- 😈 Force users to update to the latest version of the app before continuing.
- 🚧 Disable your app for maintenance using custom remotely-stored info text.
- 🆕 Inform users when a new optional update is available for your app.
- 🔗 Launch the App Store on iOS and Play Store on Android.
Package comes with built-in RESTful API and Firebase Remote Config support. However, you can also fetch your configuration data from any source by extending the VersionarteProvider class. You have total freedom over the UI allowing you to customize the user experience to fit your app's branding and style.
🚀 Motivation #
Mobile application development is unique in that any changes, whether it be adding new features, fixing bugs, or disabling the app for maintenance, requires submitting a new version to the app store and waiting for approval. Even after approval, users may still need to manually update their app to access the latest version.
To simplify the app versioning process, versionarte offers remote management of app versioning and availability. This makes the app development process more controllable.
🖋️JSON format #
versionarte has a specific JSON format, which you must use to provide the versioning details remotely. Whether you're using RemoteConfigVersionarteProvider, RestfulVersionarteProvider, or a custom VersionarteProvider, you must always use the structured JSON below:
{
"android": {
"minimum": "2.7.1",
"latest": "2.8.0",
"active": true,
"message": {
"en": "App is in maintanence mode, please come back later.",
"es": "La aplicación está en modo de mantenimiento, vuelva más tarde."
}
},
"ios": {
// same data we used for "android"
}
// "macos", "windows", "linux" will be suppoerted in next versions
}
android: This is the key that contains the object related to the Android app.minimum: This is a string key that represents the minimum version of the Android app that the user must have to use the app.latest: This is a string key that represents the latest version of the Android app that is available for download.active: This is a boolean key that represents whether the app is currently active or not. In this case, it is set to true, which means the app is currently active.message: This is an object key that contains the messages in different languages that will be displayed to the user. It has two subkeys, "en" and "es", which represent English and Spanish, respectively. Each subkey has a string value representing a message in that language.
🕹️ Usage #
Using Firebase Remote Config #
Below is a example of how to use Versionarte with Firebase Remote Config:
final result = await Versionarte.check(
versionarteProvider: RemoteConfigVersionarteProvider(),
);
In this example, we import the required packages and call the Versionarte.check function to retrieve the VersionarteResult. The RemoteConfigVersionarteProvider is used to retrieve the remote version information from Firebase Remote Config.
Then, we use the result to decide what to do next based on the versioning state. Here's an example of how to do that:
if (result == VersionarteResult.inactive) {
// TODO: Handle the case where remote version information is inactive
} else if (result == VersionarteResult.mustUpdate) {
// TODO: Handle the case where an update is required
} else if (result == VersionarteResult.couldUpdate) {
// TODO: Handle the case where an update is optional
}
There are two other values that you can receive as a result: VersionarteStatus.upToDate and VersionarteStatus.unknown. But these two are never used mostly.
Note that you don't need to try-catch the Versionarte.check function, as the called function catches all the errors inside. If anything goes wrong, an instance of VersionarteResult is still returned, with a message property containing the error message. Also, be sure to check the debug console to see the debug-only prints that the package prints.
You want to use your own RESTful API instead of FirebaseRemoteConfig? Use RestfulVersionarteProvider:
final result = await Versionarte.check(
versionarteProvider: RestfulVersionarteProvider(
url: 'https://myapi.com/getVersioning',
),
);
Maybe you want to use Firestore, Graphql or any other service to provider StoreVersioning? Extend VersionarteProvider, override getStoreVersioning, fetch serverside data, parse it into a StoreVersioning instance using StoreVersioning.fromJson factory constructor:
See the example directory for a complete sample app.
🤓 Contributors #
🐞 Bugs/Requests #
If you encounter any problems please open an issue. If you feel the library is missing a feature, please raise a ticket on GitHub and we'll look into it. Pull requests are welcome.
