dart_periphery 0.8.25-RC  dart_periphery: ^0.8.25-RC copied to clipboard
dart_periphery: ^0.8.25-RC copied to clipboard
dart_periphery is a Dart port of the native c-periphery library for Linux Peripheral I/O (GPIO, LED, PWM, SPI, I2C, MMIO and Serial peripheral I/O).
dart_periphery #
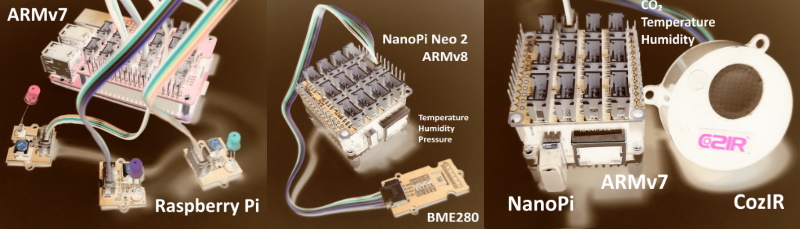
Introduction #
dart_periphery is a Dart port of the native c-periphery library for Linux Peripheral I/O (GPIO, LED, PWM, SPI, I2C, MMIO and Serial peripheral I/O). This package is specially intended for SoCs like Raspberry Pi, NanoPi, Banana Pi et al.
What is c-periphery? #
Abstract from the project web site:
c-periphery is a small C library for
- GPIO,
- LED,
- PWM,
- SPI,
- I2C,
- MMIO (Memory Mapped I/O)
- Serial peripheral I/O
interface access in userspace Linux. c-periphery simplifies and consolidates the native Linux APIs to these interfaces. c-periphery is useful in embedded Linux environments (including Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone, etc. platforms) for interfacing with external peripherals. c-periphery is re-entrant, has no dependencies outside the standard C library and Linux, compiles into a static library for easy integration with other projects, and is MIT licensed
dart_periphery binds the c-periphery library with the help of the dart:ffi mechanism. Nevertheless, dart_periphery tries to be close as possible to the original library. See following documentation. Thanks to Vanya Sergeev for his great job!
Why c-periphery? #
The number of GPIO libraries/interfaces is becoming increasingly smaller.
- The famous wiringpi library is deprecated.
- GPIO sysfs is deprecated.
dart_periphery currently has beta status. All interfaces are ported:
- GPIO example / API
- I2C example / API
- SPI example / API
- Serial example / API
- PWM example / API
- Led (onboard leds) example / API
- MMIO (Memory Mapped I/O) example / API
Examples #
GPIO #
import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
import 'dart:io';
void main() {
var config = GPIOconfig();
config.direction = GPIOdirection.GPIO_DIR_OUT;
print('Native c-periphery Version : ${getCperipheryVersion()}');
print('GPIO test');
var gpio = GPIO(18, GPIOdirection.GPIO_DIR_OUT);
var gpio2 = GPIO(16, GPIOdirection.GPIO_DIR_OUT);
var gpio3 = GPIO.advanced(5, config);
print('GPIO info: ' + gpio.getGPIOinfo());
print('GPIO native file handle: ${gpio.getGPIOfd()}');
print('GPIO chip name: ${gpio.getGPIOchipName()}');
print('GPIO chip label: ${gpio.getGPIOchipLabel()}');
print('GPIO chip name: ${gpio.getGPIOchipName()}');
print('CPIO chip label: ${gpio.getGPIOchipLabel()}');
for (var i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
gpio.write(true);
gpio2.write(true);
gpio3.write(true);
sleep(Duration(milliseconds: 200));
gpio.write(false);
gpio2.write(false);
gpio3.write(false);
sleep(Duration(milliseconds: 200));
}
gpio.dispose();
gpio2.dispose();
gpio3.dispose();
}
I2C #

import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
/// https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Barometer_Sensor-BME280/
/// Grove - Temp&Humi&Barometer Sensor (BME280) is a breakout board for Bosch BMP280 high-precision,
/// low-power combined humidity, pressure, and temperature sensor.
void main() {
// Select the right I2C bus number /dev/i2c-?
// 1 for Raspbery Pi, 0 for NanoPi (Armbian), 2 Banana Pi (Armbian)
var i2c = I2C(1);
try {
print('I2C info:' + i2c.getI2Cinfo());
var bme280 = BME280(i2c);
var r = bme280.getValues();
print('Temperature [°] ${r.temperature.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
print('Humidity [%] ${r.humidity.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
print('Pressure [hPa] ${r.pressure.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
} finally {
i2c.dispose();
}
}
import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
/// Grove - Temp&Humi Sensor(SHT31) is a highly reliable, accurate,
/// quick response and integrated temperature & humidity sensor.
void main() {
// Select the right I2C bus number /dev/i2c-?
// 1 for Raspbery Pi, 0 for NanoPi (Armbian), 2 Banana Pi (Armbian)
var i2c = I2C(1);
try {
var sht31 = SHT31(i2c);
print(sht31.getStatus());
print('Serial number ${sht31.getSerialNumber()}');
print('Sensor heater active: ${sht31.isHeaterOn()}');
var r = sht31.getValues();
print('SHT31 [t°] ${r.temperature.toStringAsFixed(2)}');
print('SHT31 [%°] ${r.humidity.toStringAsFixed(2)}');
} finally {
i2c.dispose();
}
}
SPI #
import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
void main() {
var spi = SPI(0, 0, SPImode.MODE0, 1000000);
try {
print('SPI info:' + spi.getSPIinfo());
var bme280 = BME280.spi(spi);
var r = bme280.getValues();
print('Temperature [°] ${r.temperature.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
print('Humidity [%] ${r.humidity.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
print('Pressure [hPa] ${r.pressure.toStringAsFixed(1)}');
} finally {
spi.dispose();
}
}
Serial #

import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
import 'dart:io';
///
/// [COZIR CO2 Sensor](https://co2meters.com/Documentation/Manuals/Manual_GC_0024_0025_0026_Revised8.pdf)
///
void main() {
print('Serial test - COZIR CO2 Sensor');
var s = Serial('/dev/serial0', Baudrate.B9600);
try {
print('Serial interface info: ' + s.getSerialInfo());
// Return firmware version and sensor serial number - two lines
s.writeString('Y\r\n');
var event = s.read(256, 1000);
print(event.toString());
// Request temperature, humidity and CO2 level.
s.writeString('M 4164\r\n');
// Select polling mode
s.writeString('K 2\r\n');
// print any response
event = s.read(256, 1000);
print('Response ${event.toString()}');
sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));
for (var i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
s.writeString('Q\r\n');
event = s.read(256, 1000);
print(event.toString());
sleep(Duration(seconds: 5));
}
} finally {
s.dispose();
}
}
Led #

import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
import 'dart:io';
void main() {
/// Nano Pi power led - see 'ls /sys/class/leds/'
var led = Led('nanopi:red:pwr');
try {
print('Led handle: ${led.getLedInfo()}');
print('Led name: ${led.getLedName()}');
print('Led brightness: ${led.getBrightness()}');
print('Led maximum brightness: ${led.getMaxBrightness()}');
var inverse = !led.read();
print('Original led status: ${(!inverse)}');
print('Toggle led');
led.write(inverse);
sleep(Duration(seconds: 5));
inverse = !inverse;
print('Toggle led');
led.write(inverse);
sleep(Duration(seconds: 5));
print('Toggle led');
inverse = !inverse;
led.write(inverse);
sleep(Duration(seconds: 5));
print('Toggle led');
led.write(!inverse);
} finally {
led.dispose();
}
}
PWM #
Ensure that PWM is correct enabled. e.g. see the following documentation for the Raspberry Pi.
import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
import 'dart:io';
void main() {
var pwm = PWM(0, 0);
try {
print(pwm.getPWMinfo());
pwm.setPeriodNs(10000000);
pwm.setDutyCycleNs(8000000);
print(pwm.getPeriodNs());
pwm.enable();
print("Wait 20 seconds");
sleep(Duration(seconds: 20));
pwm.disable();
} finally {
pwm.dispose();
}
}
MMIO #
Memory Mapped I/O: Turns on a led at pin 18 on a Raspberry Pi using MMIO. This direct register access example is derived from elinux.org.
import 'package:dart_periphery/dart_periphery.dart';
import 'dart:io';
const int BCM2708_PERI_BASE = 0x3F000000; // Raspberry Pi 3
const int GPIO_BASE = BCM2708_PERI_BASE + 0x200000;
const int BLOCK_SIZE = 4 * 1024;
/// Helper class for the hardcore bit manipulation.
class MemMappedGPIO {
MMIO mmio;
MemMappedGPIO(this.mmio);
// #define INP_GPIO(g) *(gpio+((g)/10)) &= ~(7<<(((g)%10)*3))
void setPinInput(final int pin) {
var offset = (pin ~/ 10) * 4;
var value = mmio[offset];
value &= (~(7 << (((pin) % 10) * 3)));
mmio[offset] = value;
}
// #define OUT_GPIO(g) *(gpio+((g)/10)) |= (1<<(((g)%10)*3))
void setPinOutput(final int pin) {
setPinInput(pin);
var offset = (pin ~/ 10) * 4;
var value = mmio[offset];
value |= (1 << (((pin) % 10) * 3));
mmio[offset] = value;
}
// #define GPIO_SET *(gpio+7) - sets bits which are 1 ignores bits which are 0
void setPinHigh(int pin) {
mmio[7 * 4] = 1 << pin;
}
// #define GPIO_CLR *(gpio+10) - clears bits which are 1 ignores bits which are 0
void setPinLow(int pin) {
mmio[10 * 4] = 1 << pin;
}
// #define GET_GPIO(g) (*(gpio+13)&(1<<g)) - 0 if LOW, (1<<g) if HIGH
int getPin(int pin) {
return mmio[13 * 4] & (1 << pin);
}
}
void main() {
// Needs root rights and the GPIO_BASE must be correct!
// var mmio = MMIO(GPIO_BASE, BLOCK_SIZE);
var mmio = MMIO.advanced(0, BLOCK_SIZE, '/dev/gpiomem');
var gpio = MemMappedGPIO(mmio);
try {
print(mmio.getMMIOinfo());
var pin = 18;
print('Led (pin=18) on');
gpio.setPinOutput(pin);
gpio.setPinHigh(pin);
sleep(Duration(seconds: 10));
gpio.setPinLow(pin);
print('Led (pin=18) off');
} finally {
mmio.dispose();
}
}
Install Dart on Raspian and Armbian #
1.) Go to the home directory
cd ~
2.) Download the last stable Dart SDK form archiv for your CPU architecture/OS.
ARMv7 #
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/dart-archive/channels/stable/release/2.12.4/sdk/dartsdk-linux-arm-release.zip
unzip dartsdk-linux-arm-release.zip
ARMv8 #
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/dart-archive/channels/stable/release/2.12.4/sdk/dartsdk-linux-arm64-release.zip
unzip dartsdk-linux-arm64-release.zip
x86 #
https://storage.googleapis.com/dart-archive/channels/stable/release/2.12.4/sdk/dartsdk-linux-ia32-release.zip
unzip dartsdk-linux-ia32-release.zip
x86_64 #
https://storage.googleapis.com/dart-archive/channels/stable/release/2.12.4/sdk/dartsdk-linux-x64-release.zip
unzip dartsdk-linux-x64-release.zip
3.) Unpack and install SDK
sudo mv dart-sdk /opt/
sudo chmod -R +rx /opt/dart-sdk
4.) Add the Dart SDK to the path
nano ~/.profile
following command
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/dart-sdk/bin
at the end of the file and call
source ~/.profile
to apply the changes.
Test the installion
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ dart --version
Dart SDK version: 2.12.4 (stable) (Thu Apr 15 12:26:53 2021 +0200) on "linux_arm"
Native libraries #
Currently dart_periphery ships with four prebuild native c-periphery libraries for ARMv7/ARMv8/X86/X86_64
Following methods can be used to overwrite the loading of the prebuild library.
But be aware, any of these methods must be called before any dart_periphery interface is used!
useSharedLibray();
If this method is called, dart_periphery loads the shared library. For this case c-periphery must be installed as a shared library. See for section Shared Library for details.
To load a custom library call
setCustomLibrary(String absolutePath)
This method can be helpful in any case of a problem and for a currently not supported platform.
For a dart native binary, which can be deployed
dart compile exe i2c_example.dart
call
void useLocalLibrary()
The appropriate library should be in same dirctory as the exe.
flutter-pi #
dart_periphery works with flutter-pi, a light-weight Flutter Engine Embedder for Raspberry Pi. For futter-pi the appropriate library must be copied inside the flutter asset directory.
- In most cases the ARMv7 library: libperiphery_arm.so
- ARMv8 libperiphery_aarch64.so
See last section, native libraries for details.
Tested SoC hardware #
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B, OS: Raspian
- NanoPi with a Allwinner H3, Quad-core 32-bit CPU, OS: Armbian
- NanoPi M1 with a Allwinner H3, Quad-core 32-bit CPU: OS Armbian
- NanoPi Neo2 with a Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit CPU, OS: Armbian
- Banana Pi BPI-M1 with a Allwinner A20 Dual-core, OS: Armbian
Supported devices (sensors, actuators, expansion hats and displays) #
- SGP30: tVOC and eCO2 Gas Sensor
- BME280: Temperature, humidity and pressure sensor.
- BME680: Temperature, humidity pressure and gas (Indoor Airy Quaility) sensor.
- SHT31: Temperature and humidity sensor.
- CozIR: CO2, temperature and humidity sensor.
- Grove Gesture can recognize 9 basic gestures.
- MPU-6050 Six-Axis (Gyro + Accelerometer) sensor.
- FriendlyARM BakeBit Set
- Grove Base Hat/GrovePi Plus
- SSD1306 OLED (in progress)
Next steps #
- Add GPIO documentation for different SoCs.
- Port hardware devices from the mattjlewis / diozero Java Project to dart_periphery
Test matrix #
| Architecture | GPIO | GPIOsysfs | I2C | SPI | Serial | MMIO¹ | PWM | LED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARM ² | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ☐ | ✅ | ✅ |
| AARCH64 ³ | ❌⁴ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ☐ | ✅ | ✅ |
| X86 ⁵ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| X86_64 ⁵ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
☐ missing test | ✅ test passed | ❌ test failed
¹ Delayed until FFI inline @Array() support in Dart Version >=2.13 is available
³ NanoPi Neo2 with a Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit CPU
⁴ Fails for NanoPi, NanoPi Neo2 and Banana Pi on Armbian- same behaviour like the original c-peripherey test program. Point of deeper investigations
⁵ no X86/X86_64 SOC for testing available
Help wanted #
- Testing dart_periphery on different SoC platforms
- Documentation review - I am not a native speaker.
- Code review - this is my first public Dart project, I am a Java developer and probably I tend to solve problems rather in the Java than in the Dart way.
