crdt_lf 2.5.0  crdt_lf: ^2.5.0 copied to clipboard
crdt_lf: ^2.5.0 copied to clipboard
Conflict-free replicated data type (CRDT) - Local-first implementation provided in dart
CRDT LF #
- CRDT LF
A Conflict-free Replicated Data Type (CRDT) implementation in Dart. This library provides solutions for:
- Text Editing.
- List Editing.
- Map Editing.
- Set Editing.
Supporting:
- Fugue Algorithm for Text Editing to minimize interleaving.
- Observed-Removed (OR) for conflict resolution.
Features #
- ⏱️ Hybrid Logical Clock: Uses HLC for causal ordering of operations
- 🔄 Automatic Conflict Resolution: Automatically resolves conflicts in a CRDT
- 📦 Local Availability: Operations are available locally as soon as they are applied
Design #
Operation based #
The synchronization mechanism is operation-based (CmRDT). Each document manages synchronization by propagating only the operations. Locally, each handler (list, text, etc.) applies these operations to resolve its state. It's possible to create snapshots to establish an initial state on which operations are resolved. This is useful to prevent the memory requirements of the system from growing indefinitely.
Operation resolution is handled by each individual handler. This design allows each handler to implement its own operation resolution logic according to its specific requirements. The library includes simple implementations like CRDTList, where interleaving is managed solely through HLC timestamps, as well as more sophisticated systems like OR-Sets and Fugue Text. Each handler provides documentation that describes its approach to operation resolution.
Transaction #
Each operation created by an handler is registered in the document. The document manages operations through a transaction system. A transaction is considered an atomic operation, and notifications to subscribers are sent only when the transaction is completed. If not explicitly declared, each operation is registered in an implicit transaction.
An explicit transaction creates an environment where operations are grouped together and applied atomically. At the end of the transaction, contiguous operations can be compacted into fewer operations through compound algorithms to reduce the number of changes created.
graph TD
A[Operation Request] --> B{Transaction Active?}
B -->|No| C[Start Implicit Transaction]
B -->|Yes| D[Queue Operation]
C --> E[Queue Operation]
E --> F[Update Handler Cache]
F --> G[Commit Transaction]
D --> F
G --> H[Flush Transaction]
H --> I[Compact Operations]
I --> N[Process Each Operation]
N --> O[Create Change]
O --> P[Apply to Document]
P --> T[Notify Subscribers]
T --> U[Transaction Complete]
The diagram was created using Mermaid. GitHub natively supports this tool, but if you are unable to view them, you can use the official vscode extension or the, Mermaid Live Editor.
Getting Started #
Add this to your package's pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
crdt_lf: ^1.0.0
Usage #
Basic Usage #
import 'package:crdt_lf/crdt_lf.dart';
void main() {
// Create a new document
final doc = CRDTDocument(
peerId: PeerId.parse('45ee6b65-b393-40b7-9755-8b66dc7d0518'),
);
// Create a text handler
final text = CRDTFugueTextHandler(doc, 'text1');
// Insert text
text.insert(0, 'Hello');
// Delete text
text.delete(0, 2); // Deletes "He"
// Get current value
print(text.value); // Prints "llo"
}
Dart Distributed Collaboration Example #
Flutter Distributed Collaboration Example #
Sync #
A sync library is available in the crdt_socket_sync package. And it's used to synchronize the CRDT state between peers. More info in the README of the sync package.
A flutter example is available in the flutter_example and provide a synced version of the "Flutter Distributed Collaboration" Example.
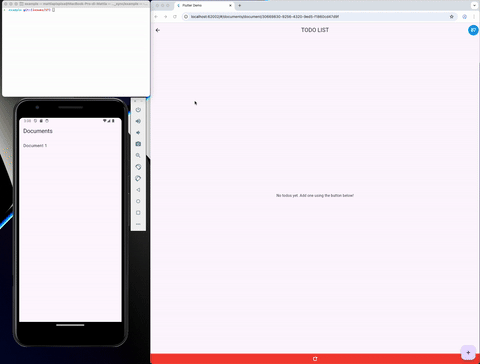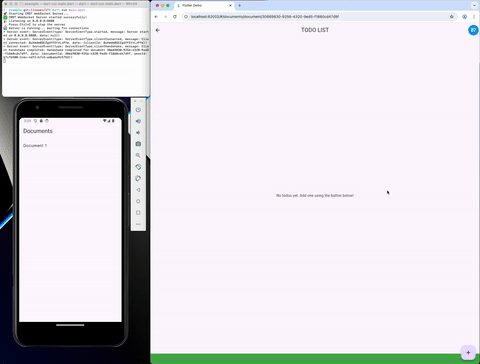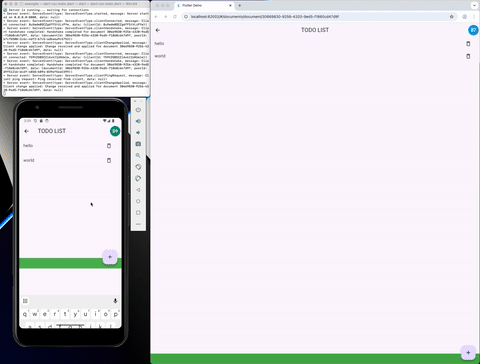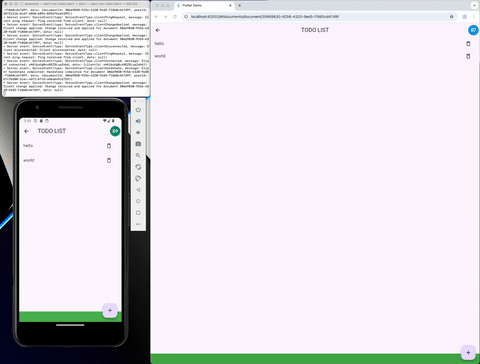
Persistence #
Persistence is not directly handled in this library but there are some out of the box solutions:
- crdt_lf_hive: adapters and utils for persist data using Hive.
Benchmarks #
This package includes a suite of benchmarks to ensure performance and stability. You can find the latest results here.
To run the benchmarks yourself, execute the following script from the packages/crdt_lf directory:
./benchmark/run.sh
or run:
melos run benchmark
Architecture #
The library is built above the hlc_dart package and provide a solution to implement CRDT systems.
CRDTDocument #
The main document class that manages the CRDT state and handles synchronization between peers.
Identity
documentId: identifies the document/resource (used for routing, persistence, and ACLs). It does not participate in operation identifiers.peerId: identifies the peer/author generating operations. It is embedded intoOperationIdtogether with the Hybrid Logical Clock.
If not provided, both are generated: peerId and documentId.
Handlers #
Handlers are the core components of the library. They manage the state of a specific type of data and provide operations to modify it.
CRDTFugueTextHandler: Handles text editing with the Fugue algorithm.CRDTListHandler: Handles list editing.CRDTTextHandler: Handles text editing.CRDTMapHandler: Handles map editing.CRDTORSetHandler: Handles set editing with the Observed-Removed (OR) algorithm.CRDTORMapHandler: Handles map editing with the Observed-Removed (OR) algorithm.
final doc = CRDTDocument(
documentId: 'todo-list-123',
peerId: PeerId.parse('45ee6b65-b393-40b7-9755-8b66dc7d0518'),
);
final list = CRDTListHandler(doc, 'todo-list');
list.insert(0, 'Buy apples');
list.insert(1, 'Buy milk');
list.delete(0);
print(list.value); // Prints "[Buy milk]"
Every handler can be found in the handlers folder.
Working with Complex Types
When using CRDTListHandler<T> or CRDTMapHandler<T> with complex object types (e.g., your own custom classes) for T, it's crucial to understand how data is managed.
The value of your complex object is directly embedded within the Change's payload. This has two important implications:
-
Serialization: If you plan to persist these
Changes (e.g., usingcrdt_lf_hive) or send them over a network, you must have a strategy to serialize and deserialize your custom objects. The raw object cannot be stored or transmitted as-is. A common approach is to convert your object to aMap<String, dynamic>(e.g., by implementingtoJson()and afromJson()factory). -
Immutability and Value Semantics: When a
Changeis created, it captures the state of thevalueat that specific moment. If you later mutate the original object, theChangewill still hold the old state. This can lead to unexpected behavior. It is highly recommended to treat your complex objects as immutable. When you need to modify an object, create a new instance with the updated values instead of mutating the existing one. This ensures that eachChangeis a predictable and self-contained snapshot of the operation.
Example with a custom class:
class MyData {
final String name;
final int count;
MyData(this.name, this.count);
// You need a way to serialize
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => {'name': name, 'count': count};
// And a way to deserialize
factory MyData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return MyData(json['name'], json['count']);
}
}
// When using with a handler
final list = CRDTListHandler<MyData>(doc, 'my-data-list');
// GOOD: Create a new instance for the change
final data = MyData('item1', 1);
list.insert(0, data);
// BAD: Mutating the object after insertion
// This will NOT be reflected in the CRDT history
// data.count = 2; // Avoid this
// Instead, for updates, create a new instance
final updatedData = MyData('item1', 2);
list.update(0, updatedData);
Alternative Approach: Store Raw Data
A more robust pattern is to always store raw, serializable data (like Map<String, dynamic>) inside the handler. This forces serialization at the system's boundary and avoids accidental mutation issues.
// 1. Declare the handler with a raw type
final rawList = CRDTListHandler<Map<String, dynamic>>(doc, 'my-raw-list');
// 2. Serialize before inserting/updating
final data = MyData('item2', 1);
rawList.insert(0, data.toJson());
// 3. Deserialize when reading the value
final myDataList = rawList.value.map((map) => MyData.fromJson(map)).toList();
print(myDataList.first.name); // Prints "item2"
Transaction #
To manage operations in a transaction, use the runInTransaction method of the document.
doc.runInTransaction(() {
listHandler.insert(0, 'item1');
listHandler.insert(1, 'item2');
});
// only here doc notifies subscribers about the transaction completion
Within a transaction can also be executed changes and imports. Those actions are applied immediately but notified only at the end of the transaction.
doc.runInTransaction(() {
listHandler.insert(0, 'item1');
listHandler.insert(1, 'item2');
// immediately applied
doc.createChange(listHandler.insert(0, 'item1'));
// immediately applied
doc.importSnapshot(otherDocument.takeSnapshot());
});
// Insertions are compacted, processed and applied to the document.
// Doc notifies subscribers about the transaction completion
DAG #
A Directed Acyclic Graph that maintains the causal ordering of operations.
Change #
Represents a modification to the CRDT state, including operation ID, dependencies, and timestamp.
Frontiers #
A structure that manages the frontiers (latest operations) of the CRDT.
Snapshot #
A snapshot of the CRDT state, including the version vector and the data.
Project Status #
This library is currently in progress and under active development. While all existing functionality is thoroughly tested, we are continuously working on improvements and new features.
Roadmap #
A roadmap is available in the project page. The roadmap provides a high-level overview of the project's goals and the current status of the project.
Contributing #
We welcome contributions! Whether you want to:
- Fix bugs
- Add new features
- Improve documentation
- Optimize performance
- Or something else
Feel free to:
- Check out our GitHub repository
- Look at the open issues
- Submit a Pull Request
Acknowledgments #
- Fugue Algorithm
- Hybrid Logical Clock
- A comprehensive study of Convergent and Commutative Replicated Data Types
- An O(ND) Difference Algorithm and its Variations (Myers diff algorithm)
Packages #
Other bricks of the crdt "system" are:






