simple_3d_renderer 2.0.0  simple_3d_renderer: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
simple_3d_renderer: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
Sp3dObj renderer. Includes cameras, lights, worlds and more.
simple_3d_renderer #
(en)Japanese ver is here.
(ja)この解説の日本語版はここにあります。
Overview #
This package is for rendering Sp3dObj.
Sp3dObj is an implementation of the Simple 3D Format created for science.
It is created mainly for use by scientists.
Please refer to the following for the packages to be used together.
Usage #
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d/simple_3d.dart';
import 'package:util_simple_3d/util_sp3d_geometry.dart';
import 'package:util_simple_3d/f_sp3d_material.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d_renderer/sp3d_renderer.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d_renderer/sp3d_v2d.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d_renderer/sp3d_world.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d_renderer/sp3d_camera.dart';
import 'package:simple_3d_renderer/sp3d_light.dart';
void main() async {
runApp(new MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
final k = GlobalKey();
late List<Sp3dObj> objs = [];
late Sp3dWorld world;
bool isLoaded = false;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
// Create Sp3dObj.
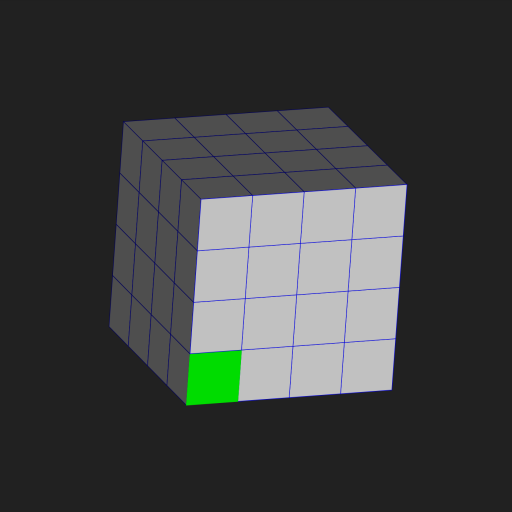
Sp3dObj obj = UtilSp3dGeometry.cube(200,200,200,4,4,4);
obj.materials.add(FSp3dMaterial.green.deep_copy());
obj.fragments[0].faces[0].materialIndex=1;
obj.materials[0] = FSp3dMaterial.grey.deepCopy()..strokeColor=Color.fromARGB(255, 0, 0, 255);
obj.rotate(Sp3dV3D(1,1,0).nor(), 30*3.14/180);
this.objs.add(obj);
loadImage();
}
void loadImage() async {
this.world = Sp3dWorld(objs);
this.world.initImages().then(
(List<Sp3dObj> errorObjs){
setState(() {
this.isLoaded = true;
});
}
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
if (!this.isLoaded) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Sp3dRenderer',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Color.fromARGB(255, 0, 255, 0),
),
backgroundColor: Color.fromARGB(255, 33, 33, 33),
body: Container()
)
);
}
else {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Sp3dRenderer',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Color.fromARGB(255, 0, 255, 0),
),
backgroundColor: Color.fromARGB(255, 33, 33, 33),
body: Column(
children: [
Sp3dRenderer(
k,
Size(800, 800),
Sp3dV2D(400, 400),
this.world,
// If you want to reduce distortion, shoot from a distance at high magnification.
Sp3dCamera(Sp3dV3D(0, 0, 30000), 60000),
Sp3dLight(Sp3dV3D(0, 0, -1), syncCam: true)
)
],
),
),
);
}
}
}
Use Image File #
For example, rewrite sample code as follows.(*Note that some unnecessary parameters remain for simplicity)
sample_image.png #

// Chenge Cube of initState().
Sp3dObj obj = UtilSp3dGeometry.cube(200,200,200,1,1,1);
--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Chenge function
void loadImage() async {
this.objs[0].fragments[0].faces[0].materialIndex=1;
this.objs[0].fragments[0].faces[1].materialIndex=1;
this.objs[0].fragments[0].faces[2].materialIndex=1;
this.objs[0].fragments[0].faces[3].materialIndex=1;
this.objs[0].materials[1].imageIndex = 0;
// You can also use the image by adding the image directly under the project like this and listing the asset in pubspec.yaml.
this.objs[0].images.add(await _readFileBytes("./assets/images/sample_image.png"));
this.world = Sp3dWorld(objs);
this.world.initImages().then(
(List<Sp3dObj> errorObjs){
setState(() {
this.isLoaded = true;
});
}
);
}
// Add function
Future<Uint8List> _readFileBytes(String filePath) async {
ByteData bd = await rootBundle.load(filePath);
return bd.buffer.asUint8List(bd.offsetInBytes,bd.lengthInBytes);
}

Triangle mesh #
If the drawing destination of the image is a triangular mesh, the image is automatically divided into triangles with the vertices at the upper left, lower left, and lower right, and displayed.
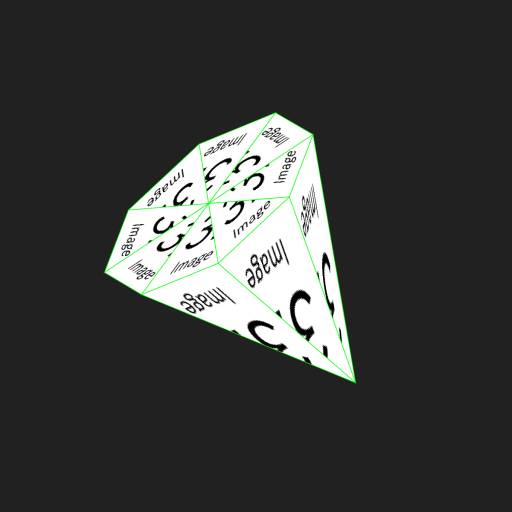
You can also use the Sp3dMaterial parameters to control the cutout position with respect to the triangular mesh.
*Note that the size of the image of paste to cone is (width, height) = (128, 128).
Since textureCoordinates specifies the position where you want to cut out the image, it indicate the points on the image.
And this image is (0,0) in the upper left and (128,128) in the lower right.
For example, the following sample is cut out at the upper left, the middle of the lower side, and the upper right.
In the case of a square mesh, it is necessary to specify two triangles, so six vertices are required.
Sp3dObj obj = UtilSp3dGeometry.cone(100,200);
obj.materials[0].strokeColor = Color.fromARGB(255, 0, 255, 0);
obj.materials[0].textureCoordinates = [Offset(0,0),Offset(64,128),Offset(128,0)];

Support #
If you need paid support, please contact my company.
SimpleAppli Inc.
Rendering Speed (10 paint average) #
It is a consideration of the time required for drawing on a web browser
in debug mode on a midrange machine with CPU 3.40Ghz and 16GB memory as of Sp3dRenderer ver 0.0.3.
There are some speed issues (CPU Run, Single thread).
In the case of real-time rendering, the limit is about 1000 cubes (8000 vertices), and 2500 cubes (20000 vertices) or more is heavy.
For models such as spheres with many vertices, the amount that can be operated comfortably is much smaller.
Note: Not all objects will have similar performance due to the impact of speedup logic.
/// use cube obj(8 vertices / 1 obj)
Sp3dObj obj = UtilSp3dGeometry.cube(5, 5, 5, 1, 1, 1);
- 100 cube 4 ms / paint. (800 vertices, 250.0 fps)
- 500 cube 19 ms / paint.
- 1000 cube 38 ms / paint. (8000 vertices, 26.3 fps)
- 2500 cube 95 ms / paint. (20000 vertices, 10.5 fps)
- 5000 cube 197 ms / paint.
/// use sphere obj(72 vertices / 1 obj)
Sp3dObj obj = UtilSp3dGeometry.sphere(2.5);
- 100 sphere 46 ms / paint. (7200 vertices, 21.7 fps)
- 500 sphere 236 ms / paint.
- 1000 sphere 473 ms / paint.
- 2500 sphere 1219 ms / paint.
- 5000 sphere 2532 ms / paint. (360000 vertices)
About version control #
The C part will be changed at the time of version upgrade.
- Changes such as adding variables, structure change that cause problems when reading previous files.
- C.X.X
- Adding methods, etc.
- X.C.X
- Minor changes and bug fixes.
- X.X.C
License #
This software is released under the MIT License, see LICENSE file.
Copyright notice #
The “Dart” name and “Flutter” name are trademarks of Google LLC.
*The developer of this package is not Google LLC.