google_mlkit_digital_ink_recognition 0.14.2  google_mlkit_digital_ink_recognition: ^0.14.2 copied to clipboard
google_mlkit_digital_ink_recognition: ^0.14.2 copied to clipboard
A Flutter plugin to use Google's ML Kit Digital Ink Recognition to recognize handwritten text on a digital surface in hundreds of languages, as well as classify sketches.
Google's ML Kit Digital Ink Recognition for Flutter #
A Flutter plugin to use Google's ML Kit Digital Ink Recognition to recognize handwritten text on a digital surface in hundreds of languages, as well as classify sketches.
PLEASE READ THIS before continuing or posting a new issue:
-
Google's ML Kit was build only for mobile platforms: iOS and Android apps. Web or any other platform is not supported, you can request support for those platform to Google in their repo.
-
This plugin is not sponsored or maintained by Google. The authors are developers excited about Machine Learning that wanted to expose Google's native APIs to Flutter.
-
Google's ML Kit APIs are only developed natively for iOS and Android. This plugin uses Flutter Platform Channels as explained here.
Messages are passed between the client (the app/plugin) and host (platform) using platform channels as illustrated in this diagram:
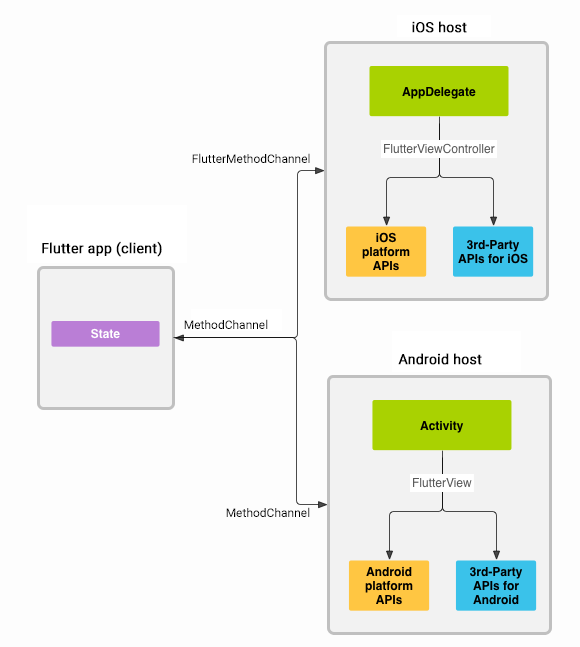
Messages and responses are passed asynchronously, to ensure the user interface remains responsive. To read more about platform channels go here.
Because this plugin uses platform channels, no Machine Learning processing is done in Flutter/Dart, all the calls are passed to the native platform using
MethodChannelin Android andFlutterMethodChannelin iOS, and executed using Google's native APIs. Think of this plugin as a bridge between your app and Google's native ML Kit APIs. This plugin only passes the call to the native API and the processing is done by Google's API. It is important that you understand this concept when it comes to debugging errors for your ML model and/or app. -
Since the plugin uses platform channels, you may encounter issues with the native API. Before submitting a new issue, identify the source of the issue. You can run both iOS and/or Android native example apps by Google and make sure that the issue is not reproducible with their native examples. If you can reproduce the issue in their apps then report the issue to Google. The authors do not have access to the source code of their native APIs, so you need to report the issue to them. If you find that their example apps are okay and still you have an issue using this plugin, then look at our closed and open issues. If you cannot find anything that can help you then report the issue and provide enough details. Be patient, someone from the community will eventually help you.
Requirements #
iOS #
- Minimum iOS Deployment Target: 15.5
- Xcode 15.3.0 or newer
- Swift 5
- ML Kit does not support 32-bit architectures (i386 and armv7). ML Kit does support 64-bit architectures (x86_64 and arm64). Check this list to see if your device has the required device capabilities. More info here.
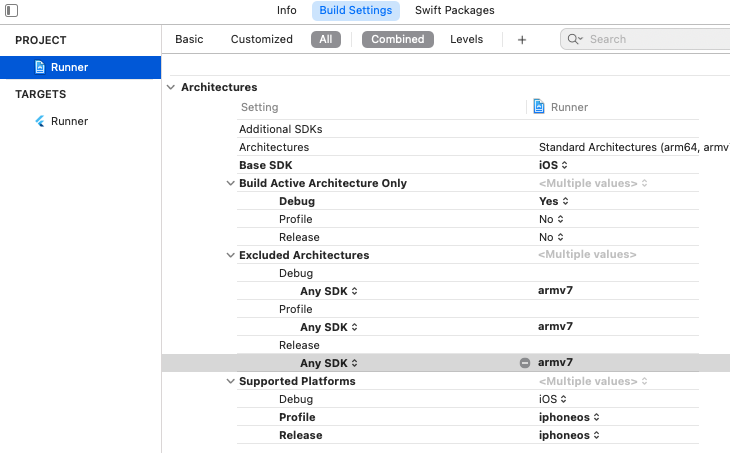
Since ML Kit does not support 32-bit architectures (i386 and armv7), you need to exclude armv7 architectures in Xcode in order to run flutter build ios or flutter build ipa. More info here.
Go to Project > Runner > Building Settings > Excluded Architectures > Any SDK > armv7
Your Podfile should look like this:
platform :ios, '15.5' # or newer version
...
# add this line:
$iOSVersion = '15.5' # or newer version
post_install do |installer|
# add these lines:
installer.pods_project.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings["EXCLUDED_ARCHS[sdk=*]"] = "armv7"
config.build_settings['IPHONEOS_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET'] = $iOSVersion
end
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
flutter_additional_ios_build_settings(target)
# add these lines:
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
if Gem::Version.new($iOSVersion) > Gem::Version.new(config.build_settings['IPHONEOS_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET'])
config.build_settings['IPHONEOS_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET'] = $iOSVersion
end
end
end
end
Notice that the minimum IPHONEOS_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET is 15.5, you can set it to something newer but not older.
Android #
- minSdkVersion: 21
- targetSdkVersion: 35
- compileSdkVersion: 35
Usage #
Digital Ink Recognition #
Create an instance of DigitalInkRecognizer
String languageCode; // BCP-47 Code from https://developers.google.com/ml-kit/vision/digital-ink-recognition/base-models?hl=en#text
final digitalInkRecognizer = DigitalInkRecognizer(languageCode: languageCode);
Process ink
final p1 = StrokePoint(x: x1, y: y1, t: DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch); // make sure that `t` is a long
final p2 = StrokePoint(x: x1, y: y1, t: DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch); // make sure that `t` is a long
Stroke stroke1 = Stroke(); // it contains all of the StrokePoint
stroke1.points = [p1, p2, ...]
Ink ink = Ink(); // it contains all of the Stroke
ink.strokes = [stroke1, stroke2, ...];
final List<RecognitionCandidate> candidates = await digitalInkRecognizer.recognize(ink);
for (final candidate in candidates) {
final text = candidate.text;
final score = candidate.score;
}
Make sure you download the language model before processing any Ink.
To improve the accuracy of text recognition you can set an writing area and pre-context. More details here.
String preContext;
double width;
double height;
final context = DigitalInkRecognitionContext(
preContext: preContext,
writingArea: WritingArea(width: width, height: height),
);
final List<RecognitionCandidate> candidates = await digitalInkRecognizer.recognize(ink, context: context);
Release resources with close()
digitalInkRecognizer.close();
Managing remote models #
Create an instance of model manager
final modelManager = DigitalInkRecognizerModelManager();
Check if model is downloaded
final bool response = await modelManager.isModelDownloaded(model);
Download model
final bool response = await modelManager.downloadModel(model);
Delete model
final bool response = await modelManager.deleteModel(model);
Example app #
Find the example app here.
Contributing #
Contributions are welcome. In case of any problems look at existing issues, if you cannot find anything related to your problem then open an issue. Create an issue before opening a pull request for non trivial fixes. In case of trivial fixes open a pull request directly.


