flutter_sound 3.1.1  flutter_sound: ^3.1.1 copied to clipboard
flutter_sound: ^3.1.1 copied to clipboard
Flutter plugin that relates to sound like audio and recorder.
Flutter Sound #
 This plugin provides simple recorder and player functionalities for both `android` and `ios` platforms. This only supports default file extension for each platform.
This plugin handles file from remote url.
This plugin can handle playback stream from native (To sync exact time with bridging).
This plugin provides simple recorder and player functionalities for both `android` and `ios` platforms. This only supports default file extension for each platform.
This plugin handles file from remote url.
This plugin can handle playback stream from native (To sync exact time with bridging).
Breaking News #
3.0.0release has breaking features have been added by the work on code nameflautoin #243- OGG/OPUS support on iOS
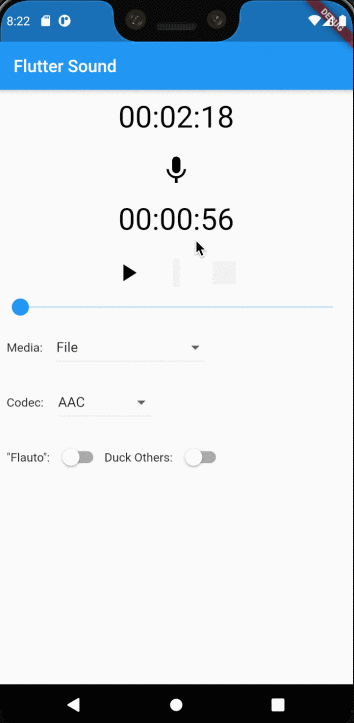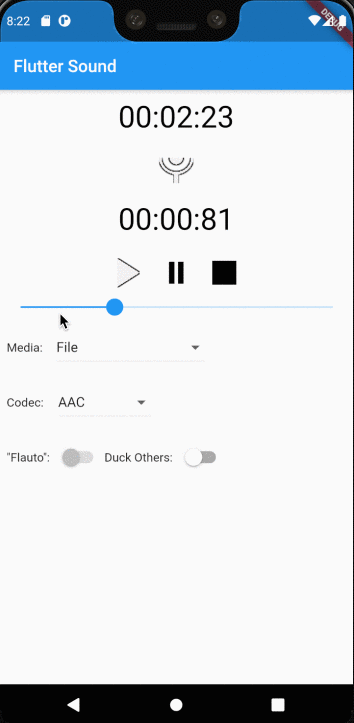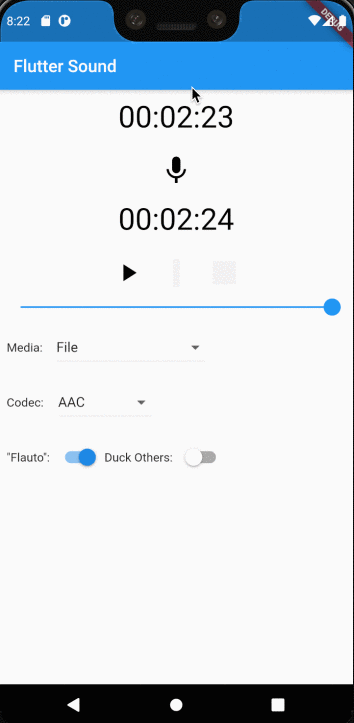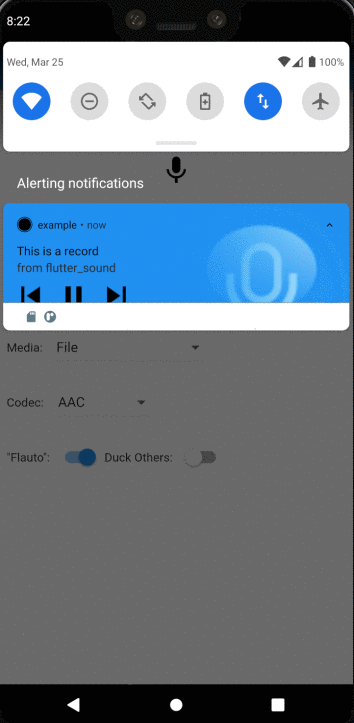
- Playing in lock screen
- Playing in notification
- Support tracking
Please honor all wonderful contributors Larpoux, bsutton, salvatore373 🎉!
Free Read #
Getting Started #
For help getting started with Flutter, view our online documentation.
Install #
For help on adding as a dependency, view the documentation.
Add flutter_sound as a dependency in pubspec.yaml. The actual version is flauto: ^3.0.0
The Flutter-Sound sources are here.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_sound: ^3.0.0
FFmpeg #
flutter_sound makes use of flutter_ffmpeg. Please, look to flutter_ffmpeg documentation to see how to add it to your App.
- On iOS you will have to enter something like that in your
Podfile
# Prepare symlinks folder. We use symlinks to avoid having Podfile.lock
# referring to absolute paths on developers' machines.
system('rm -rf .symlinks')
system('mkdir -p .symlinks/plugins')
plugin_pods = parse_KV_file('../.flutter-plugins')
plugin_pods.each do |name, path|
symlink = File.join('.symlinks', 'plugins', name)
File.symlink(path, symlink)
if name == 'flutter_ffmpeg'
pod name+'/audio-lts', :path => File.join(symlink, 'ios')
else
pod name, :path => File.join(symlink, 'ios')
end
end
- On Android you will have to enter the following line in your
pubspec.yamlfile.
ext.flutterFFmpegPackage = 'audio-lts'
Post Installation #
On iOS you need to add a usage description to info.plist:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>This sample uses the microphone to record your speech and convert it to text.</string>
<key>UIBackgroundModes</key>
<array>
<string>audio</string>
</array>
On Android you need to add a permission to AndroidManifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
Migration Guide #
To migrate to 3.0.0 you must migrate your Android app to Android X by following the Migrating to AndroidX Guide.
Methods #
| Func | Param | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| initialize | void |
Initializes the media player and all the callbacks for the player and the recorder. This procedure is implicitely called during the Flutter Sound constructors. So you probably will not use this function yourself. | |
| releaseMediaPlayer | void |
Resets the media player and cleans up the device resources. This must be called when the player is no longer needed. | |
| setSubscriptionDuration | double sec |
String message |
Set subscription timer in seconds. Default is 0.010 if not using this method. |
| startRecorder | String uri, int sampleRate, int numChannels, t_CODEC codec |
String uri |
Start recording. This will return uri used. |
| stopRecorder | String message |
Stop recording. | |
| pauseRecorder | String message |
Pause recording. | |
| resumeRecorder | String message |
Resume recording. | |
| startPlayer | String fileUri, t_CODEC codec, whenFinished() |
Starts playing the file at the given URI. | |
| startPlayerFromBuffer | Uint8List dataBuffer, t_CODEC codec, whenFinished() |
String message |
Start playing using a buffer encoded with the given codec |
| stopPlayer | String message |
Stop playing. | |
| pausePlayer | String message |
Pause playing. | |
| resumePlayer | String message |
Resume playing. | |
| seekToPlayer | int milliSecs position to goTo |
String message |
Seek audio to selected position in seconds. Parameter should be less than audio duration to correctly placed. |
| iosSetCategory | SESSION_CATEGORY, SESSION_MODE, options |
Boolean | Set the session category on iOS. |
| androidAudioFocusRequest | int focusGain |
Boolean | Define the Android Focus request to use in subsequent requests to get audio focus |
| setActive | bool enabled |
Boolean | Request or Abandon the audio focus |
Subscriptions #
| Subscription | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|
| onRecorderStateChanged | <RecordStatus> |
Able to listen to subscription when recorder starts. |
| onPlayerStateChanged | <PlayStatus> |
Able to listen to subscription when player starts. |
Default uri path #
When uri path is not set during the function call in startRecorder or startPlayer, records are saved/read to/from a temporary directory depending on the platform.
Codec compatibility #
Actually, the following codecs are supported by flutter_sound:
| AAC | OGG/Opus | CAF/Opus | MP3 | OGG/Vorbis | PCM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iOS encoder | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| iOS decoder | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Android encoder | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Android decoder | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
This table will eventually be upgrated when more codecs will be added.
FlutterSoundRecorder Usage #
Creating instance.
In your view/page/dialog widget's State class, create an instance of FlutterSoundRecorder. Before acessing the FlutterSoundRecorder API, you must initialize it with initialize(). When finished with this FlutterSoundRecorder instance, you must release it with release().
FlutterSoundRecorder flutterSoundRecorder = new FlutterSoundRecorder().initialize();
...
...
flutterSoundRecorder.release();
Starting recorder with listener.
Future<String> result = await FlutterSoundRecorder.startRecorder(codec: t_CODEC.CODEC_AAC,);
result.then(path) {
print('startRecorder: $path');
_recorderSubscription = flutterSoundRecorder.onRecorderStateChanged.listen((e) {
DateTime date = new DateTime.fromMillisecondsSinceEpoch(e.currentPosition.toInt());
String txt = DateFormat('mm:ss:SS', 'en_US').format(date);
});
}
The recorded file will be stored in a temporary directory. If you want to take your own path specify it like below. We are using path_provider in below so you may have to install it.
Directory tempDir = await getTemporaryDirectory();
File outputFile = await File ('${tempDir.path}/flutter_sound-tmp.aac');
String path = await flutterSoundRecorder.startRecorder(outputFile.path, codec: t_CODEC.CODEC_AAC,);
Actually on iOS, you can choose from three encoders :
- AAC (this is the default)
- CAF/OPUS
- OGG/OPUS
Recently, Apple added a support for encoding with the standard OPUS codec. Unfortunatly, Apple encapsulates its data in its own proprietary envelope : CAF. This is really stupid, this is Apple. To encode with OPUS you do the following :
await flutterSoundRecorder.startRecorder(foot.path, codec: t_CODEC.CODEC_OPUS,)
On Android the OPUS codec is not yet supported by flutter_sound Recorder. (But Player is OK on Android)
Stop recorder
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundRecorder.stopRecorder();
result.then(value) {
print('stopRecorder: $value');
if (_recorderSubscription != null) {
_recorderSubscription.cancel();
_recorderSubscription = null;
}
}
You MUST ensure that the recorder has been stopped when your widget is detached from the ui. Overload your widget's dispose() method to stop the recorder when your widget is disposed.
@override
void dispose() {
flutterSoundRecorder.release();
super.dispose();
}
Pause recorder
On Android this API verb needs al least SDK24.
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundRecorder.pauseRecorder();
Resume recorder
On Android this API verb needs al least SDK24.
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundRecorder.resumeRecorder();
Using the amplitude meter
The amplitude meter allows displaying a basic representation of the input sound. When enabled, it returns values ranging 0-120dB.
//// By default this option is disabled, you can enable it by calling
setDbLevelEnabled(true);
//// You can tweak the frequency of updates by calling this function (unit is seconds)
updateDbPeakProgress(0.8);
//// You need to subscribe in order to receive the value updates
_dbPeakSubscription = flutterSoundRecorder.onRecorderDbPeakChanged.listen((value) {
setState(() {
this._dbLevel = value;
});
});
FlutterSoundPlayer Usage #
Creating instance.
In your view/page/dialog widget's State class, create an instance of FlutterSoundPlayer. Before acessing the FlutterSoundPlayer API, you must initialize it with initialize(). When finished with this FlutterSoundPlayer instance, you must release it with release().
FlutterSoundPlayer flutterSoundPlayer = new FlutterSoundPlayer().initialize();
...
...
flutterSoundPlayer.release();
Start player
- To start playback of a record from a URL call startPlayer.
- To start playback of a record from a memory buffer call startPlayerFromBuffer
You can use both startPlayer or startPlayerFromBuffer to play a sound. The former takes in a URI that points to the file to play, while the latter takes in a buffer containing the file to play and the codec to decode that buffer.
Those two functions can have an optional parameter whenFinished:() for specifying what to do when the playback will be finished.
// An example audio file
final fileUri = "https://file-examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/file_example_MP3_700KB.mp3";
String result = await flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayer
(
fileUri,
whenFinished: ()
{
print( 'I hope you enjoyed listening to this song' );
},
);
// Load a local audio file and get it as a buffer
Uint8List buffer = (await rootBundle.load('samples/audio.mp3'))
.buffer
.asUint8List();
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayerFromBuffer
(
buffer,
whenFinished: ()
{
print( 'I hope you enjoyed listening to this song' );
},
);
You must wait for the return value to complete before attempting to add any listeners to ensure that the player has fully initialised.
Directory tempDir = await getTemporaryDirectory();
File fin = await File ('${tempDir.path}/flutter_sound-tmp.aac');
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayer(fin.path);
result.then(path) {
print('startPlayer: $path');
_playerSubscription = flutterSoundPlayer.onPlayerStateChanged.listen((e) {
if (e != null) {
DateTime date = new DateTime.fromMillisecondsSinceEpoch(e.currentPosition.toInt());
String txt = DateFormat('mm:ss:SS', 'en_US').format(date);
this.setState(() {
this._isPlaying = true;
this._playerTxt = txt.substring(0, 8);
});
}
});
}
Start player from buffer
For playing data from a memory buffer instead of a file, you can do the following :
Uint8List buffer = (await rootBundle.load(assetSample[_codec.index])).buffer.asUint8List();
String result = await flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayerFromBuffer
(
buffer,
codec: t_CODEC.CODEC_AAC,
whenFinished: ()
{
print( 'I hope you enjoyed listening to this song' );
},
);
Stop player
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundPlayer.stopPlayer();
result.then(value) {
print('stopPlayer: $result');
if (_playerSubscription != null) {
_playerSubscription.cancel();
_playerSubscription = null;
}
}
You MUST ensure that the player has been stopped when your widget is detached from the ui. Overload your widget's dispose() method to stop the player when your widget is disposed.
@override
void dispose() {
flutterSoundPlayer.stopPlayer();
super.dispose();
}
Pause player
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundPlayer.pausePlayer();
Resume player
Future<String> result = await flutterSoundPlayer.resumePlayer();
iosSetCategory(), androidAudioFocusRequest() and setActive() - (optional)
Those three functions are optional. If you do not control the audio focus with the function setActive(), flutter_sound will require the audio focus each time the function startPlayer() is called and will release it when the sound is finished or when you call the function stopPlayer().
Before controling the focus with setActive() you must call iosSetCategory() on iOS or androidAudioFocusRequest() on Android. setActive() and androidAudioFocusRequest() are useful if you want to duck others.
Those functions are probably called just once when the app starts.
After calling this function, the caller is responsible for using correctly setActive()
probably before startRecorder or startPlayer, and stopPlayer and stopRecorder.
You can refer to iOS documentation to understand the parameters needed for iosSetCategory() and to the Android documentation to understand the parameter needed for androidAudioFocusRequest().
Remark : those three functions does work on Android before SDK 26.
if (_duckOthers)
{
if (Platform.isIOS)
await flutterSoundPlayer.iosSetCategory( t_IOS_SESSION_CATEGORY.PLAY_AND_RECORD, t_IOS_SESSION_MODE.DEFAULT, IOS_DUCK_OTHERS | IOS_DEFAULT_TO_SPEAKER );
else if (Platform.isAndroid)
await flutterSoundPlayer.androidAudioFocusRequest( ANDROID_AUDIOFOCUS_GAIN_TRANSIENT_MAY_DUCK );
} else
{
if (Platform.isIOS)
await flutterSoundPlayer.iosSetCategory( t_IOS_SESSION_CATEGORY.PLAY_AND_RECORD, t_IOS_SESSION_MODE.DEFAULT, IOS_DEFAULT_TO_SPEAKER );
else if (Platform.isAndroid)
await flutterSoundPlayer.androidAudioFocusRequest( ANDROID_AUDIOFOCUS_GAIN );
}
...
...
flutterSoundPlayer.setActive(true); // Get the audio focus
flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayer(aSound);
flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayer(anotherSong);
flutterSoundPlayer.setActive(false); // Release the audio focus
Seek player
To seek to a new location the player must already be playing.
String Future<result> = await flutterSoundPlayer.seekToPlayer(miliSecs);
Setting subscription duration (Optional). 0.010 is default value when not set.
/// 0.01 is default
flutterSoundPlayer.setSubscriptionDuration(0.01);
Setting volume.
/// 1.0 is default
/// Currently, volume can be changed when player is running. Try manage this right after player starts.
String path = await flutterSoundPlayer.startPlayer(fileUri);
await flutterSoundPlayer.setVolume(0.1);
Release the player
You MUST ensure that the player has been released when your widget is detached from the ui.
Overload your widget's dispose() method to release the player when your widget is disposed.
In this way you will reset the player and clean up the device resources, but the player will be no longer usable.
@override
void dispose() {
flutterSoundPlayer.release();
super.dispose();
}
TrackPlayer #
TrackPlayer is a new flutter_sound module which is able to show controls on the lock screen. Using TrackPlayer is very simple : just use the TrackPlayer constructor instead of the regular FlutterSoundPlayer.
trackPlayer = TrackPlayer();
You must startPlayerFromTrack to play a sound. This function takes in 1 required argument and 3 optional arguments:
- a
Track, which is the track that the player is going to play; whenFinished:(): A call back function for specifying what to do when the song is finishedonSkipBackward:(), A call back function for specifying what to do when the user press the skip-backward button on the lock screenonSkipForward:(), A call back function for specifying what to do when the user press the skip-forward button on the lock screen
path = await trackPlayer.startPlayerFromTrack
(
track,
whenFinished: ( )
{
print( 'I hope you enjoyed listening to this song' );
},
onSkipBackward: ( )
{
print( 'Skip backward' );
stopPlayer( );
startPlayer( );
},
onSkipForward: ( )
{
print( 'Skip forward' );
stopPlayer( );
startPlayer( );
},
);
Create a Track object
In order to play a sound when you initialized the player with the audio player features, you must create a Track object to pass to startPlayerFromTrack.
The Track class is provided by the flutter_sound package. Its constructor takes in 1 required argument and 3 optional arguments:
trackPath(required): aStringrepresenting the path that points to the audio file to play. This must be provided ifdataBufferis null, but you cannot provide both;dataBuffer(required): aUint8List, a buffer that contains an audio file. This must be provided iftrackPathis null, but you cannot provide both;trackTitle: theStringto display in the notification as the title of the track;trackAuthortheStringto display in the notification as the name of the author of the track;albumArtUrlaStringrepresenting the URL that points to the image to display in the notification as album art.- or
albumArtAsset: the name of an asset to show in the nofitication
// Create with the path to the audio file
Track track = new Track(
trackPath: "https://file-examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/file_example_MP3_700KB.mp3", // An example audio file
trackTitle: "Track Title",
trackAuthor: "Track Author",
albumArtUrl: "https://file-examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/file_example_PNG_1MB.png", // An example image
);
// Load a local audio file and get it as a buffer
Uint8List buffer = (await rootBundle.load('samples/audio.mp3'))
.buffer
.asUint8List();
// Create with the buffer
Track track = new Track(
dataBuffer: buffer,
trackTitle: "Track Title",
trackAuthor: "Track Author",
albumArtUrl: "https://file-examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/file_example_PNG_1MB.png", // An example image
);
Informations on a record #
There are two utilities functions that you can use to have informations on a file.
- FlutterSoundHelper.FFmpegGetMediaInformation(<A_file_path>);
- FlutterSoundHelper.duration(<A_file_path>)
The informations got with FFmpegGetMediaInformation() are documented here. The integer returned by flutterSound.duration() is the number of milli-seconds for the given record.
int duration = await flutterSoundHelper.duration( this._path[_codec.index] );
Map<dynamic, dynamic> info = await flutterSoundHelper.FFmpegGetMediaInformation( uri );
TODO #
- ✅ Seeking example in
Exampleproject - ✅ Volume Control
- ✅ Sync timing for recorder callback handler
DEBUG #
When you face below error,
* What went wrong:
A problem occurred evaluating project ':app'.
> versionCode not found. Define flutter.versionCode in the local.properties file.
Please add below to your example/android/local.properties file.
flutter.versionName=1.0.0
flutter.versionCode=1
flutter.buildMode=debug
Help Maintenance #
I've been maintaining quite many repos these days and burning out slowly. If you could help me cheer up, buying me a cup of coffee will make my life really happy and get much energy out of it.


