flutter_control 0.15.1+2  flutter_control: ^0.15.1+2 copied to clipboard
flutter_control: ^0.15.1+2 copied to clipboard
Flutter Control is library to simply maintain App and State management. Provides some basic Widgets and Controllers to start with.
Flutter Control is complex library to maintain App and State management.
Helps to separate Business Logic from UI and with Communication, Localization, Routing and passing arguments/values/events around.
Simplified structure of core classes in Flutter Control. Full diagram is at bottom of this page..
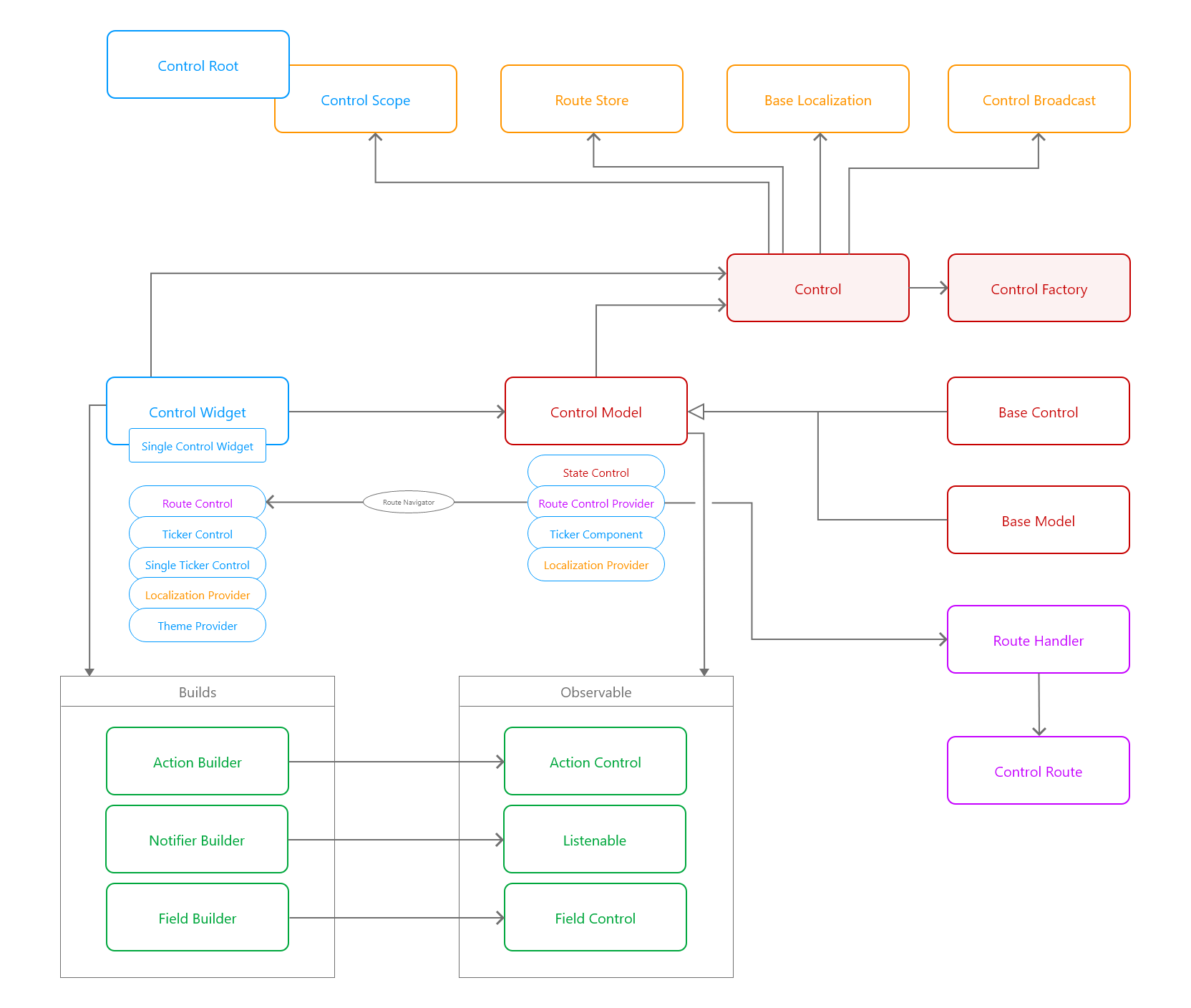
Flutter Control Core
- [ControlBase] Wraps App and initializes Control, Factory, Localization, Injector and Broadcaster. It's just shortcut to start with Flutter Control.
- [ControlFactory] Initializes and can store Controllers, Models and other objects. Dependency Injection is provided during object initialization and also on demand.
Factory has own Storage. Objects in this storage are accessible via custom key or Type. Best practice is to use type as a key..
Comes with [ControlProvider] a class to easily access core functions from any part of App. Provider has two parts - Static and Widget. With static part is possible to 'get', 'set', 'init' and 'inject' objects. Widget part is StatelessWidget that provides object from Factory.
Factory is one and only singleton in this library.
Core objects of Flutter Control are stored in Factory Storage by default and are accessible by their [Type] or via Providers.
ControlBase(
locales: {
'en': AssetPath().localization('en'),
},
entries: {
CounterController: CounterController(),
},
initializers: {
Counter: (_) => CounterModel(),
},
injector: Injector.of({
Counter: (item, args) => item.controller = ControlProvider.get('counter'),
}),
loader: (context) => LoadingPage(),
root: (context) => CounterPage(),
app: (context, key, home) {
return MaterialApp(
key: key,
home: home,
title: 'Flutter Control Example',
);
},
);
-
[BaseControlModel] is base class to maintain Business Logic parts of App.
[BaseController] is extended version of [BaseControlModel] with more functionality. Mainly used for pages or complex Widgets and also to separate robust Logic parts.
[BaseModel] is extended but lightweight version of [BaseControlModel]. Mainly used for Items in dynamic List or to separate/reuse Logic parts.
This Controllers comes with few [mixin] classes to extend base functionality:- [RouteController] to provide navigation outside of Widget.
- [StateController] to notify state of whole Widget.
-
[ControlWidget] is base abstract class (StatefulWidget) to maintain UI parts of App. Widget is created with default [ControlState] to correctly reflect lifecycle of Widget to Models and Controllers. So there is no need to create custom [State].
If used correctly, this Widget will Init all containing Controllers and pass arguments to these Controllers.
This Widget comes with few [mixin] classes:- [RouteControl] to abstract navigation and easily pass arguments and init other Pages.
- [TickerControl] and [SingleTickerControl] to create [State] with [Ticker] and provide access to [vsync].
[SingleControlWidget] is used to work with one Controller. This controller can be passed through constructor/init [args] or grabbed from [ControlFactory].
[BaseControlWidget] is used when there is no need to construct Controllers. Controllers still can be passed through constructor or init [args].
class CounterModel extends BaseModel with StateController {
int count = 0;
void increase() {
count++;
notifyState();
}
}
class CounterPage extends SingleControlWidget<CounterModel> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Text(controller.count.toString()),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: controller.increase,
child: Text('+'),
),
);
}
}
After hitting '+' button State of CounterPage will be notified and whole Widget is re-build.
-
[ActionControl] is one type of Observable used in this Library. It's quite lightweight and is used to notify Widgets and to provide events about value changes.
Has three variants - Single (just one listener), Broadcast (multiple listeners) and Broadcast Listener (subscribes to Global Broadcaster).
On the Widget side is [ControlBuilder] to dynamically build Widgets. It's also possible to use [ControlBuilderGroup] for multiple Observables.
Value is set directly, but can be used privately and with [ActionControlSub] interface provide subscription functionality to public.
Upon dismiss every [ControlSubscription] is closed. -
[FieldControl] is more robust Observable solution around [Stream] and [StreamController]. Primarily is used to notify Widgets and to provide events about value changes.
Can listen [Stream], [Future] or subscribe to another FieldControl with possibility to filter and convert values.
FieldControl comes with pre-build primitive variants as [StringControl], [DoubleControl], etc., where is possible to use validation, regex or value clamping. And also [ListControl] to work with Iterables.
On the Widget side is [FieldBuilder] and [FieldStreamBuilder] to dynamically build Widgets. Also [FieldBuilderGroup] for use with multiple Observables.
It's possible to set value directly, via [FieldSink] or [FieldSinkConverter].
Upon dismiss every [FieldSubscription] is closed.
class CounterController extends BaseController {
final count = IntegerControl();
void increase() => count.value++;
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
count.dispose();
}
}
class CounterPage extends SingleControlWidget<CounterController> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: FieldBuilder<int>(
controller: controller.count,
builder: (context, value) {
return Text(value.toString());
}),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: controller.increase,
child: Text('+'),
),
);
}
}
After hitting '+' button State of FieldBuilder will be notified and only Text Widget is re-build.
There is more ways how to pass and init Controllers in [ControlWidget] and listen about [State] lifecycle.
- Constructor: we can pass Controllers as arguments with other [args].
CounterPage({Key key, CounterController controller, int defaultValue: 10}): super(key: key, args:[controller, defaultValue]);
- Lazy load: Construct them manually or from Factory by overriding [initControllers].
final controller = SuperController();
@override
List<BaseControlModel> initControllers() {
return [
controller,
CounterController(),
ControlProvider.get<CounterModel>(),
];
}
- Pass them via [Initializable] interface. This method is same as Constructor [args]. Both methods can be combined with different arguments.
[init] is also called by [RouteControl], when passing arguments from one page to another.
init(Map args);
- On demand during build statically or via Provider Widget, and new [args] can be pushed to objects:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final controller = ControlProvider.get(CounterController, {'msg': 'static invoke'});
return ControlProvider<CounterController>(
args: 10,
builder: (context, value) => Center(
child: Text((controller == value).toString()),
),
);
}
Arguments are then passed into Controllers as a [Map]. So you need to know 'key' or 'Type' to retrieve them. Static class [Parse] and their extensions can help..
@override
void onInit(Map args) {
int count = args.getArg<int>(defaultValue: -1);
String message = Parse.getArg<String>(args, key: 'msg', defaultValue: 'no message');
}
[BaseController] by default prevents 'multi init'. But this behaviour can be of course overridden.
Other Important classes
- [BaseLocalization] Json based localization, that supports simple strings, plurals and dynamic structures.
Easy access via [LocalizationProvider] mixin. Localization object is stored in Factory, so is accessible without context and can be used even in Controllers, Entities, etc.
Localization is initialized and loaded in [ControlBase] by default.
And by default [ControlWidget] uses this localization.
class HelloControl extends BaseControlWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(localize('hello_world'));
}
}
class HelloText extends StatelessWidget with LocalizationProvider {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(localize('hello_world'));
}
}
- [ControlBroadcast] Event stream across whole App. Broadcaster is part of [ControlFactory] and is stored there.
With [BroadcastProvider] is possible to subscribe to any stream and send data or events from one end of App to another, even to Widgets.
BroadcastProvider.subscribe<BasketItem>(BasketAdd, (item) => addToBasket(item));
BroadcastBuilder<BasketItem>(
key: BasketAdd,
builder: (context, item) => Text(
'New item added to basket: ${item.name}',
),
);
BroadcatProvider.broadcast(BasketAdd, BasketItem(name: 'socks'));
- [ControlTheme] wraps [ThemeData], [MediaQuery] into [Device] class and [AssetPath].
Theme is cached on their first use, so 'Theme.of' is called just once per Widget.
Control Theme adds some parameters and getters on top of standard Theme.
Easy access via [ThemeProvider] a mixin class that initializes [ControlTheme].
Custom [ControlTheme] class builder can be used in [ControlBase] constructor to modify default params and provide more of them.
class HelloControl extends BaseControlWidget with ThemeProvider<MyTheme> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(theme.padding),
child: Text(
localize('hello_world'),
style: fontPrimary.title,
),
);
}
}
- [PageRouteProvider] Specifies Route and WidgetBuilder settings for [RouteHandler]. With [WidgetInitializer] passing [args] to Widgets and Controllers during navigation.
Use [RouteControl] mixin to enable this navigation in Widget.
PageRouteProvider get counterPageRoute => PageRouteProvider.of(
identifier: 'counter',
builder: (context) => CounterPage(),
);
class HelloPage extends BaseControlWidget with RouteControl {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return FlatButton(
onPressed: () => counterPageRoute.navigator(this).openRoute(),
child: Text(
'open counter page',
),
);
}
}
Sometimes is handy to navigate from Controller or Model and for these scenarios exists [RouteController] mixin.
Widget still needs to be implemented with [RouteControl].
class HelloController extends BaseController with RouteController {
void navigateToNextPage() => openPage(counterPageRoute);
}
class HelloPage extends SingleControlWidget<HelloController> with RouteControl {
HelloController initController() => HelloController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return FlatButton(
onPressed: controller.navigateToNextPage,
child: Text(
'open counter page',
),
);
}
}
Other classes
-
[InputField] Wrapper of [TextField] to provide more functionality and control via [InputController].
-
[DisposeHandler] - mixin for any class, helps with object disposing.
-
[PrefsProvider] - mixin for any class, helps to store user preferences.
-
[FutureBlock] Retriggerable delay.
-
[DelayBlock] Delay to wrap a block of code to prevent 'super fast' completion and UI jiggles.
-
[Parse] Helps to parse json primitives and Iterables. Also helps to look up Lists and Maps for objects.
-
[WidgetInitializer] Helps to initialize Widgets with init data.
-
[UnitId] Unique Id generator based on Time, Index or just Random.
-
and more..
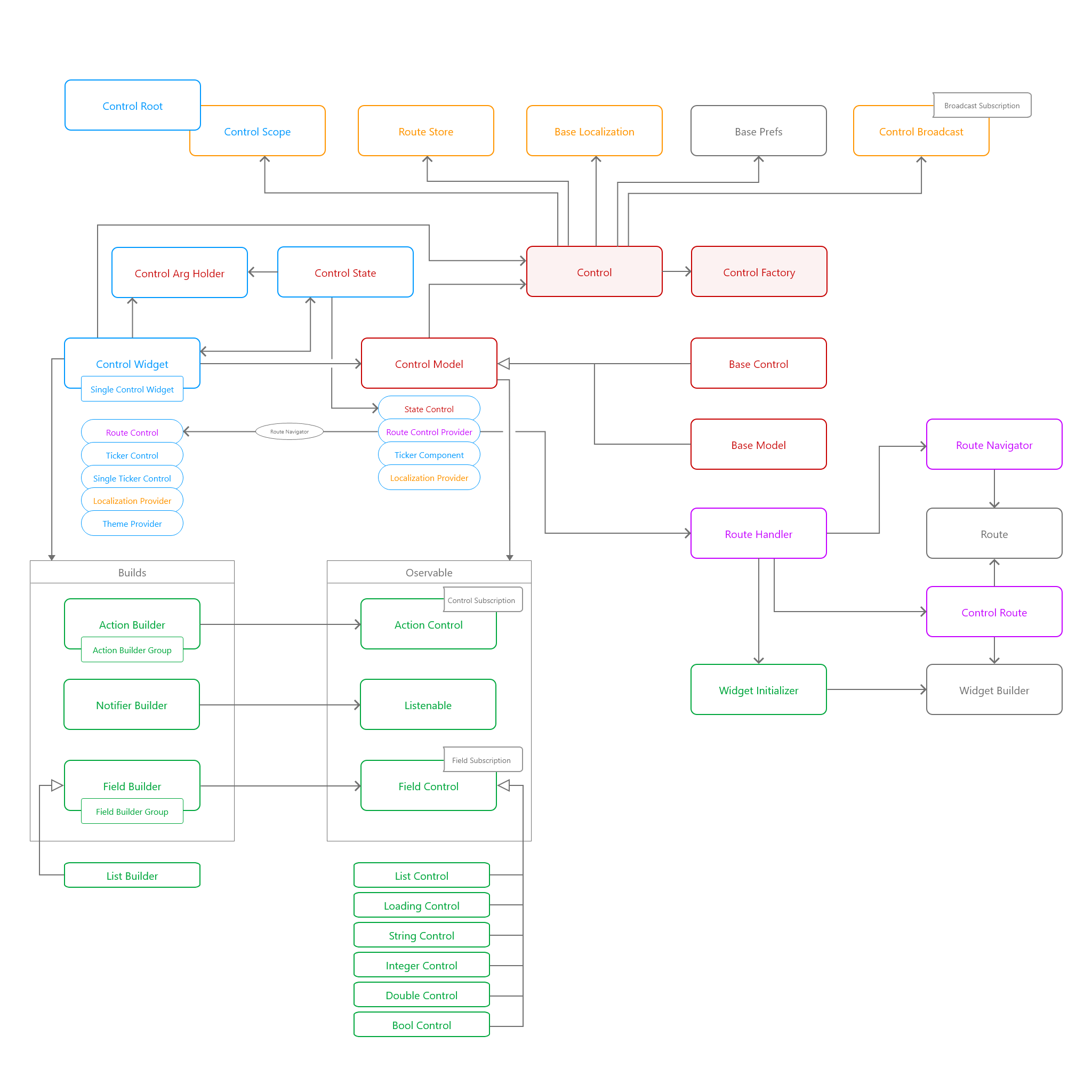
Full Core Structure