text_similarity 1.0.1  text_similarity: ^1.0.1 copied to clipboard
text_similarity: ^1.0.1 copied to clipboard
Implementation of Levenshtein's Automaton to find similarities between a String and a set of known words.
Text Similarity #
This package is an implementation of Levenshtein's Automaton. With this package, you can find similarities between a String and a set of known words.
Created by Pedro Lemos (@pedrolemoz) in 15/09/2023 #
About Levenshtein's Automaton #
A Levenshtein's Automaton for a string w and a number n is a non-deterministic finite automaton (NFA) that accepts the set of strings with maximum distance of n from a string w.
This distance is measured as the mininum number of operations (insertions, removals and substitutions) on the symbols to transform one string in another one.
For example, consider the following automaton constructed from the string "WORLD":
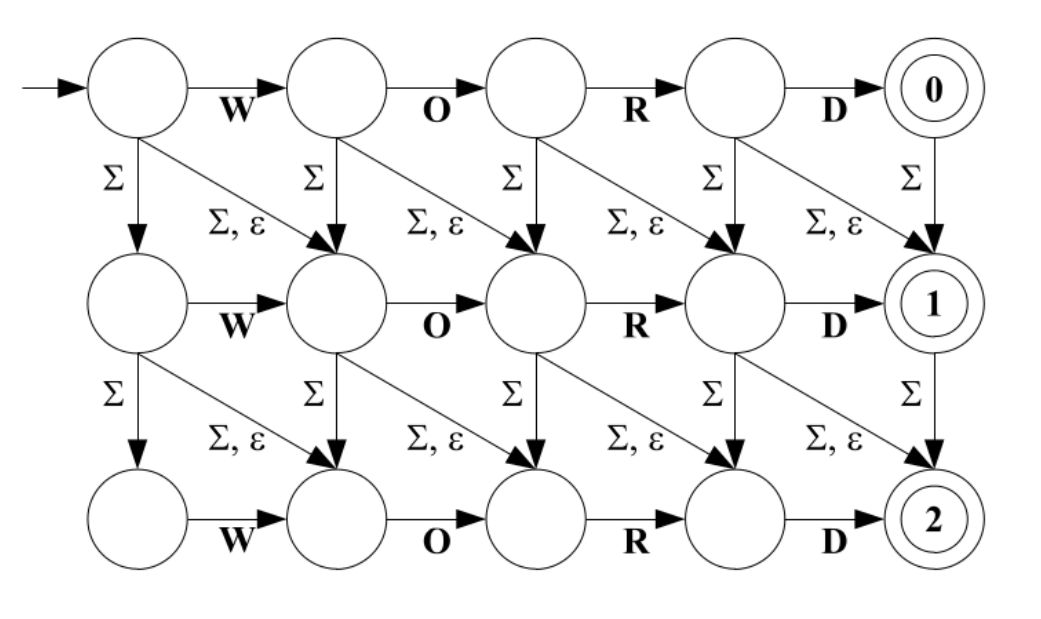
In this example, Σ (sigma) represents any symbol from the current alphabet, and ε (epsilon) represents any symbol from any alphabet (including whitespaces). Note that the strings "WORD", "WOD", "WOOD" and "WORLD" are accepted by the automaton, since the maximum distance (n) is 2.
Usage #
You are able to instantiate the TextSimilarity class directly, but there is an extension applied on String to reduce boilerplate:
void main() {
final textSimilarity = TextSimilarity();
final results = textSimilarity.similarities(
input: 'maçã',
distance: 2,
candidates: ['maca', 'massa', 'mapa', 'faca'],
);
print(results); // {maca, mapa}
}
or
void main() {
final results = 'maçã'.similarities(
distance: 2,
candidates: ['maca', 'massa', 'mapa', 'faca'],
);
print(results); // {maca, mapa}
}
Futhermore, if you are interested in the generated Levenshtein's Automaton, you can use the LevenshteinAutomaton class to instatiate your own automaton:
void main() {
final automaton = LevenshteinAutomaton(input: 'maçã', distance: 2);
print(automaton.evaluate('mapa')); // true
print(automaton.evaluate('faca')); // false
}
Possible applications #
With Levenshtein's Automaton, you can:
- find and correct misspelled words;
- find words in a regular language instead of a finite dictionary;
- suggest words using typed characters;
- full-text searches in databases, capable of returning relevant results even if a query has spelling errors;
- fuzzy matching, finding texts that come close to a query;
- remove inconsistencies from texts.
It's important to note that everything that's possible to do with a Levenshtein's automaton is possible to do with a regular expression. However, building a regular expression that does the same thing as this automaton does isn't an easy task.