sqflite_orm 0.1.11  sqflite_orm: ^0.1.11 copied to clipboard
sqflite_orm: ^0.1.11 copied to clipboard
Cross-platform SQLite ORM for Flutter and Dart with automatic migrations, relationships, query builder, and web UI.
SQLite ORM #
A comprehensive Flutter/Dart SQLite ORM package with cross-platform support (desktop, Android, iOS), automatic migrations, relationship handling, query builder, and a web-based database management UI.
Features #
- Cross-Platform: Automatic FFI initialization for desktop (Windows, Linux, macOS) and mobile (Android, iOS)
- Type-Safe ORM: Strong typing with Dart generics
- Simplified Registration: Automatic column inference from models - no boilerplate needed
- Runtime Validation: Schema mismatch detection at runtime
- Automatic Migrations: Generate migrations from model changes
- Associations: Full support for eager loading with
include()(Sequelize-style) - Query Builder: Fluent, type-safe query API with
findAll(),findOne(),findByPk() - CRUD Operations:
create(),insert(),update(),delete()methods - Web UI: Full-featured database management interface with pagination and table browser
- Web Debug Mode: Automatically start Web UI during development (works in both Flutter and pure Dart)
- Transactions: Full transaction support with rollback
Installation #
Add to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
sqflite_orm: ^0.1.11
Quick Start #
1. Define Your Models #
import 'package:sqflite_orm/sqflite_orm.dart';
@Table(name: 'users')
class User extends BaseModel {
@PrimaryKey()
@Column(name: 'id')
int? id;
@Column(name: 'name')
String? name;
@Column(name: 'email')
String? email;
@Column(name: 'createdAt')
DateTime? createdAt;
@override
Map<String, dynamic> toMap() {
return {
'id': id,
'name': name,
'email': email,
'createdAt': createdAt?.toIso8601String(),
};
}
@override
BaseModel fromMap(Map<String, dynamic> map) {
return User()
..id = map['id'] as int?
..name = map['name'] as String?
..email = map['email'] as String?
..createdAt = map['createdAt'] != null
? DateTime.parse(map['createdAt'])
: null;
}
@override
String get tableName => 'users';
}
2. Initialize Database #
final db = await DatabaseManager.initialize(
path: 'app.db',
version: 1,
models: [User, Post, Comment],
instanceCreators: {
User: () => User(),
Post: () => Post(),
Comment: () => Comment(),
},
// Optional: Enable Web UI for development
webDebug: true,
webDebugPort: 4800,
);
Note: FFI initialization is handled automatically for desktop platforms. No manual setup needed!
3. CRUD Operations #
Create Records
// Method 1: Using create() - returns model instance
final user = await db.query<User>().create({
'name': 'John Doe',
'email': 'john@example.com',
'createdAt': DateTime.now(),
});
print('Created user: ${user.name} (ID: ${user.id})');
// Method 2: Using insert() - returns inserted ID
final user = User()
..name = 'Jane Smith'
..email = 'jane@example.com';
final id = await db.query<User>().insert(user);
Read Records
// Find all records
final users = await db.query<User>().findAll();
// Find one record
final user = await db.query<User>().findOne();
// Find by primary key
final user = await db.query<User>().findByPk(123);
// Find with conditions
final users = await db.query<User>()
.whereClause(WhereClause().equals('email', 'john@example.com'))
.findAll();
// Find with ordering and pagination
final users = await db.query<User>()
.orderBy('createdAt', descending: true)
.limit(10)
.offset(0)
.findAll();
// Count records
final count = await db.query<User>()
.whereClause(WhereClause().equals('active', true))
.count();
Update Records
// Update using model instance
final user = await db.query<User>().findByPk(123);
if (user != null) {
user.name = 'Updated Name';
await db.query<User>().update(user);
}
// Update using values map
final rowsUpdated = await db.query<User>()
.whereClause(WhereClause().equals('id', 123))
.updateValues({'name': 'Updated Name'});
Delete Records
// Delete with conditions
final rowsDeleted = await db.query<User>()
.whereClause(WhereClause().equals('id', 123))
.delete();
4. Associations (Eager Loading) #
Register relationships and use include() for eager loading, similar to Sequelize:
// Register relationships (after database initialization)
final registry = ModelRegistry();
final postInfo = registry.getInfo(Post);
if (postInfo != null) {
final updatedInfo = ModelInfo(
tableName: postInfo.tableName,
modelType: postInfo.modelType,
columns: postInfo.columns,
primaryKey: postInfo.primaryKey,
foreignKeys: postInfo.foreignKeys,
relationships: {
'author': RelationshipInfo(
type: 'ManyToOne',
targetType: User,
foreignKey: 'userId',
),
'comments': RelationshipInfo(
type: 'OneToMany',
targetType: Comment,
foreignKey: 'postId',
),
},
factory: postInfo.factory,
);
registry.register(Post, updatedInfo);
}
// Use include() for eager loading
final post = await db.query<Post>()
.include(['author', 'comments'])
.findByPk(1);
// Access loaded relationships
final author = post?.getRelation<User>('author');
final comments = post?.getRelationList<Comment>('comments') ?? [];
// findAll() with include
final posts = await db.query<Post>()
.include(['author'])
.findAll();
// findOne() with include
final user = await db.query<User>()
.include(['posts'])
.findOne();
5. Transactions #
// Use queryWithTransaction() inside transactions
await db.transaction((txn) async {
final user1 = await db.queryWithTransaction<User>(txn).create({
'name': 'User 1',
'email': 'user1@example.com',
});
final user2 = await db.queryWithTransaction<User>(txn).create({
'name': 'User 2',
'email': 'user2@example.com',
});
// If any operation fails, transaction is rolled back automatically
});
6. Web Debug Mode #
Enable Web UI automatically during development:
final db = await DatabaseManager.initialize(
path: 'app.db',
version: 1,
models: [User, Post],
instanceCreators: {
User: () => User(),
Post: () => Post(),
},
// Automatically start Web UI
webDebug: true,
webDebugPort: 4800,
// webDebugPassword: 'secret', // Note: sqflite_dev does not support password protection
);
When the Web UI starts, you'll see output like:
✓ Web UI server started
Local: http://localhost:4800
Network: http://192.168.1.100:4800
(Access from your PC using the Network URL above)
Accessing from PC when debugging on Android:
When debugging your Flutter app on an Android device, the Web UI server automatically:
- Binds to all network interfaces (0.0.0.0) to allow network access
- Detects and displays your device's local IP address
- Provides both Local and Network URLs
To access from your PC:
- Ensure both your PC and Android device are on the same Wi‑Fi network
- Use the Network URL shown in the console output (e.g.,
http://192.168.1.100:4800) - Open this URL in your PC's browser to access the Web UI
Note: The Local URL (http://localhost:4800) works when running on emulators or when accessing from the device itself.
Web UI Features #
The web UI provides a modern interface for database management:
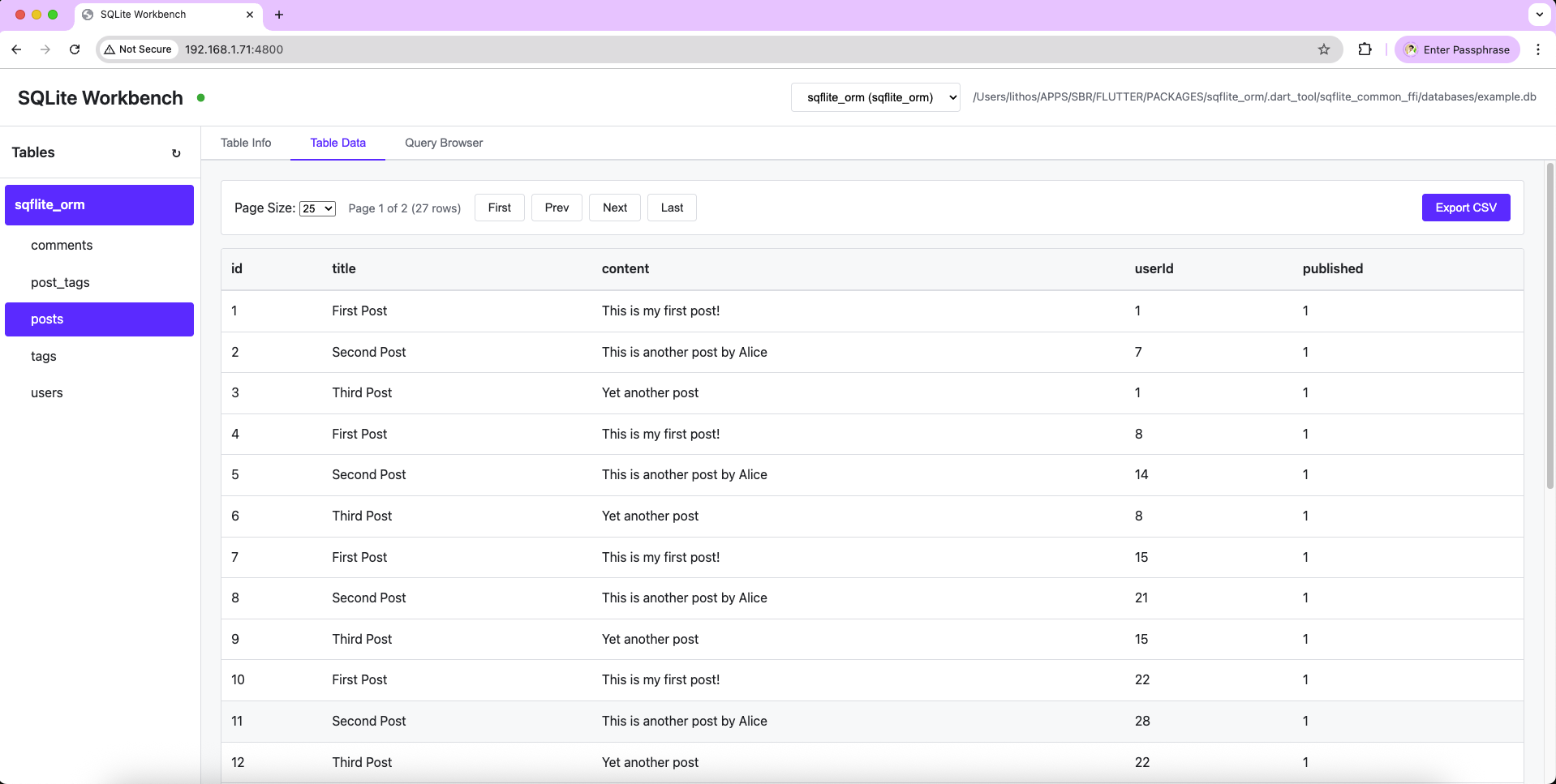
- Table Browser: Left sidebar listing all database tables
- Data Grid: Browse and view table data with pagination
- Pagination: Configurable page size (10, 25, 50, 100, 200 rows)
- SQL Query Editor: Execute custom SQL queries
- Schema Viewer: View table structure and column information
- Network Access: Access from your PC when debugging on Android devices
- Cross-Platform: Works in both Flutter and pure Dart environments
Accessing the Web UI #
Local Access (Emulator/Desktop):
- Access at
http://localhost:4800(or your configured port)
Network Access (Android Device):
- When debugging on an Android device, the server automatically detects and displays your device's IP address
- Use the Network URL shown in the console (e.g.,
http://192.168.1.100:4800) from your PC's browser - Both devices must be on the same Wi‑Fi network
Query Builder API #
Find Methods #
// Find all
final users = await db.query<User>().findAll();
// Find first
final user = await db.query<User>().findFirst();
// Find one (alias for findFirst)
final user = await db.query<User>().findOne();
// Find by primary key
final user = await db.query<User>().findByPk(123);
Where Clauses #
// Equals
.whereClause(WhereClause().equals('email', 'john@example.com'))
// Greater than
.whereClause(WhereClause().greaterThan('age', 18))
// Less than
.whereClause(WhereClause().lessThan('age', 65))
// Multiple conditions
.whereClause(WhereClause()
.equals('status', 'active')
.greaterThan('createdAt', DateTime(2024, 1, 1)))
Ordering and Pagination #
.orderBy('createdAt', descending: true)
.limit(10)
.offset(20)
Associations #
.include(['author', 'comments', 'tags'])
Annotations #
@Table #
Marks a class as a database table.
@Table(name: 'users')
class User extends BaseModel { ... }
@Column #
Marks a field as a database column.
@Column(name: 'email')
String? email;
@PrimaryKey #
Marks a field as a primary key.
@PrimaryKey()
@Column(name: 'id')
int? id;
@ForeignKey #
Marks a field as a foreign key.
@ForeignKey(table: 'users', column: 'id')
@Column(name: 'userId')
int? userId;
Migrations #
Migrations are handled automatically. When you change your models and increment the version number, the package will:
- Detect new tables
- Create missing tables
- Add missing columns to existing tables
- Validate schema changes
For complex migrations, you can provide a custom onUpgrade callback:
final db = await DatabaseManager.initialize(
path: 'app.db',
version: 2,
models: [User, Post],
instanceCreators: {
User: () => User(),
Post: () => Post(),
},
onUpgrade: (db, oldVersion, newVersion) async {
if (oldVersion < 2) {
// Custom migration logic
await db.execute('ALTER TABLE users ADD COLUMN phone TEXT');
}
},
);
Complete Example #
See example/example.dart for a comprehensive example including:
- Model definitions
- CRUD operations
- Associations and eager loading
- Transactions
- Complex queries
- Web UI integration
Run the example:
dart run example/example.dart
Real-World Examples #
Finzo - Income & Expense Management App #
Finzo is a real-world Flutter application that demonstrates the use of sqflite_orm in production. It's an income and expense management app that showcases:
- Complex model relationships
- Transaction handling for financial operations
- Data persistence and management
- Cross-platform compatibility (Android, iOS, Desktop, Web)
Check out the Finzo repository to see how sqflite_orm is used in a complete application.
API Reference #
DatabaseManager #
static Future<DatabaseManager> initialize({
required String path,
required int version,
required List<Type> models,
Map<Type, BaseModel Function()>? instanceCreators,
Database? Function(Database db, int oldVersion, int newVersion)? onUpgrade,
Database? Function(Database db, int version)? onCreate,
bool webDebug = false,
int webDebugPort = 4800,
String? webDebugPassword,
})
QueryBuilder #
// Query methods
Future<List<T>> findAll()
Future<T?> findFirst()
Future<T?> findOne()
Future<T?> findByPk(dynamic primaryKeyValue)
Future<int> count()
Future<int> delete()
// CRUD methods
Future<T> create(Map<String, dynamic> values)
Future<int> insert(T model)
Future<int> update(T model)
Future<int> updateValues(Map<String, dynamic> values)
// Query building
QueryBuilder<T> whereClause(WhereClause clause)
QueryBuilder<T> orderBy(String column, {bool descending = false})
QueryBuilder<T> limit(int count)
QueryBuilder<T> offset(int count)
QueryBuilder<T> include(List<String> associations)
QueryBuilder<T> select(List<String> columns)
// Transactions
QueryBuilder<T> queryWithTransaction(Transaction txn)
License #
MIT