shouldly 0.4.0+1  shouldly: ^0.4.0+1 copied to clipboard
shouldly: ^0.4.0+1 copied to clipboard
A simple, extensible BDD assertion library which focuses on giving great error messages when the assertion fails.

shouldly is an assertion concept that focuses on
- writing assertions as plain English sentences
- and giving better error messages when the assertion fails while being simple and terse.
Inspired from Fluent Assertion, Shouldly, should.js
Features #
- More readable test code
- Better test failure messages
- Conjunction support (
and) - Custom assertions
Readability #
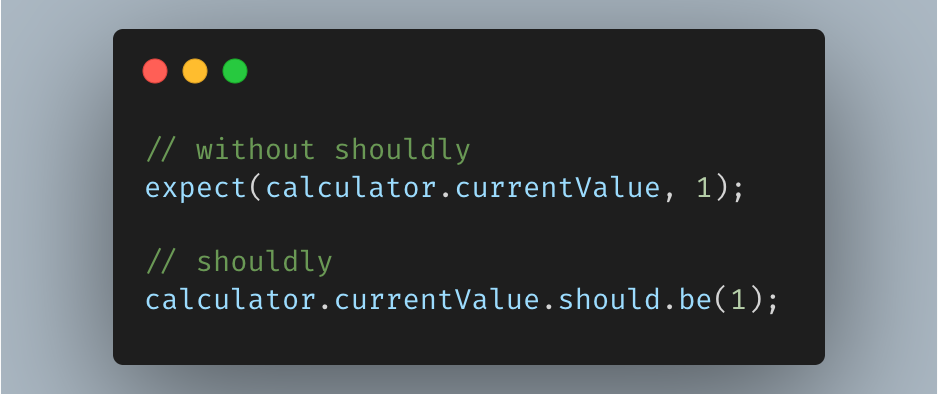
More readable test code as plain English sentence.
// without shouldly
expect(calculator.currentValue, 1);
// shouldly
calculator.currentValue.should.be(1);
No more: Mix Up with parameters #
You can mix up with Expected or Actual 🤔. But with shouldly there is no way to mix up.
// without shouldly
expect(playerCharacter.health, 100);
expect(100, playerCharacter.health);
// shouldly
playerCharacter.health.should.be(100);
No more: single heap of assertion methods #
Every single type of class has his own assertions.
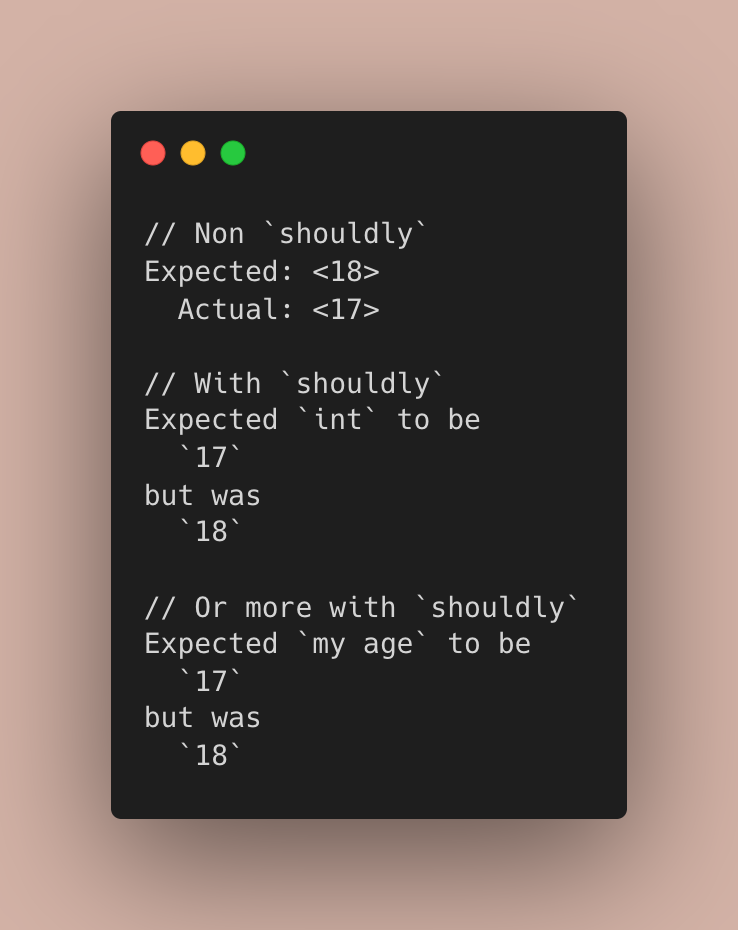
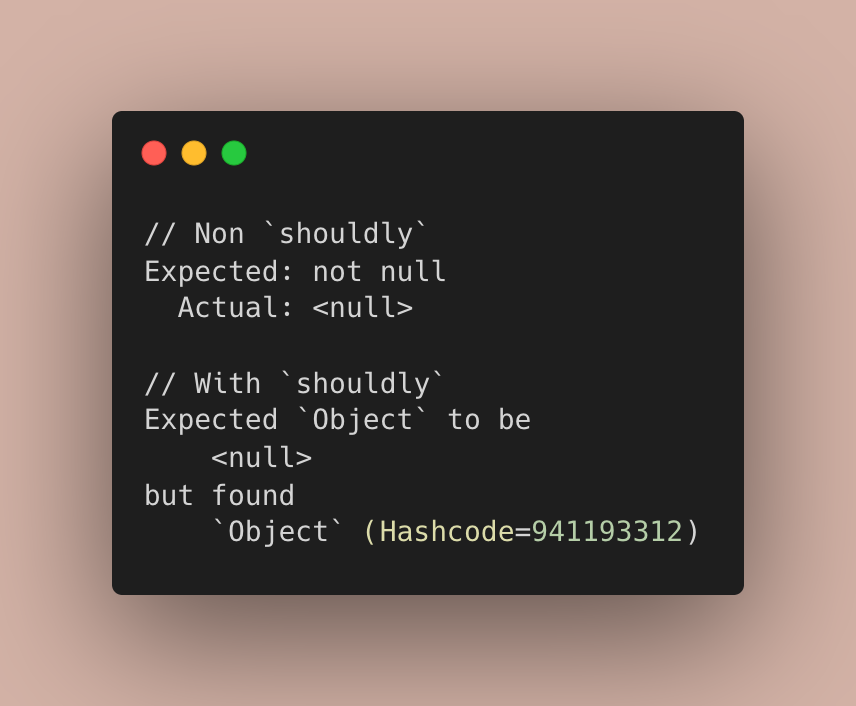
Better test failure messages #
To get more contextual information

Conjunctions #
This is a real English sentence, is it not?
13.should.beOdd().and.beGreaterOrEqualThan(13);
participants.should.contain('Andrew').and.not.contain('Bobby');
Custom matchers #
extension CustomNumAssertions on NumericAssertions {
NumericAssertions get beNegative {
if (subject >= 0) {
throw ShouldlyTestFailureError('Number\n should be negative');
}
return NumericAssertions(subject);
}
}
Or more exotic matchers #
test('Custom matchers', () {
final bobby = Customer(
isMarried: true,
gender: Gender.male,
);
bobby.should.beMale.and.beMarried;
final kate = Customer(
isMarried: true,
gender: Gender.female,
);
kate.should.beMarried.and.not.beMale;
});
Getting started #
Simple add shouldly dependency into your project.
Usage #
Objects #
Every single object has following assertion methods:
| Method | Example |
|---|---|
| be | 1.should.be(1); |
| beOfType | 2.0.should.beOfType<double>(); |
| beAssignableTo | 3.should.beAssignableTo<int>(); |
| beNull | null.should.beNull(); |
| beOneOf | 5.should.beOneOf([1, 2, 5]); |
Booleans #
| Method | Example |
|---|---|
| beFalse | true.should.beTrue(); |
| beTrue | true.should.not.beFalse(); |
test('false should be `false`', () {
false.should.beFalse();
});
test('false should not be `true`', () {
false.should.not.beTrue();
});
Numbers #
| Method | Example |
|---|---|
| bePositive | 1.should.bePositive(); |
| beNegative | (-1).should.beNegative(); |
| beZero | 0.should.beZero(); |
| beOdd | 7.should.beOdd(); |
| beEven | 2.should.beEven(); |
| beGreaterThan | 3.should.beGreaterThan(2); |
| beAbove | 3.should.beAbove(2); |
| beLessThan | 3.should.beLessThan(4); |
| beBelow | 3.should.beBelow(4); |
| beGreaterOrEqualThan | 3.should.beGreaterOrEqualThan(3); |
| beLessOrEqualThan | 3.should.beLessOrEqualThan(3); |
| beWithin | 3.should.beWithin(1,5); |
| beCloseTo | pi.should.beCloseTo(3.14, delta: 0.01); |
| beTolerantOf | pi.should.beTolerantOf(3.14, tolerance: 1%); |
test('Int should be type of `int`', () {
2.should.beEven();
10.should.beGreaterThan(9);
9.99.should.not.beCloseTo(10.0, delta: 0.01);
});
Strings #
test('should not start with substring', () {
'Flutter'.should.not.startWith('A');
});
DateTimes #
// before
DateTime(2021, 9, 9).should.beBefore(DateTime(2021, 9, 10));
DateTime(2021, 9, 9).should.not.beBefore(DateTime(2021, 9, 9));
// close to
DateTime(2021, 9, 9, 1, 1, 1, 2).should.beCloseTo(
DateTime(2021, 9, 9, 1, 1, 1, 3),
delta: Duration(milliseconds: 1),
);
Iterables #
test('should contain', () {
[1, 200, 3].should.contain(200);
});
test('should not contain', () {
[1, 2, 4].should.not.contain(3);
});
test('with every element in collection is true for predicate', () {
[3, 5, 7, 9].should.every((item) => item < 10);
});
test('with some elements in collection is true for predicate', () {
[3, 5, 7, 9].should.any((item) => item > 8);
});
Maps #
final subject = {
'name': 'John',
'age': 18,
};
test('should contain key', () {
subject.should.containKey('name');
});
test('should contain key with exact value', () {
subject.should.containKeyWithValue('age', 18);
});
Functions #
Should.throwException(() => someMethodWitchThrowException(params:));
Should.throwError<ExactError>(() => someMethodWitchThrowExactError(params:));
test('async function should throw exception', () async {
await Should.throwAsync(() {
Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 100));
throw Exception('test');
});
});
test('async function should throw exact exception', () async {
await Should.throwAsync<CustomException>(() {
Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 100));
throw CustomException('custom exception test');
});
});
test('should complete in a duration', () async {
await Should.completeIn(
Duration(seconds: 1),
func: () => slowFunction(
Duration(milliseconds: 900),
),
);
});
Objects #
test('should be not null', () {
final obj = Object();
obj.should.not.beNull();
});
test('should be null', () {
const Object? obj = null;
obj.should.beNull();
});
test('should be type of `int`', () {
const obj = 1;
obj.should.beOfType<int>();
});
test('should be assignable to `num`', () {
const obj = 1;
obj.should.beAssignableTo<num>();
});
Enums #
test('should not be equal', () {
seasons.spring.should.not.be(seasons.winter);
});
test('should not be type of', () {
seasons.spring.should.not.beOfType<level>();
});
test('should be assignable to `Enum`', () {
seasons.spring.should.beAssignableTo<Enum>();
});
More examples here
Writing Custom Matchers #
extension CustomerExtension on Customer {
CustomerAssertions get should => CustomerAssertions(this);
}
class CustomerAssertions extends BaseAssertions<Customer, CustomerAssertions> {
CustomerAssertions(
Customer? subject, {
bool isReversed = false,
String? subjectLabel,
}) : super(subject, isReversed: isReversed, subjectLabel: subjectLabel);
CustomerAssertions get beMarried {
if (isReversed) {
if (subject!.isMarried) {
throw ShouldlyTestFailure('Customer should not be married');
}
} else {
if (!subject!.isMarried) {
throw ShouldlyTestFailure('Customer should be married');
}
}
return CustomerAssertions(subject);
}
CustomerAssertions get beMale {
if (isReversed) {
if (subject!.gender == Gender.male) {
throw ShouldlyTestFailure('Customer should be female');
}
} else {
if (subject!.gender != Gender.male) {
throw ShouldlyTestFailure('Customer should be male');
}
}
return CustomerAssertions(subject);
}
@override
CustomerAssertions copy(
Customer? subject, {
bool isReversed = false,
String? subjectLabel,
}) =>
CustomerAssertions(
subject,
isReversed: isReversed,
subjectLabel: subjectLabel,
);
}
Recommendations #
You can improve the readability of the rest of your test code with given_when_then_unit_test, which enhances the test report readability as well.
Changelog #
Please see the Changelog page to know what's recently changed.
Contributing #
Feel free to contribute to this project.
If you find a bug or want a feature, but don't know how to fix/implement it, please fill an issue.
If you fixed a bug or implemented a new feature, please send a pull request.
We accept the following contributions:
- Ideas how to improve
- Reporting issues
- Fixing bugs
- More tests
- More class integrations (Functions, Futures, Functions)
- Improving documentation and comments

