s_client 3.0.0  s_client: ^3.0.0 copied to clipboard
s_client: ^3.0.0 copied to clipboard
Safe-by-default HTTP client with dual backend support (http/dio), never throws exceptions, returns result tuples, supports interceptors, retry logic, and type-safe JSON parsing.
s_client #
A powerful HTTP client package for Flutter that lets you choose your backend: lightweight http or feature-rich dio — with a single, unified API.
🎯 Why s_client? #
One API, Two Backends — Switch between http and dio with a single line of configuration. No code changes needed.
Safe by Design — All requests are wrapped in try-catch internally. No runtime crashes, ever. Handle responses with onSuccess/onError callbacks or the result tuple.
// Use lightweight http package (great for simple apps)
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.http));
// OR use feature-rich dio package (advanced features)
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.dio));
// Your code stays exactly the same!
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
);
// OR simply make your request with your desired clientType for this specific request, overriding the SClient configuration
// with optional callbacks for clean, safe error handling — no try-catch needed!
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
clientType: ClientType.dio, // Override just for this request
onSuccess: (response) => print('Got ${response.body}'),
onError: (error) => print('Failed: ${error.message}'),
);
Features #
- 🔄 Dual Backend Support: Switch between
httpordioanytime — same code, different engine - 🔀 Per-Request Override: Use different backends for individual requests
- 🛡️ Safe by Default: All requests internally wrapped in try-catch blocks — no unhandled exceptions
- 📦 Unified API: Every method returns a result tuple AND supports optional callbacks
- 🔄 Type-Safe JSON Parsing: Built-in support for JSON deserialization with
getJson,getJsonList,postJson - ⚙️ Customizable Status Codes: Define what constitutes success vs error responses
- 🔌 Interceptors: Built-in logging, authentication, and caching interceptors
- 🔁 Retry Logic: Automatic retries with exponential backoff
- ❌ Request Cancellation: Cancel individual requests or all pending requests
- 📁 File Operations: Upload and download files with progress callbacks
Demo #
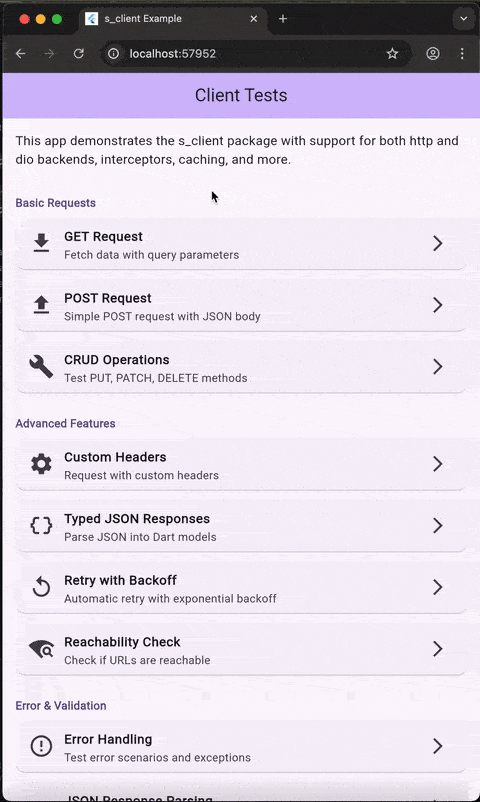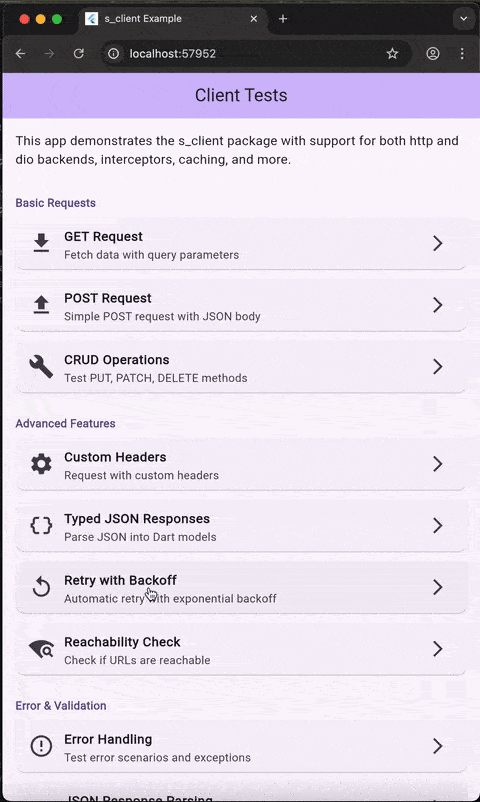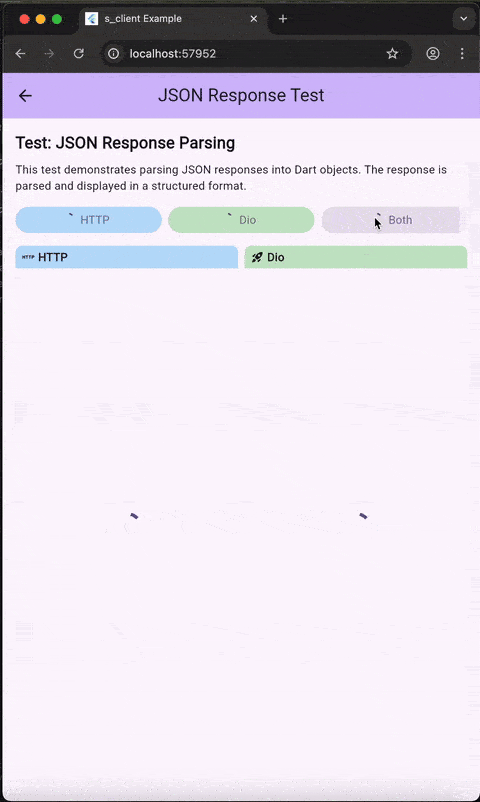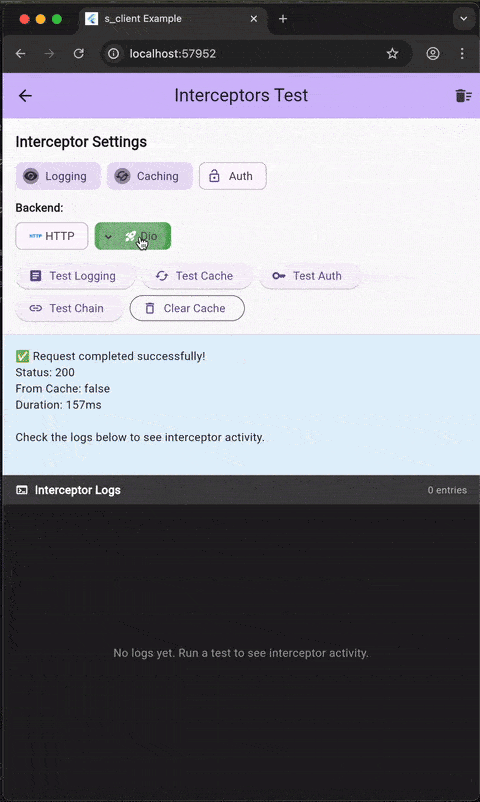
The example app demonstrates all features including:
- GET/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD requests with HTTP and Dio backends
- Typed JSON parsing with
getJsonandgetJsonList - Interceptors (logging, caching, authentication)
- Retry logic with exponential backoff
- Error handling scenarios
- Reachability checking
- Form submission with validation
- Side-by-side comparison of HTTP vs Dio backends
Installation #
Add to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
s_client: ^3.0.0
Quick Start #
Import #
import 'package:s_client/s_client.dart';
Basic Usage #
// Choose your backend once
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.http)); // or ClientType.dio
// Returns (ClientResponse?, ClientException?) tuple
// All requests are internally wrapped in try-catch - NEVER throws!
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
);
if (error != null) {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
} else {
print('Success: ${response!.body}');
}
Backend Switching #
The core feature of s_client — seamlessly switch between HTTP clients.
Global Configuration #
Set the default backend for all requests:
// Use lightweight http package
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.http));
// Or use feature-rich dio package
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.dio));
// All your existing code continues to work unchanged!
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(url: '/users');
Per-Request Override #
Override the backend for individual requests:
// Global config uses http
SClient.configure(const ClientConfig(clientType: ClientType.http));
// But this specific request uses dio
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
clientType: ClientType.dio, // Override just for this request
);
// Works with all methods: get, post, put, patch, delete, head, download, uploadFile
final (data, err) = await SClient.instance.post(
url: '/upload',
body: {'data': 'value'},
clientType: ClientType.dio, // Use dio for this upload
);
When to Use Each Backend #
ClientType.http |
ClientType.dio |
|---|---|
| Simple apps with basic HTTP needs | Advanced interceptors |
| Smaller package size | File upload/download with progress |
| Fewer dependencies | Request cancellation |
| More control over request/response handling |
Safe by Default #
Unlike raw HTTP clients, s_client never throws exceptions. Every request is wrapped in internal try-catch blocks:
// ❌ Raw http/dio - can crash your app
try {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse(url));
// Handle response...
} catch (e) {
// You MUST remember to catch!
}
// ✅ s_client - always safe, never crashes
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(url: url);
if (error != null) {
// Handle error gracefully
}
// No try-catch needed - the package handles it for you!
API Patterns #
Tuple-Based API (Functional Style) #
All methods return a (response, error) tuple:
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(url: '/users');
if (error != null) {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
} else {
print('Success: ${response!.body}');
}
With Optional Callbacks #
Same methods, with optional callbacks — returns tuple AND invokes callbacks:
await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
onSuccess: (response) {
print('Success: ${response.body}');
},
onError: (error) {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
},
onStatus: {
401: (code, response) => refreshToken(),
429: (code, response) => handleRateLimit(),
},
);
Best of Both Worlds #
// Use callbacks for UI updates AND inspect the result for logging/analytics
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
onSuccess: (response) => updateUI(response),
onError: (error) => showSnackbar(error.message),
);
// Can still use the result for additional processing
if (response != null) {
analytics.logSuccess(response.statusCode);
}
Using Data from Both Callback AND Tuple Result #
The callback receives the exact same object as the tuple result:
// Capture data from callback
String? extractedUsername;
ClientResponse? callbackResponse;
// Make request - use data in BOTH places
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: 'https://api.example.com/user/123',
onSuccess: (resp) {
callbackResponse = resp;
final userData = jsonDecode(resp.body);
extractedUsername = userData['username'];
print('Callback: User is $extractedUsername');
_updateUserCache(userData); // Side effect
},
);
// ALSO use the same data from the tuple result
if (response != null) {
final userData = jsonDecode(response.body);
final email = userData['email'];
print('Tuple: Email is $email');
print('Username from callback was: $extractedUsername');
// Both response objects are identical!
assert(identical(response, callbackResponse)); // true
}
Key Benefits:
- Callbacks fire before the method returns, so side effects happen immediately
- The tuple result gives you structured error handling and flow control
- Both receive the same response object, so you can access data from either
- Use callbacks for: logging, analytics, UI updates, caching
- Use tuple for: business logic, error handling, data processing
HTTP Methods #
All methods return a result tuple AND support optional callbacks:
GET #
// Tuple only
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(url: '/users');
// With callbacks (still returns tuple)
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(
url: '/users',
onSuccess: (response) => print(response.body),
onError: (error) => print(error.message),
);
POST #
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.post(
url: '/users',
body: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30},
onSuccess: (response) => print('Created: ${response.body}'),
onError: (error) => print('Error: ${error.message}'),
);
PUT, PATCH, DELETE, HEAD #
All follow the same unified pattern.
Typed JSON Parsing #
class User {
final String name;
final int age;
User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json)
: name = json['name'],
age = json['age'];
}
// GET with automatic JSON parsing
await SClient.instance.getJson<User>(
url: 'https://api.example.com/user/1',
fromJson: User.fromJson,
onSuccess: (user, response) {
print('Hello ${user.name}, age ${user.age}');
},
onError: (error) {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
},
);
// GET list of objects
await SClient.instance.getJsonList<User>(
url: 'https://api.example.com/users',
fromJson: User.fromJson,
onSuccess: (users, response) {
print('Got ${users.length} users');
},
onError: (error) {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
},
);
PUT, PATCH, DELETE with JSON Parsing #
// PUT with automatic JSON deserialization
await SClient.instance.putJson<User>(
url: 'https://api.example.com/user/1',
body: {'name': 'Updated Name'},
fromJson: User.fromJson,
onSuccess: (user, response) => print('Updated: ${user.name}'),
);
// PATCH with automatic JSON deserialization
await SClient.instance.patchJson<User>(
url: 'https://api.example.com/user/1',
body: {'age': 31},
fromJson: User.fromJson,
onSuccess: (user, response) => print('Patched: ${user.name}'),
);
// DELETE with automatic JSON deserialization
await SClient.instance.deleteJson<User>(
url: 'https://api.example.com/user/1',
fromJson: User.fromJson,
onSuccess: (user, response) => print('Deleted user confirmed'),
);
File Operations #
Download to Memory #
final (bytes, error) = await SClient.instance.download(
url: 'https://example.com/file.pdf',
onSuccess: (bytes) => saveFile(bytes),
onError: (error) => print('Download failed: ${error.message}'),
onProgress: (current, total) {
print('Progress: ${(current / total * 100).toStringAsFixed(1)}%');
},
);
Download to File #
// Save directly to file with FileAccessMode control (Dio 5.8+)
final (file, error) = await SClient.instance.downloadToFile(
url: 'https://example.com/large-file.zip',
savePath: '/path/to/save/file.zip',
fileAccessMode: FileAccessMode.write, // write, append, writeOnly, writeOnlyAppend
onSuccess: (file) => print('Saved to: ${file.path}'),
onError: (error) => print('Download failed: ${error.message}'),
onProgress: (current, total) {
print('Progress: ${(current / total * 100).toStringAsFixed(1)}%');
},
);
// Resume a download by appending to existing file
final (file, error) = await SClient.instance.downloadToFile(
url: 'https://example.com/large-file.zip',
savePath: '/path/to/partial-file.zip',
fileAccessMode: FileAccessMode.append, // Continue from existing bytes
);
Upload #
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.uploadFile(
url: '/upload',
filePath: '/path/to/file.pdf',
fileField: 'file',
onSuccess: (response) => print('Uploaded'),
onError: (error) => print('Upload failed'),
onProgress: (current, total) {
print('Progress: ${(current / total * 100).toStringAsFixed(1)}%');
},
);
Configuration #
Global Configuration #
SClient.configure(
const ClientConfig(
clientType: ClientType.dio, // or ClientType.http
baseUrl: 'https://api.example.com',
connectTimeout: Duration(seconds: 30),
receiveTimeout: Duration(seconds: 30),
defaultHeaders: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
),
);
Retry Logic #
SClient.configure(
const ClientConfig(
maxRetries: 3,
retryDelay: Duration(seconds: 1),
exponentialBackoff: true,
retryStatusCodes: {408, 429, 500, 502, 503, 504},
),
);
Custom Success/Error Codes #
SClient.configure(
const ClientConfig(
successCodes: {200, 201, 204},
errorCodes: {400, 401, 403, 404, 500},
),
);
Interceptors #
Logging Interceptor #
SClient.configure(
ClientConfig(
interceptors: [
LoggingInterceptor(
logRequest: true,
logResponse: true,
logRequestHeaders: true,
logResponseHeaders: true,
logRequestBody: true,
logResponseBody: true,
maxBodyLength: 1000,
prettyPrintJson: true,
),
],
),
);
Or simply enable logging:
SClient.configure(
const ClientConfig(
enableLogging: true, // Adds LoggingInterceptor automatically
),
);
Authentication Interceptor #
// Bearer Token
SClient.configure(
ClientConfig(
interceptors: [
AuthInterceptor(
authType: AuthType.bearer,
tokenProvider: () => 'your-token-here',
),
],
),
);
// API Key
SClient.configure(
ClientConfig(
interceptors: [
AuthInterceptor(
authType: AuthType.apiKey,
apiKeyHeaderName: 'X-API-Key',
tokenProvider: () => 'your-api-key',
),
],
),
);
// Basic Auth
SClient.configure(
ClientConfig(
interceptors: [
AuthInterceptor(
authType: AuthType.basic,
username: 'user',
password: 'pass',
),
],
),
);
Cache Interceptor #
SClient.configure(
ClientConfig(
interceptors: [
CacheInterceptor(
defaultMaxAge: Duration(minutes: 5),
maxEntries: 100,
cacheOnlySuccess: true,
),
],
),
);
Custom Interceptor #
class CustomInterceptor extends ClientInterceptor {
@override
Future<ClientRequest?> onRequest(ClientRequest request) async {
// Modify request
final headers = Map<String, String>.from(request.headers);
headers['X-Custom-Header'] = 'value';
return request.copyWith(headers: headers);
}
@override
Future<ClientResponse> onResponse(
ClientRequest request,
ClientResponse response,
) async {
// Process response
return response;
}
@override
Future<bool> onError(
ClientRequest request,
Object error,
int attemptCount,
) async {
// Return true to retry, false to propagate error
return false;
}
}
Request Cancellation #
// Cancel a specific request
await SClient.instance.get(
url: '/users',
cancelKey: 'users-request',
);
SClient.instance.cancel('users-request');
// Cancel all pending requests
SClient.instance.cancelAll();
Error Handling #
ClientException Types #
enum ClientErrorType {
connectionTimeout,
sendTimeout,
receiveTimeout,
cancelled,
badResponse,
connectionError,
badCertificate,
unknown,
}
Handling Errors #
final (response, error) = await SClient.instance.get(url: '/users');
if (error != null) {
if (error.isTimeout) {
print('Request timed out');
} else if (error.isConnectionError) {
print('No internet connection');
} else if (error.isCancelled) {
print('Request was cancelled');
} else {
print('Error: ${error.message}');
}
}
Testing #
The package includes comprehensive test coverage:
flutter test
License #
MIT License
Contributing #
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.