refena_inspector 2.0.0  refena_inspector: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
refena_inspector: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
The inspector developer utility app for the Refena state management library.

The inspector for Refena.
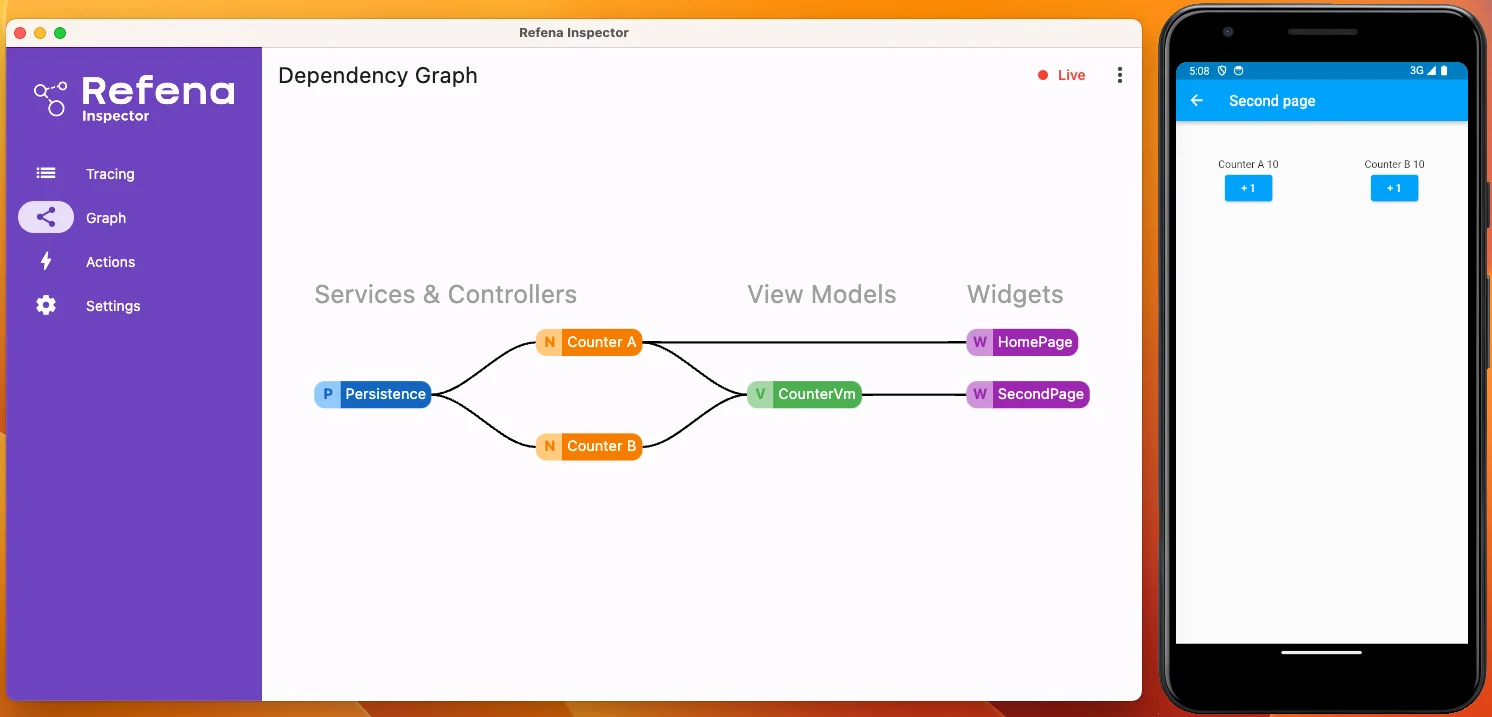
Usage #
Add the refena_inspector_client and refena_inspector packages to your project.
# pubspec.yaml
dependencies:
refena_inspector_client: <version>
dev_dependencies:
refena_inspector: <version>
Also add .refena_inspector to your .gitignore file.
# .gitignore
.refena_inspector/
Add the RefenaInspectorObserver to your RefenaContainer or RefenaScope.
This observer will handle the communication between your app and the inspector.
void main() {
// or "RefenaScope" for Flutter projects
RefenaContainer(
observers: [
RefenaInspectorObserver(), // <-- Add this observer
RefenaTracingObserver(),
RefenaDebugObserver(),
],
);
}
Then start the inspector before your app is running:
dart run refena_inspector
Running the inspector afterwards also works, but it takes longer to connect.
You can configure the observer with custom actions:
RefenaInspectorObserver(
actions: {
'Test message': (Ref ref) => ref.message('test'),
'Authentication': {
'Register': InspectorAction(
params: {
'name': ParamSpec.string(required: true),
'age': ParamSpec.int(defaultValue: 20),
},
action: (ref, params) {
ref.message('Registering ${params['name']}');
},
),
'Logout': (Ref ref) => throw 'Logout error',
},
},
);
As you can see, you can use nested maps to create a tree of actions.
One action can be either a void Function(Ref) or an InspectorAction.
You should use InspectorAction when you need to define parameters for the action.

