ndk 0.2.0-dev003  ndk: ^0.2.0-dev003 copied to clipboard
ndk: ^0.2.0-dev003 copied to clipboard
Nostr Development Kit - the most performant lib for all your nostr usecases
Dart Nostr Development Kit (NDK) #
NDK (Nostr Development Kit) is a Dart library that enhances the Nostr development experience.
NDK supplies you with high-level usecases like lists or metadata while still allowing you to use low-level queries enhanced with inbox/outbox (gossip) by default.
Our Target is to make it easy to build constrained Nostr clients, particularly for mobile devices.
Table of Contents:
- Dart Nostr Development Kit (NDK)
- Getting started
- Features / what does NDK do?
- Common terminology
- Changelog 🔗
- Library development 🏗️
$~~~~~~~~~~~$
Getting started #
Prerequisites #
- dart SDK
Prerequisites ndk_rust_verifier #
- android SDK (also for desktop builds)
- flutter SDK
- rust ( + toolchain for target)
Rust toolchain android:
rustup target add \
aarch64-linux-android \
armv7-linux-androideabi \
x86_64-linux-android \
i686-linux-android
Rust toolchain ios:
# 64 bit targets (real device & simulator):
rustup target add aarch64-apple-ios x86_64-apple-ios
# New simulator target for Xcode 12 and later
rustup target add aarch64-apple-ios-sim
# 32 bit targets (you probably don't need these):
rustup target add armv7-apple-ios i386-apple-ios
Install #
Ndk has a core package ndk and optional packages like rust_verifier and amber.
flutter pub add ndk
Optional:
flutter pub add ndk_rust_verifier
flutter pub add ndk_amber
Import #
import 'package:ndk/ndk.dart';
Optional:
import 'package:ndk_rust_verifier/ndk_rust_verifier.dart';
import 'package:ndk_amber/ndk_amber.dart';
Usage #
more examples 🔗
import 'package:ndk/ndk.dart';
import 'package:ndk_rust_verifier/ndk_rust_verifier.dart';
// init
final ndk = Ndk(
NdkConfig(
eventVerifier: RustEventVerifier(),
cache: MemCacheManager(),
),
);
// query
final response = ndk.requests.query(
filters: [
Filter(
authors: ['hexPubkey']
kinds: [Nip01Event.TEXT_NODE_KIND],
limit: 10,
),
],
);
// result
await for (final event in response.stream) {
print(event);
}
We strongly recommend using
RustEventVerifier()for client applications. It uses a separate thread for signature verification and is therefore more performant. $~~~~~~~~~~~$
Features / what does NDK do? #
- return nostr data based on filters (any kind).
- automatically discover the best relays to satisfy the provided request (using gossip)
- specify desired coverage on each request (e.g. x relays per pubkey)
- publish nostr events to optimal relays or explicit relays
- cache responses to save network bandwidth
- stream directly from cache and network (if needed)
- query and subscription, e.g., get data once; subscribe to data.
- plugin cache interface, bring your own db or use included ones:
inMemory - plug in verifier interface, bring your own event verifier, or use included ones:
bip340, rust - plug in event signer interface, bring your own event signer, or use included ones:
bip340, amber - contact list support, you can convert nostr_event to contact_list
- nip51 list support, you can convert nostr_event to nip51_list
- nip05 caching
not Included #
- ready to use feeds, you have to build them on your own (🚫 not planned)
- create && manage keypairs. You have to provide them (🚫 not planned)
- file upload (🔜 planned)
- threading, you can do this on your own if you move ndk or only the event_verifier into its own thread (🔜 planned)
- support for request overrides (you have to close and reopen requests) (🤔 unsure)
NIPs #
- ✅ Event Builders / WebSocket Subscriptions (NIP-01)
- ✅ User Profiles (edit/follow/unfollow - NIP-02)
- ✅ Private Messages (NIP-04)
- ✅ Nostr Address (NIP-05)
- ✅ Event Deletion (NIP-09)
- ✅ Relay Info (NIP-11)
- ✅ Reactions (NIP-25)
- ✅ Lists (NIP-51)
- ✅ Relay List Metadata (NIP-65)
- ✅ Wallet Connect API (NIP-47)
- ❌ Bech Encoding support (NIP-19)
- ❌ Zaps (private, public, anon, non-zap) (NIP-57)
- ❌ Badges (NIP-58)
Performance #
There are two main constrains that we aim for: battery/compute and network bandwidth.
network
Inbox/Outbox (gossip) is our main pillar to help avoid unnecessary nostr requests. We try to leverage the cache as much as possible.
Even splitting the users filters into smaller relay tailored filters if we know the relay has the information we need.
compute
Right now the most compute intensive operation is verifying signatures.
We use the cache to determine if we have already seen the event and only if it is unknown signature verification is done.
To make the operation as optimized as possible we strongly recommend using RustEventVerifier() because it uses a separate thread for verification.
$~~~~~~~~~~~$
Gossip/outbox model of relay discovery and connectivity #
The simplest characterization of the gossip model is just this: reading the posts of people you follow from the relays that they wrote them to.
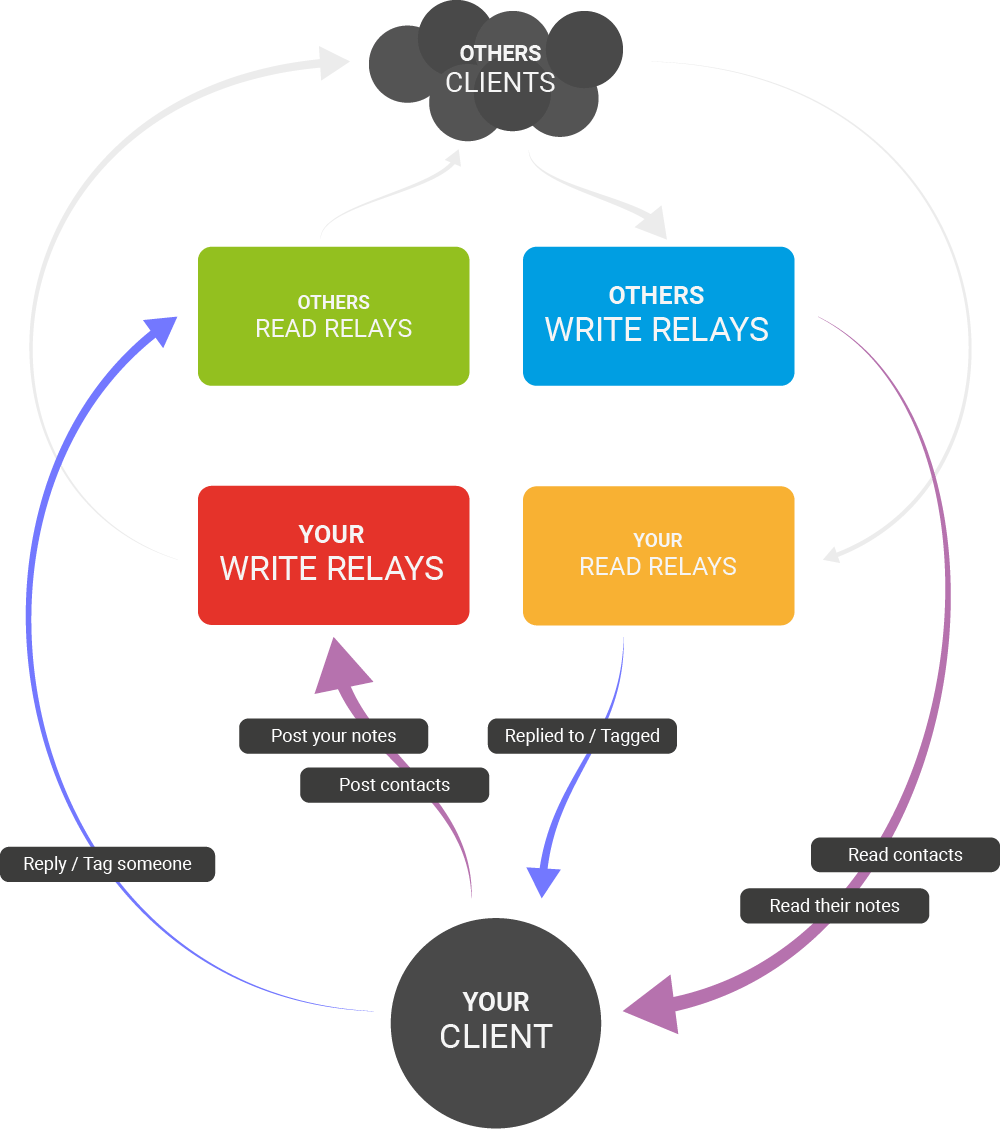
more details on https://mikedilger.com/gossip-model/
Common terminology #
| term | explanation | simmilar to |
|---|---|---|
| broadcastEvent | push event to nostr network/relays | postEvent, publishEvent |
| JIT | Just In Time, e.g. as it happens | - |
| query | get data once and close the request | get request |
| subscription | stream of events as they come in | stream of data |
| bootstrapRelays | default relays to connect when nothing else is specified | seed relays, initial relays |
| engine | optimized network resolver for nostr requests | - |
$~~~~~~~~~~~$
Changelog 🔗 #
$~~~~~~~~~~~$
Library development 🏗️ #
Setup #
Install prerequisites
run melos bootstrap to install all dependencies.
If you work on rust code (packages/rust_verifier/rust_builder/rust) run flutter_rust_bridge_codegen generate --watch to generate the rust dart glue code.
Run build runner: (e.g for generating mocks)
dart run build_runner build
Architecture #
The repo is setup as a monorepo and packages are split to enable user choice of what to include.
The main package is ndk which is the main entry point for the lib user.
Other packages like rust_verifier or amber are optional and can be included if needed.
NDK uses Clean Architecture. Reasons for it being clear separation of concerns and therefore making it more accessible for future contributors.
You can read more about it here.
For initialization we use presentation_layer/init.dart to assemble all dependencies, these are then exposed in presentation_layer/ndk.dart the main entry point for the lib user.
Global state is realized via a simple [GlobalState] object created by ndk.dart.
The lib user is supposed to keep the [NDK] object in memory.
Other state objects are created on demand, for example [RequestState] for each request.
Folder Structure of ndk #
lib/
├── config/
│ └── # Configuration files
├── shared/
│ ├── nipX/ # NIP-specific code folders
│ └── # Internal code, no external dependencies
├── data_layer/
│ ├── data_sources/
│ │ └── # External APIs, WebSocket implementations, etc.
│ ├── models/
│ │ └── # Data transformation (e.g., JSON to entity)
│ └── repositories/
│ └── # Concrete repository implementations
├── domain_layer/
│ ├── entities/
│ │ └── # Core business objects
│ ├── repositories/
│ │ └── # Repository contracts
│ └── usecases/
│ └── # Business logic / use cases
├── presentation_layer/
│ └── # API design (exposing use cases to the outside world)
└── ndk.dart # Entry point, directs to presentation layer
Engines #
NDK ships with two network Engines. An Engine is part of the code that resolves nostr requests over the network and handles the WebSocket connections.
Its used to handle the inbox/outbox (gossip) model efficiently.
Lists Engine:
Precalculates the best possible relays based on nip65 data. During calculation relay connectivity is taken into account. This works by connecting and checking the health status of a relay before its added to the ranking pool.
This method gets close to the optimal connections given a certain pubkey coverage.
Just in Time (JIT) Engine:
JIT Engine does the ranking on the fly only for the missing coverage/pubkey. Healthy relays are assumed during ranking and replaced later on if a relay fails to connect.
To Avoid rarely used relays and spawning a bunch of unessecary connections, already connected relays get a boost, and a usefulness score is considered for the ranking.
For more information look here
Custom Engine
If you want to implement your own engine with custom behavior you need to touch the following things:
- implement
NetworkEngineinterface - write your response stream to
networkControllerin theRequestState - if you need global state you can register your own data type in
global_state.dart - initialize your engine in
init.dart
The current state solution is not ideal because it requires coordination between the engine authors and not enforceable by code. If you have ideas how to improve this system, please reach out.
The network engine is only concerned about network requests! Caching and avoiding concurrency is handled by separate usecases. Take a look at
requests.dartusecase to learn more.


