isolator 1.0.1  isolator: ^1.0.1 copied to clipboard
isolator: ^1.0.1 copied to clipboard
Isolator is a package, which offer to you a simple way for creating two-component states with isolated part and frontend part of any kind - BLoC, MobX, ChangeNotifier and others
isolator #
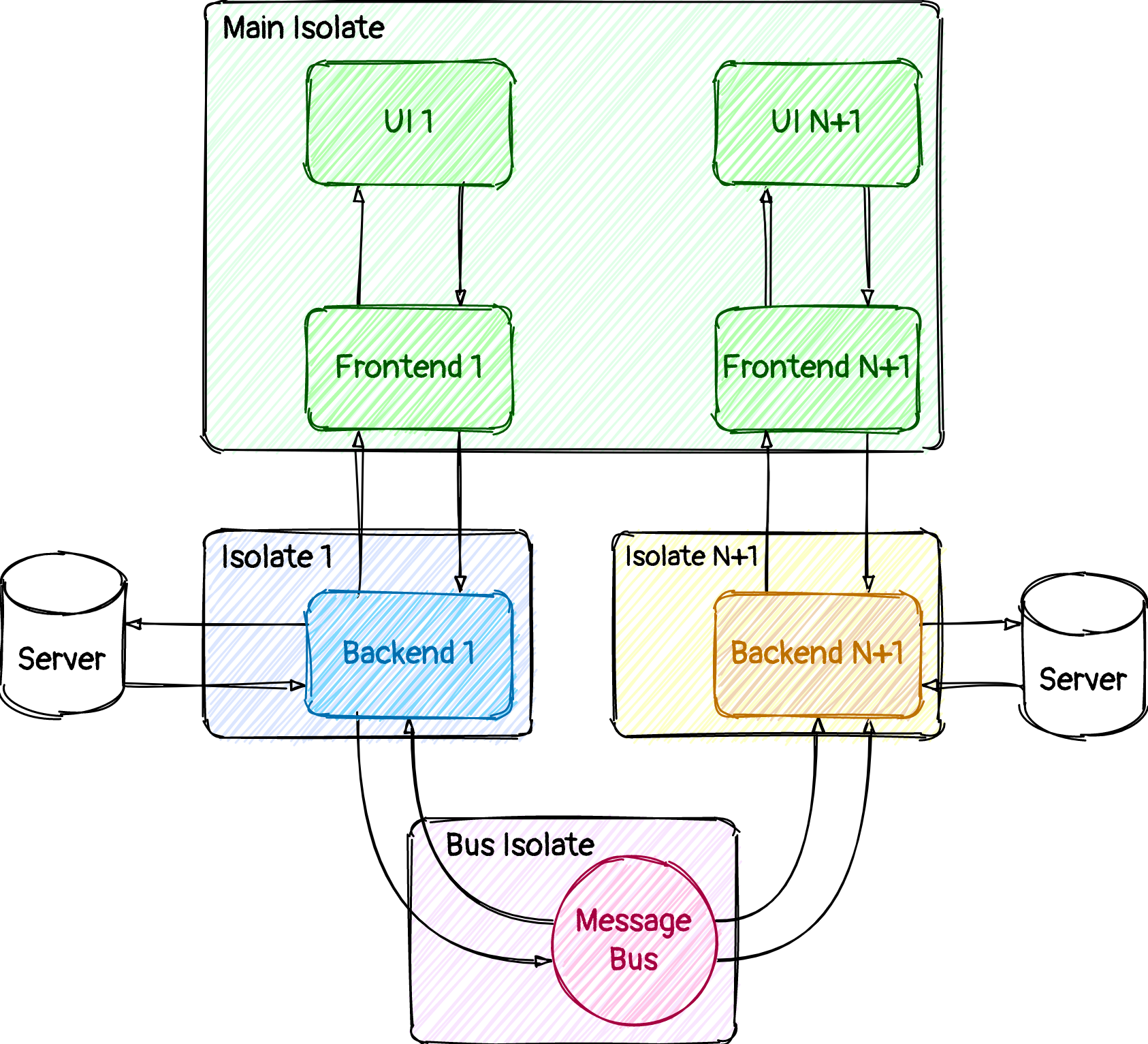
Isolator is a package, which offer to you a simple way for creating two-component states with isolated part and frontend part of any kind (BLoC, MobX, ChangeNotifier and many others). With this package you can take out all business logic from main thread (main isolate) in separated isolates with easiest way to do this.
This package is a proofed in production concept, when you take out heavy business logic to isolates for achievement a fully cleared from any junks application. With this package you can easy create a so-called "Backend" - class with your logic and second class, which uses a special mixin "Frontend" - a state of any kind - BLoC / MobX / ChangeNotifier (as in an example).
Possibilities:
- Send events from Frontend to Backend
- Call Backend's method in synchronous style from Frontend
- Subscribe on events, which Frontend can handle
- Have a hook, which will run on every new event in Frontend
- Send large data from Backend to Frontend via chunks automatically
- Send events between Backends
- Call Backend's method in synchronous style from another Backend
- Have always stable 60 / 90 / 120 / 144 and more FPS of your app
Example of interaction between Frontend and Backend #
import 'package:flutter/cupertino.dart';
import 'package:isolator/isolator.dart';
/// Values for tests
const int VALUE_AFTER_CREATION = 11;
const int ASYNC_INT = 10;
const int SYNC_INT = 12;
enum TestEvent {
intSync,
intAsync,
intAsyncWithReturn,
chunks,
observer,
errorOnBackend,
invalidType,
afterCreation,
chunksCancel,
}
/// Frontend - anything else, what you want to use a state of your app
class FrontendTest with Frontend<TestEvent>, ChangeNotifier {
int asyncIntFromBackend = 0;
int syncIntFromBackend = 0;
int valueAfterCreation = 0;
bool isErrorHandled = false;
List<int> intChunks = [];
List<int> intChunksCancel = [];
/// You can get any value (after calculating it on the backend) in synchronous style
/// When you using [runBackendMethod] function - you call your Backend's method, which
/// matches the passed event id, and get back value in that place
///
/// It most simplest way to use Isolator
Future<int> getValueFromBackendSynchronously() async {
final int intFromBackend = await runBackendMethod(TestEvent.intSync);
syncIntFromBackend = intFromBackend;
return syncIntFromBackend;
}
/// Also, you can use asynchronous style
/// It is the way, when you send some params (with event id) to Backend
/// Then, Backend handle it, and after that you handle Backend response via Frontend task
void sendEventToBackend() {
send(TestEvent.intAsync);
}
/// You can return value from backend with simple "return" keyword
/// without using [send] method of your Backend
/// To see that - open [_returnIntBack] method of [BackendTest]
void sendEventToBackendAndReturnResponseOnBackend() {
send(TestEvent.intAsyncWithReturn);
}
/// When you want get a large amount of data from the Backend
/// You can use [sendChunks] method of the Backend
/// For example - see method [_returnChunks] of [BackendTest]
void loadChunks() {
send(TestEvent.chunks);
}
/// If you start loading 1th portion of chunks
/// and does not finished it before loading 2th
/// portion - 1th portion loading should be stopping
/// 1th transaction will aborted
void loadChunksWithCanceling() {
send(TestEvent.chunksCancel);
}
/// This method need for test cases
void invalidType() {
send(TestEvent.invalidType);
}
/// This method need for test cases
void runError() {
send(TestEvent.errorOnBackend);
}
/// It is a task for handle Backend response
/// for event id [TestEvent.intAsync]
void _setValueFromBackend(int intFromBackend) {
this.asyncIntFromBackend = intFromBackend;
}
/// Task for handle [sendChunks] event must take a [List] of data
void _setIntChunks(List<int> intChunks) {
this.intChunks.clear();
this.intChunks.addAll(intChunks);
}
void _setIntChunksCancel(List<int> intChunks) {
this.intChunksCancel.clear();
this.intChunksCancel.addAll(intChunks);
}
/// This method need for test cases
void _taskWithInvalidType(String intFromBackend) {
// WAITING FOR ERROR
}
/// This method need for test cases
void _handleError(dynamic error) {
isErrorHandled = true;
}
/// This method need for test cases
void _setValueAfterCreation(int valueAfterCreation) {
this.valueAfterCreation = valueAfterCreation;
}
/// Before using Backend with Frontend, you should init your Backend
/// To do this - simple use [initBackend] method of your Frontend
Future<void> init(int id) async {
await initBackend<int>(_backendFabric, data: VALUE_AFTER_CREATION, backendType: BackendTest, uniqueId: '$id');
}
/// If you want to destroy Backend - use [killBackend] method
/// It can be useful, if your state lifetime is shorter than lifetime of app
void kill() {
killBackend();
}
/// Hook, which calls on every error
/// Which throws in the Backend
@override
Future<void> onError(dynamic error) async {
print(error);
}
/// Hook, which calls on every event from the Backend
@override
void onBackendResponse() {
notifyListeners();
}
/// [tasks] - Map of methods, which calls on events with
/// matched ids from Backend
@override
Map<TestEvent, Function> get tasks => {
TestEvent.intAsync: _setValueFromBackend,
TestEvent.intAsyncWithReturn: _setValueFromBackend,
TestEvent.chunks: _setIntChunks,
TestEvent.chunksCancel: _setIntChunksCancel,
TestEvent.invalidType: _taskWithInvalidType,
TestEvent.afterCreation: _setValueAfterCreation,
};
/// [errorsHandlers] - Map of methods, which calls, if error
/// was thrown in the Backend, while Backend handle operation
/// with matched event id
@override
Map<TestEvent, ErrorHandler> get errorsHandlers => {
TestEvent.errorOnBackend: _handleError,
};
}
/// Backend - class, which will handle your logic in separate isolate
class BackendTest extends Backend<TestEvent> {
BackendTest(BackendArgument<int> argument) : super(argument) {
_sendValueAfterCreation(argument.data!);
}
int counterOfChunksCancel = 0;
/// You can send value to the Frontend with [send] method
/// Also, you can use this method any times in all of you Backend methods
void _sendIntBack() {
send(TestEvent.intAsync, ASYNC_INT);
send(TestEvent.observer);
}
/// Or you can simply return the value and your Frontend will receive a message with exact event id
/// For example - there Frontend will receive event [TestEvent.intAsyncWithReturn] with value [ASYNC_INT]
int _returnIntBack() {
return ASYNC_INT;
}
void _sendValueAfterCreation(int value) {
send(TestEvent.afterCreation, value);
}
int _returnSyncInt() {
return SYNC_INT;
}
int _returnValue() {
return SYNC_INT;
}
void _throwError() {
throw Exception('Manual error');
}
/// Example of using [sendChunks] method for sending a large amount of data
/// from the Backend to the Frontend without junks of your interface
void _returnChunks() {
final List<int> chunks = [];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
chunks.add(i);
}
/// You can control delay between chunks and amount of items in one chunk
/// to achieve a lowest time for the data transfering and doesn't have any junks
sendChunks(TestEvent.chunks, chunks, delay: const Duration(milliseconds: 3), itemsPerChunk: 1000);
}
void _returnChunksWithCancel() {
counterOfChunksCancel++;
final List<int> chunks = [];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
if (counterOfChunksCancel > 1) {
chunks.add(counterOfChunksCancel);
} else {
chunks.add(i);
}
}
sendChunks(TestEvent.chunksCancel, chunks, delay: const Duration(milliseconds: 3), itemsPerChunk: 1000);
}
/// [operations] - Map of methods, which similar to [tasks] of Frontend
/// every operation will handle events from the Frontend with matched event id
@override
Map<TestEvent, Function> get operations => {
TestEvent.intAsync: _sendIntBack,
TestEvent.intAsyncWithReturn: _returnIntBack,
TestEvent.intSync: _returnSyncInt,
TestEvent.invalidType: _returnValue,
TestEvent.errorOnBackend: _throwError,
TestEvent.chunks: _returnChunks,
TestEvent.chunksCancel: _returnChunksWithCancel,
};
}
class AnotherFrontend {
AnotherFrontend(this.frontendTest);
final FrontendTest frontendTest;
int intFromFrontendTest = 0;
void subscriptionForFrontendTest() {
this.intFromFrontendTest = frontendTest.asyncIntFromBackend;
}
/// You can subscribe on every available (your) event of your Frontend
void subscribe() {
frontendTest.onEvent(TestEvent.observer, subscriptionForFrontendTest);
}
}
void _backendFabric(BackendArgument<int> argument) {
BackendTest(argument);
}
Exampe of interaction between Backend and Backend #
First Backend #
import 'package:isolator/isolator.dart';
import 'another_test_states.dart';
/// Values for tests
const int OPERATION_VALUE = 89;
const int HANDLER_VALUE = 63;
const int BACK_VALUE = 812;
enum OneEvents {
setValue,
notificationOperation,
notificationHandler,
bidirectional,
computeValue,
computeValueOperation,
}
class OneTestFrontend with Frontend<OneEvents> {
int value = 0;
void setValue(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
Future<void> init() async {
await initBackend(createOneBackend, backendType: OneTestBackend);
}
void dispose() {
killBackend();
}
@override
Map<OneEvents, Function> get tasks {
return {
OneEvents.setValue: setValue,
};
}
}
class OneTestBackend extends Backend<OneEvents> {
OneTestBackend(BackendArgument<void> argument) : super(argument);
void _setValueWithOperation() {
send(OneEvents.setValue, OPERATION_VALUE);
}
void _setValueWithHandler(int value) {
send(OneEvents.setValue, HANDLER_VALUE + value);
}
void _setValueWithHandlerAndSendItBack(int value) {
send(OneEvents.setValue, HANDLER_VALUE + value);
sendToAnotherBackend(AnotherTestBackend, AnotherEvents.bidirectionalNotificationBack, HANDLER_VALUE + value);
}
int _returnBackValue(int value) {
return BACK_VALUE + value;
}
@override
Map<OneEvents, Function> get operations {
return {
OneEvents.notificationOperation: _setValueWithOperation,
OneEvents.computeValueOperation: _returnBackValue,
};
}
/// [busHandlers] are similar to [operations], but have any type of key and was made for
/// being called from another isolates BUT
/// also, you can call operation from different isolates too
@override
Map<dynamic, Function> get busHandlers {
return {
OneEvents.notificationHandler: _setValueWithHandler,
OneEvents.bidirectional: _setValueWithHandlerAndSendItBack,
OneEvents.computeValue: _returnBackValue,
};
}
}
void createOneBackend(BackendArgument<void> argument) {
OneTestBackend(argument);
}
Second Backend #
import 'package:isolator/isolator.dart';
import 'one_test_states.dart';
/// Values for tests
const int VALUE_TO_ONE_BACKEND = 28;
const int BIDIRECTIONAL_VALUE = 158;
const int SYNC_VALUE = 451;
enum AnotherEvents {
notificationOperation,
notificationHandler,
bidirectionalNotification,
bidirectionalNotificationBack,
computeHandler,
computeOperation,
setValue,
}
class AnotherTestFrontend with Frontend<AnotherEvents> {
int valueFromBackend = 0;
void _setValue(int value) {
valueFromBackend = value;
}
void callNotificationOperation() {
send(AnotherEvents.notificationOperation);
}
void callNotificationHandler() {
send(AnotherEvents.notificationHandler);
}
void callBidirectionalNotificationHandler() {
send(AnotherEvents.bidirectionalNotification, BIDIRECTIONAL_VALUE);
}
void callOneBackendHandlerMethod() {
send(AnotherEvents.computeHandler, SYNC_VALUE);
}
void callOneBackendOperationMethod() {
send(AnotherEvents.computeOperation, SYNC_VALUE);
}
Future<void> init() async {
await initBackend(createAnotherBackend, backendType: AnotherTestBackend);
}
void dispose() {
killBackend();
}
@override
Map<AnotherEvents, Function> get tasks {
return {
AnotherEvents.setValue: _setValue,
};
}
}
class AnotherTestBackend extends Backend<AnotherEvents> {
AnotherTestBackend(BackendArgument<void> argument) : super(argument);
/// Send message to different Backend with calling one of [operations] methods
void notificationOperation() {
sendToAnotherBackend(OneTestBackend, OneEvents.notificationOperation);
}
/// Send message to different Backend with calling one of [busHandlers] methods
void notificationHandler() {
sendToAnotherBackend(OneTestBackend, OneEvents.notificationHandler, VALUE_TO_ONE_BACKEND);
}
/// Send message to different Backend and getting message back
void bidirectionalNotification(int value) {
sendToAnotherBackend(OneTestBackend, OneEvents.bidirectional, value);
}
/// Getting message back from different Backend
void bidirectionalNotificationBack(int value) {
send(AnotherEvents.setValue, value);
}
/// Call one of [busHandlers] methods of different backend in synchronous style
Future<void> callOneBackendHandlerMethod(int value) async {
final int valueFromOneBackend = await runAnotherBackendMethod(OneTestBackend, OneEvents.computeValue, value);
send(AnotherEvents.setValue, valueFromOneBackend);
}
/// Call one of [operations] methods of different backend in synchronous style
Future<void> callOneBackendOperationMethod(int value) async {
final int valueFromOneBackend = await runAnotherBackendMethod(OneTestBackend, OneEvents.computeValueOperation, value);
send(AnotherEvents.setValue, valueFromOneBackend);
}
@override
Map<AnotherEvents, Function> get operations {
return {
AnotherEvents.notificationOperation: notificationOperation,
AnotherEvents.notificationHandler: notificationHandler,
AnotherEvents.bidirectionalNotification: bidirectionalNotification,
AnotherEvents.bidirectionalNotificationBack: bidirectionalNotificationBack,
AnotherEvents.computeHandler: callOneBackendHandlerMethod,
AnotherEvents.computeOperation: callOneBackendOperationMethod,
};
}
}
void createAnotherBackend(BackendArgument<void> argument) {
AnotherTestBackend(argument);
}
Restrictions #
- Backend classes can't use a native layer (method-channel)
- For one backend - one isolate (too many isolates take much time for initialization, for example: ~6000ms for 30 isolates at emulator in dev mode if do it coherently)