isolate_rpc 1.1.3  isolate_rpc: ^1.1.3 copied to clipboard
isolate_rpc: ^1.1.3 copied to clipboard
Dart Isolate RPC. A simple RPC-style designed API to ease Isolate usage.
Dart Isolate RPC. A simple RPC-style designed API to ease Isolate usage.
Features #
isolate_rpc provide a simpler solution to offload tasks into Isolate and yet can as Isolate.run(flutter compute)
alternative with better performance for Dart SDK < 2.19.0.
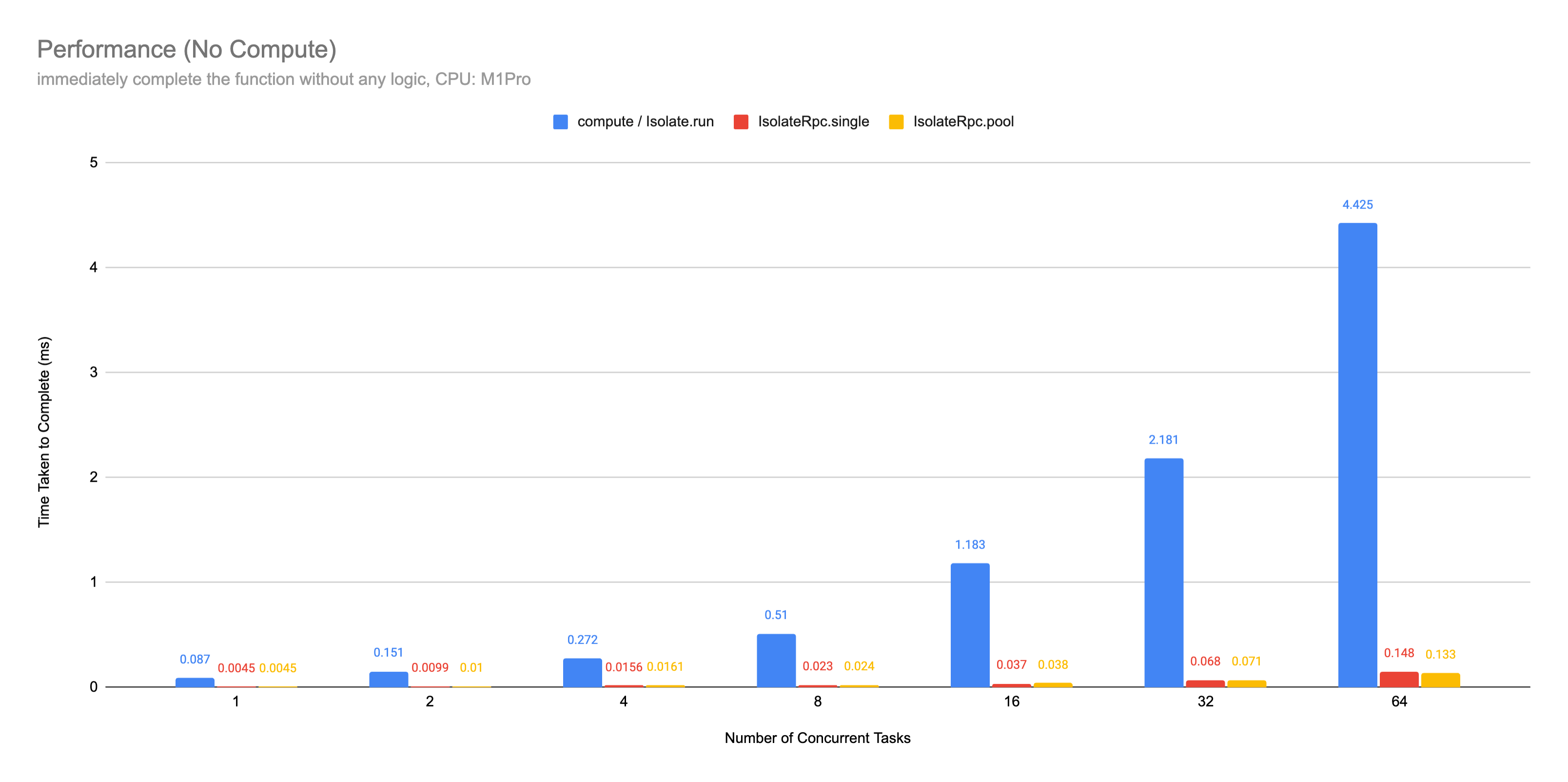
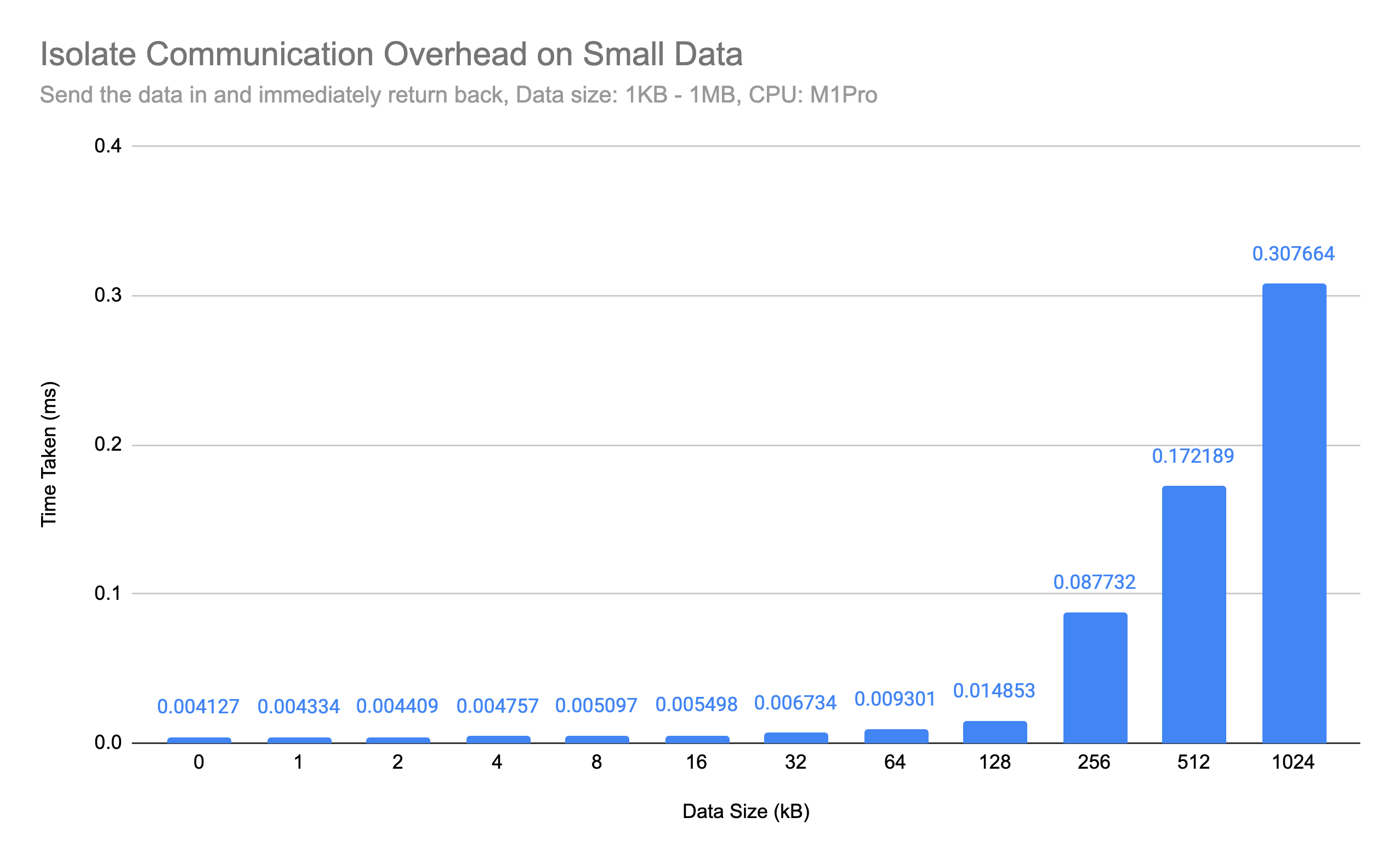
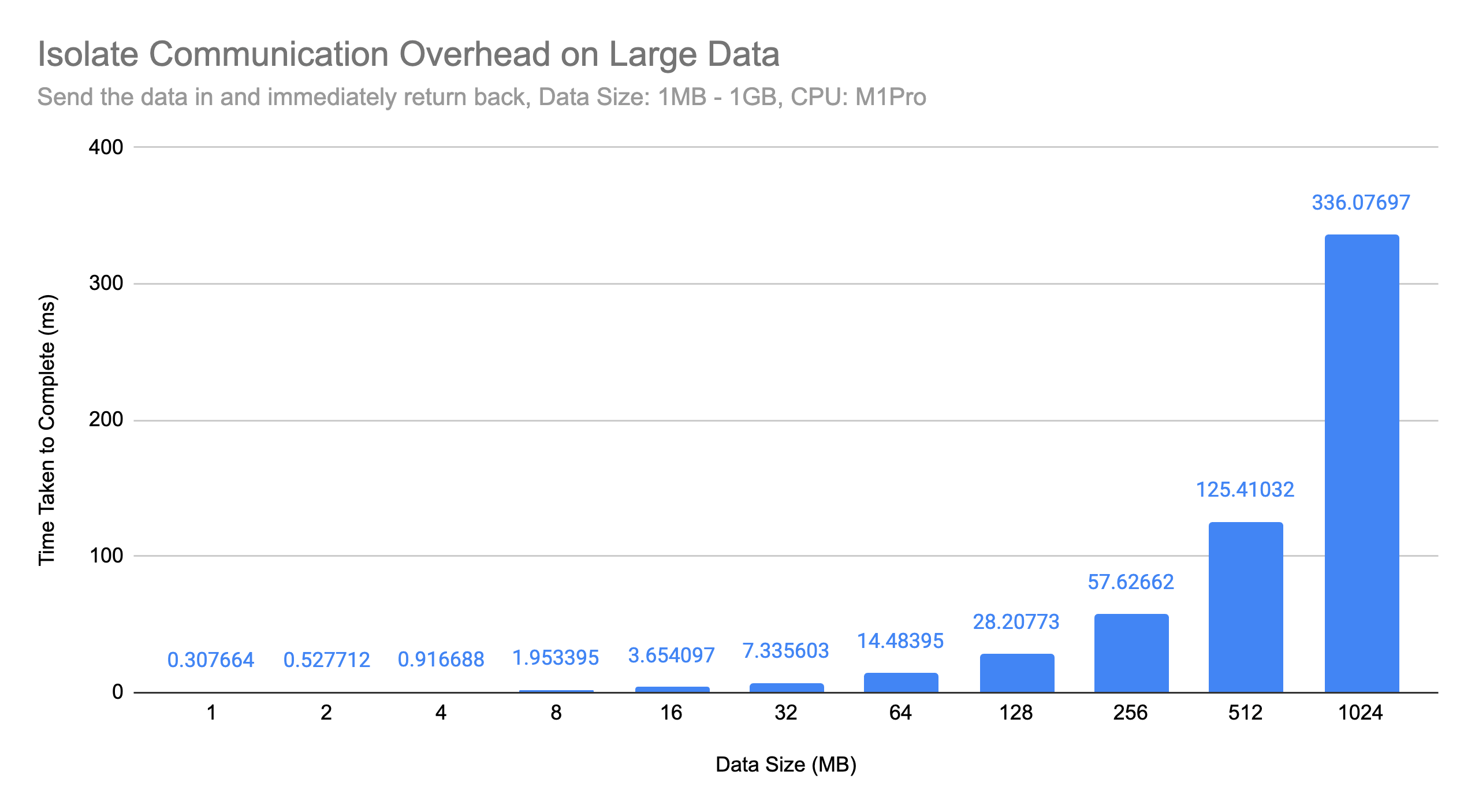
This library significantly reduced overheads of Isolate.run. Isolate.run create new
Isolate on every single call. In the M1Pro macbook benchmark, each Isolate startup overhead is about ~85us*.
Imagine if you are firing asynchronous offscreen operations constantly based on UI interactions, such as sending analytics, fetching remote API, etc., you might want to eliminate this overhead.
| Platform | Support |
|---|---|
| Flutter | ✅ |
| Dart | ✅ |
| Web | fallback to use main thread |
Getting started #
- Create a single RPC service with
IsolateRpc<RequestType, ResponseType>usingIsolateRpc.single.
import 'package:isolate_rpc/isolate_rpc.dart';
// define a single Rpc service with exactly one Isolate, isolate will be spawned immediately.
IsolateRpc<int, int> rpc = IsolateRpc.single(
processor: (data) => data + 1, // the execution logics, i.e. this is a plus one operation
debugName: "rpc" // this will be used as the Isolate name
);
- Execute with
1as an input, and receiveIsolateRpcResponse<T>response.
// execute normal RpcRequest in isolate
IsolateRpcResponse<int> resp = await rpc.execute(1);
print(resp.result); // output: 2
- Shut down the rpc when you no longer need it.
rpc.shutdown(); // close the receive port and underlying Isolate.
Advance Usage #
- Custom Request Response Type
class FooRequest {
final String? someString;
FooRequest([this.someString]);
}
class FooResponse {
final int? someInt;
FooResponse([this.someInt]);
}
IsolateRpc<FooRequest, FooResponse> rpc = IsolateRpc.single(
processor: (fooRequest) {
var str = fooRequest.someString;
if (str == null) {
throw ArgumentError("someString should not be null");
} else {
return FooResponse(int.parse(str));
}
},
debugName: "rpc"
);
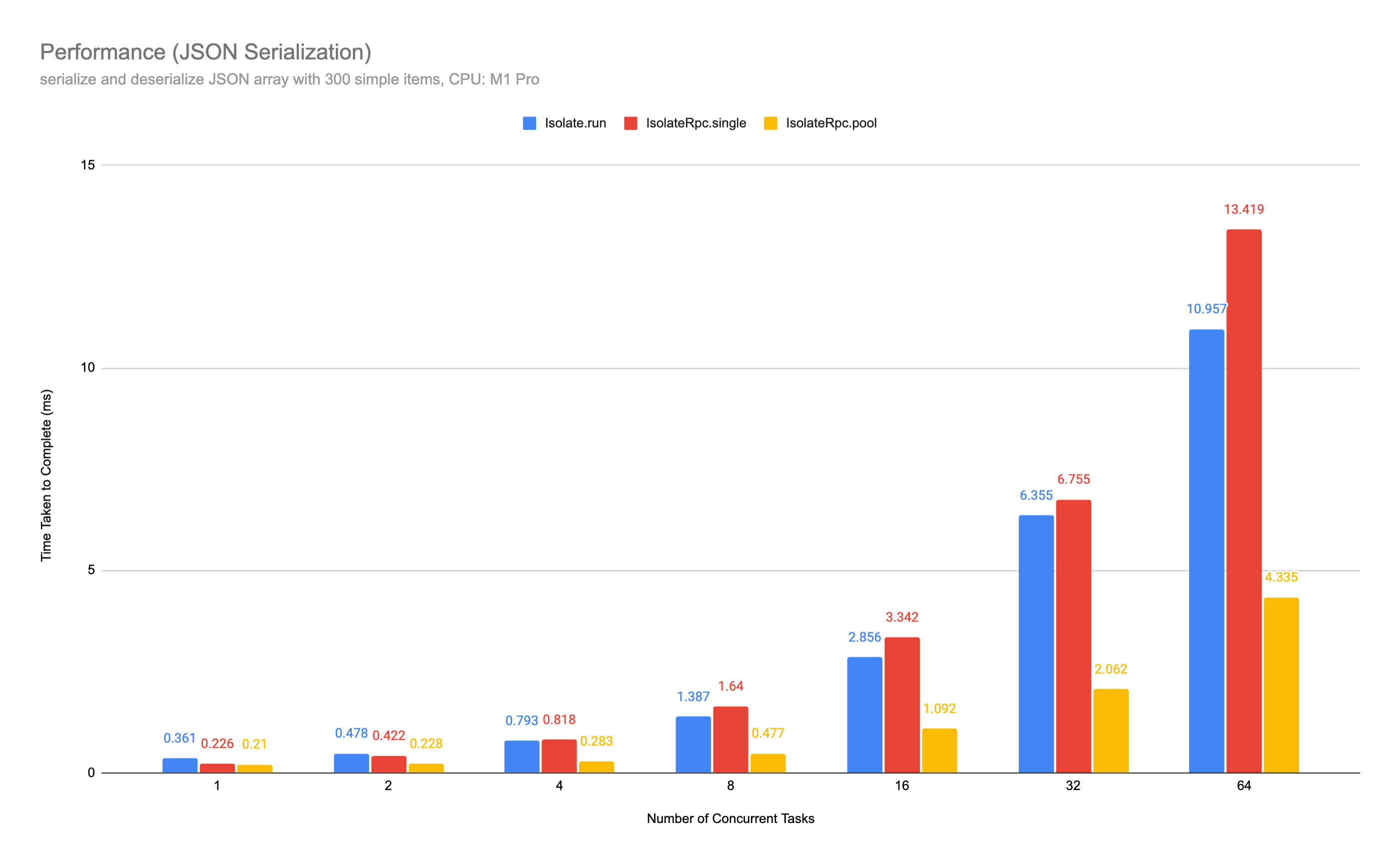
- Creating a pool of RPC services to improve performance when there are computational tasks, i.e., JSON serialization.
IsolateRpc<int, int> rpcPool = IsolateRpc.pool(
size: 4, // tune the number of Isolate spwan
processor: (data) => data + 1,
debugNamePrefix: "rpc-pool" // internally use "rpc-pool-0","rpc-pool-1","rpc-pool-2","rpc-pool-3"
);
- Creating an RPC service with
package:logginglogger to receive logging
import 'package:logging/logging.dart';
void main() {
Logger.root.level = Level.FINEST;
// pattern example to log with the Isolate
log.onRecord.listen((record) {
print('${Isolate.current.debugName}: ${record.level.name}: ${record.time}: ${record.message}');
});
// To receive all the logs from the Rpc service.
var rpc = IsolateRpc.single(
processor: (data) => data + 1,
debugName: "rpc",
logger: Logger("rpc_logger")
);
}
Cast to the underlying instance class to get more information
var rpc = IsolateRpc.single(
processor: (data) => data + 1,
debugName: "rpc"
) as IsolateRpcService<int, int>;
print(rpc.id);
print(rpc.debugName);
var rpcPool = IsolateRpc.pool(
size: 4,
processor: (data) => data + 1,
debugNamePrefix: "rpc-pool"
) as IsolateRpcExecutor<int, int>;
print(rpcPool.id);
print(rpcPool.debugName);
print(rpcPool.size);
Benchmark (compared with Isolate.run) #
NoCompute: no workload, complete immediately
Compute: large json (300 items in json array) serialization and deserialization
# execution script
dart compile exe benchmark/main.dart -o ./benchmark/main
./benchmark/main
License #
MIT