heart 0.5.8  heart: ^0.5.8 copied to clipboard
heart: ^0.5.8 copied to clipboard
Extension methods for Strings and lists, inspired by Haskell
Heart #
Extension methods for strings and lists, inspired by Haskell.
#
Alphabetical list of features: after, any, ascending, average, backwards, before, chr, chrs, concat, count, deepContains, deepEquals, descending, drop, dropWhile, every, filter, group, groupBy, head, inclusive, inclusiveString, indices, inits, insertInOrder, intercalate, interleave, intersect, intersperse, isLowerCase, isUpperCase, last, letterCount, letters, nub, product, range, rangeString, removeWhitespace, replace, riffleIn, riffleOut, shuffled, splitAt, startsWith, subtract, subtractAll, sum, tail, tails, toStringList, union, unwords, wordCount, words, zip, zip2, zip3, zip4, >, >=, <, <=, ^, *
deepEquals, deepContains
This package uses Dart's DeepCollectionEquality from collection whenever posssible, so deepEquals([1, 2], [1, 2]) returns true, even though [1, 2] == [1, 2] is normally false. [{1: 2}, {2: 3}].deepContains({2: 3}) is also true.
#
(Strings are treated as lists in Haskell, and have many of the same functions.)
ascending, descending #
Sort lists and strings:
List<int> l = [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].ascending(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
List<int> l2 = [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].descending(); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
String s = 'hello'.ascending(); // 'ehllo'
String s = 'hello'.descending(); // 'ollhe'
before, after #
Get everything before or after a sublist:
List<int>? l = [1, 2, 3, 3].before([3]); // [1, 2]
[1, 2, 3, 3].before([2, 3]) // [1]
[1, 2, 3, 3].after([2, 3]) // [3]
Optional skip parameter skips that many occurrences:
[1, 2, 3, 3].before([3], skip: 1) // [1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 3].after([3], skip: 1) // []
Returns null if doesn't contain sublist:
[1, 2, 3, 3].before([4, 5]) // null
startsWith #
Dart already has this for strings.
bool b = [1, 2, 3].startsWith([1, 2]); // true
nub #
Remove duplicates:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 1, 2].nub() // [1, 2]
String s = 'hello'.nub(); // 'helo'
Optional list or string parameter only looks at those elements:
[1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3].nub([1, 2]) // [1, 2, 3, 3]
'aaabbbcc'.nub('ab') // 'abcc'
backwards #
Reverse a string or list:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].backwards(); // [3, 2, 1]
String s = 'hello'.backwards(); // 'olleh'
shuffled #
Returns a shuffled list or string.
(Dart's shuffle method is void)
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].shuffled();
// Specify a Random object:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].shuffled(Random.secure());
String s = 'hello'.shuffled();
sum, product, average #
Add or multiply numbers in a list:
int s = [1, 2, 3].sum(); // 6
int p = [4, 5, 6].product(); // 120
double a = [11, 2, 33, 55, 7, 2, 1].average(); // 15.857142857142858
// .average() works for Strings based on character codes
'abc'.average() // 'b'
count #
Count occurrences in a list or string:
int c = [1, 2, 1, 3].count(1); // 2
// Note: '.indices([1]).length' gives same result, and can be used for sublists instead of one element
[{1,2}, [1,3]].count({1,2}) // 1
'hello world'.count('l') // 3
'hello world'.count('ll') // 1
indices #
Find where sublist occurs in a list, or substring occurs in a string:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1].indices([1]); // [0, 2, 4]
[1, 2, 1, 2, 1].indices([1, 2]) // [0, 2]
'hello'.indices('ll') // [2]
[[1,2], [1,2], {3: 4}].indices([[1, 2], {3: 4}]) // [1]
Optional exclusive parameter means the sublists at the result indices would be mutually exclusive:
[1, 1, 1, 1].indices([1, 1]) // [0, 1, 2]
[1, 1, 1, 1].indices([1, 1], exclusive: true) // [0, 2]
'aaaa'.indices('aa', exclusive: true) // [0, 2]
concat #
Concatenate nested lists or strings:
List<int> l = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].concat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
String str = ['hello', 'world'].concat(); // 'helloworld'
intersperse #
Inserts an item in between all other elements:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].intersperse(0); // [1, 0, 2, 0, 3]
String s = 'hello'.intersperse('-'); // 'h-e-l-l-o'
// Note: 'replace' method with empty list or string adds element to beginning and end
'hello'.replace('', '-') // '-h-e-l-l-o-'
intercalate (in-TER-kuh-late) #
Inserts a list between lists (or string between strings) and concatenates the result:
List<int> l = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].intercalate([0, 0]);
// [1, 2, 0, 0, 3, 4, 0, 0, 5, 6]
String s = ['hello', 'world'].intercalate('-');
// 'hello-world'
Optional count parameter only adds that many times:
[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].intercalate([0, 0], count: 1) // [1, 2, 0, 0, 3, 4, 5, 6]
filter #
Keep only elements that meet criteria:
// Keep where x^3 < 10:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4].filter((x) => pow(x, 3) < 10); // [1, 2]
Equivalent to .where().toList(), but also works on Strings:
// '<' operator defined in this package
String s = 'hello world'.filter((char) => char < 'j'); // 'he d'
any, every #
(These already exist for lists)
bool b = 'hello'.any((char) => char == 'h'); // true
bool b2 = 'hello'.every((char) => char == 'h'); // false
drop, dropWhile #
drop(n) removes first n elements. Similar to .sublist(n) or .substring(n) but doesn't throw exception for invalid n.
List<int> l = [0, 1, 2].drop(1); // [1, 2]
// Returns the same if n<=0
[0, 1, 2].drop(-1) // [0, 1, 2]
// Returns empty if n >= length
[0, 1, 2].drop(100) // []
'hello'.drop(2)
// 'llo'
dropWhile drops elements until they don't meet criteria, keeps everything after.
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1].dropWhile((x) => x < 3);
// [3, 2, 1]
// '<' operator defined in this package
String s = 'hello'.dropWhile((char) => char < 'i');
// 'llo'
replace #
Remove all occurrences or replace with a particular sublist:
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].replace([1]); // [2, 3]
[1, 1, 2, 3].replace([1, 1], [99]) // [99, 2, 3]
'aaaa'.replace('a', 'b') // 'bbbb'
Optional third parameter only replaces that many occurrences:
[1, 1, 1, 1].replace([1], [3, 4], 2) // [3, 4, 3, 4, 1, 1]
'aaaa'.replace('a', 'bc', 2) // 'bcbcaa'
subtract, subtractAll #
subtract removes elements one at a time (like Haskell's \\):
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 2, 3].subtract([1, 3]); // [1, 2, 2]
l = [1, 1, 2, 2].subtract([1, 2, 3]); // [1, 2]
// ignores 3 since it is not in original list
String s = 'hello'.subtract('eo'); // 'hll'
subtractAll removes all occurrences:
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 2].subtractAll([1]); // [2, 2]
String s = 'hello'.subtractAll('lo'); // 'he'
union, intersect #
union adds elements that aren't already present.
It doesn't remove duplicates from original, but doesn't add duplicates from input.
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].union([2, 3, 4, 4]); // [1, 1, 2, 3, 4]
String s = 'hello'.union(' world'); // 'hello wrd'
(Use .nub() to remove duplicates, and concatenate normally to keep duplicates.)
intersect keeps all elements from original list that are also in input.
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].intersect([1, 2]); // [1, 1, 2]
String s = 'hello'.intersect('world'); // 'llo'
// Remove duplicates with .nub()
head, tail(s), last, inits, #
head returns first element.
tail returns everything but the first element.
last returns the last element (Dart has this for lists but not strings).
int? i = [1, 2, 3].head(); // 1
List<int>? l = [1, 2, 3].tail(); // [2, 3]
[1].tail() // []
[].tail() // null
'hello'.head() // 'h'
'hello'.tail() // 'ello'
'hello'.last() //'o'
inits
returns a list of lists (or strings) by adding elements from the beginning:
[1, 2, 3].inits()
// [[], [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3]]
'hi'.inits()
// ['', 'h', 'hi']
tails returns a list of lists (or strings) by removing one element at a time from the beginning:
[1, 2, 3].tails()
// [[1, 2, 3], [2, 3], [3], []]
// inclusive function defined in this package
List<List<int>> twelveDaysOfChristmas = inclusive(12, 1).tails().backwards();
// [[], [1], [2, 1], [3, 2, 1], [4, 3, 2, 1], [5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]]
'hello'.tails()
// ['hello', 'ello', 'llo', 'lo', 'o', '']
insertInOrder #
Inserts a value before the first element that is >=. Does not sort.
List<double> l2 = [1.1, 2.2, 0.2].insertInOrder(1.7);
// [1.1, 1.7, 2.2, 0.2]
String s = 'ABDKEO'.insertInOrder('J'); // 'ABDJKEO'
splitAt #
Split a list or string into two:
List<List<int>> l = [5, 6, 7, 8].splitAt(2); // [[5, 6], [7, 8]]
'hello'.splitAt(2) // ['he', 'llo']
interleave #
Combine two lists or strings by taking turns:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].interleave([4, 5, 6]);
// [1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6]
'abc'.interleave('123')
// 'a1b2c3'
Extra characters get added to the end:
[1, 2, 3, 4].interleave([5])
// [1, 5, 2, 3, 4]
riffleIn, riffleOut #
Riffle shuffle: splits list or string in half and interleaves them
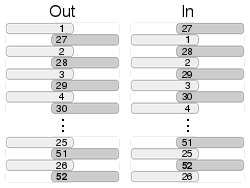
// .riffleOut interleaves first half to second.
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].riffleOut();
// [1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6]
// .riffleIn interleaves second half to first
List<int> l2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].riffleIn();
// [4, 1, 5, 2, 6, 3]
String s = '12345'.riffleOut();
// '14253'
String s2 = '12345'.riffleIn();
// '31425'
group, groupBy #
group combines consecutive elements together if they are equal:
List<List<int>> l = [1, 2, 3, 3, 1].group();
// [[1], [2], [3, 3], [1]]
List<String> ls = 'hello'.group();
// ['h', 'e', 'll', 'o']
groupBy combines consecutive elements if they meet criteria.
In this example, items are in the same sublist if they are less than the one after:
List<List<int>> l = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1].groupBy((a, b) => a < b);
// [[1, 2, 3], [2], [1]]
List<String> ls = 'HelLo'.groupBy((a, b) => a.isUpperCase() && b.isLowerCase());
// ['He', 'l', 'Lo']
chr, chrs #
chr returns a String from a character code.
chrs returns a String from a list of codes.
97.chr() // 'a'
[97, 98].chrs() // 'ab'
// .codeUnits converts back to codes
Other methods for lists #
toStringList #
Convert all elements to strings:
List<String> l = [1, 2, 3].toStringList(); // ['1', '2', '3']
zip, zip2 #
zip takes in a list of lists, returns a list of lists where corresponding elements are paired together.
List l = zip([['one','two','three'], [1,2,3]]);
// [['one', 1], ['two', 2], ['three', 3]]
zip2 takes in a list of 2 lists and performs a function between corresponding elements (similar to Haskell's zipWith):
List l = zip2([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], (a,b) => a+b); // [5, 7, 9]
zip3 and zip4 work similarly.
Other methods for Strings #
removeWhitespace #
String s = ' hello \n world '.removeWhitespace(); // 'helloworld'
// Dart's .trim() only removes leading and trailing whitespace.
words, wordCount, letters, letterCount #
words returns a list of words without whitespace.
wordCount takes the length of this List. Equivalent to words().length.
List<String> listOfWords = 'hello world'.words(); // ['hello', 'world']
int w = 'hello world'.wordCount(); // 2
letters returns a List of all the characters, with optional keepWhitespace parameter.
letterCount counts all characters, with optional keepWhitespace parameter.
List<String> listOfCharacters = 'hello world'.letters();
// ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']
int lc = 'hello world'.letterCount();
// 10
'hello world'.letters(keepWhitespace: true)
// ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', ' ', 'o', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']
'hello world'.letterCount(keepWhitespace: true)
// 11 (same as .length)
unwords #
Combine a list of strings into one, with spaces in between:
String s = ['hello', 'world'].unwords(); // 'hello world'
String s2 = 'hello world'.letters().unwords(); 'h e l l o w o r l d'
isUpperCase, isLowerCase #
Checks if all characters are upper or lower case, with optional ignoreSymbols parameter.
bool b = 'hello world'.isLowerCase(); // true
bool b2 = 'hello world'.isLowerCase(ignoreSymbols: false); // false (because of space)
bool b3 = 'Hello'.isUpperCase(); // false
bool b4 = 'Hello'.isLowerCase(); // false
bool b5 = 'á'.isLowerCase(ignoreSymbols: false); // true
// accented letters don't count as symbols
Other features #
range, inclusive #
Generates a list of integers:
// "for(int i in range(5))" is the same as "for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)"
List<int> l = range(5); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
inclusive(5) // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
range(-5) // [-4, -3, -2, -1, 0]
inclusive(-5) // [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0]
range(0) // []
inclusive(0) // [0]
With two arguments, inclusive includes the second one, range does not .
range(1, 5) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
inclusive(1, 5) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
range(1, -2) // [1, 0, -1]
inclusive(1, -2) // [1, 0, -1, -2]
Third argument adds a step count:
range(1, 5, 2) // [1, 3]
inclusive(1, 5, 2) // [1, 3, 5]
range(1, -5, -2) // [1, -1, -3]
inclusive(1, -5, -2) // [1, -1, -3, -5]
rangeString, inclusiveString #
Similar to range and inclusive. Strings must have exactly one character:
rangeString('a', 'f') // 'abcde'
rangeString('c', 'a') // 'cb'
rangeString('a', 'g', 2) // 'ace'
inclusiveString('a', 'c') // 'abc'
inclusiveString('c', 'a') // 'cba'
inclusiveString('a', 'g', 2) // 'aceg'
Operators for strings and lists #
>, >=, <, <= #
Compare elements in two lists, starting at the beginning:
[1, 2, 3] > [1, 1, 3] // true
Compare strings according to their character codes:
'b' > 'a' // true
'hello' < 'hi' // true
['a', 1] >= ['b', 1] // false
(If elements cannot be compared, both >= and <= will return false.)
^ #
Get next String by character codes:
String s = 'a' ^ 1; // 'b'
'b' ^ (-1) // 'a'
'abc' ^ 1 // 'bcd
* #
Repeat elements of a list with *
List<int> l = [1, 2] * 3; // [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2]
// Dart has this for Strings
String s = 'hello' * 3; // 'hellohellohello'