glade_forms 1.2.0  glade_forms: ^1.2.0 copied to clipboard
glade_forms: ^1.2.0 copied to clipboard
A universal way to define form validators with support of translations.

Developed with 💚 by netglade
A universal way to define form validators with support of translations.
👀 What is this? #
Glade Forms offer unified way to define reusable form inputs with support of fluent API to define input's validators and with support of translation on top of that.
Mannaging forms in Flutter is... hard. With Glade Forms you create a model that holds glade inputs, setup validation, translation, dependencies, handling of updates, and more with ease.
🚀 Getting started #
To start, setup a Model class that holds glade inputs together.
class _Model extends GladeModel {
late GladeInput<String> name;
late GladeInput<int> age;
late GladeInput<String> email;
@override
List<GladeInput<Object?>> get inputs => [name, age, email];
@override
void initialize() {
name = GladeInput.stringInput();
age = GladeInput.intInput(value: 0);
email = GladeInput.stringInput(validator: (validator) => (validator..isEmail()).build());
super.initialize();
}
}
Then use GladeFormBuilder
and connect the model to standard Flutter form and it's inputs like this:
GladeFormBuilder(
create: (context) => _Model(),
builder: (context, model) => Form(
autovalidateMode: AutovalidateMode.onUserInteraction,
child: Column(
children: [
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(labelText: 'Name'),
// connect a controller from glade input
controller: model.name.controller,
// connect a validator from glade input
validator: model.name.textFormFieldInputValidator,
// connect an on change method
onChanged: model.name.updateValueWithString,
),
TextFormField(
controller: model.age.controller,
validator: model.age.textFormFieldInputValidator,
onChanged: model.age.updateValueWithString,
decoration: const InputDecoration(labelText: 'Age'),
),
TextFormField(
controller: model.email.controller,
validator: model.email.textFormFieldInputValidator,
onChanged: model.email.updateValueWithString,
decoration: const InputDecoration(labelText: 'Email'),
),
const SizedBox(height: 10),
ElevatedButton(onPressed: model.isValid ? () {} : null, child: const Text('Save')),
],
),
),
)
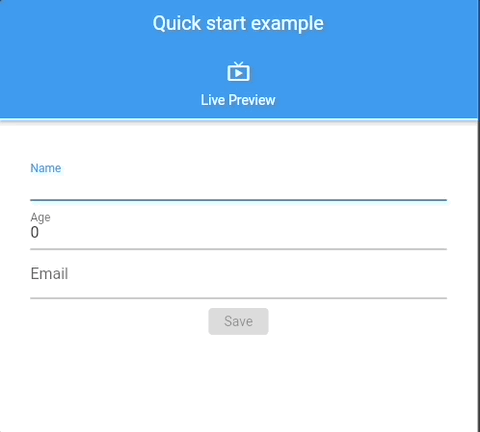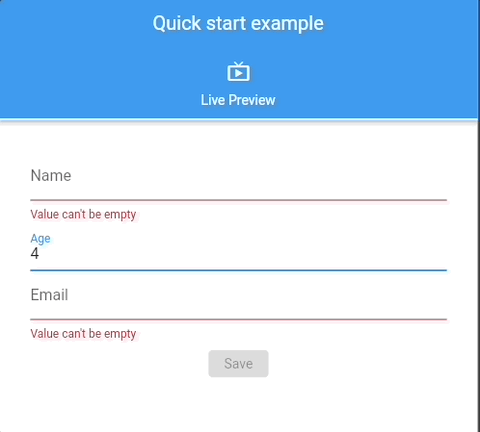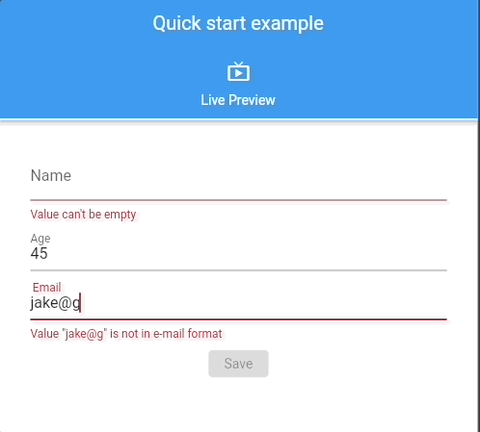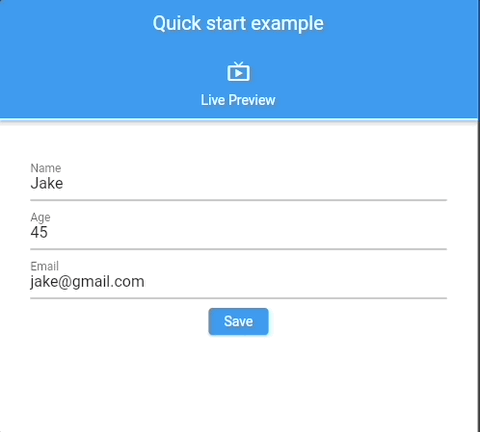
See 📖 Glade Forms Widgetbook, complex, examples.
✨ Features #
GladeInput #
Each form's input is represented by instance of GladeInput<T> where T is value held by input.
For simplicity we will interchange input and GladeInput<T>.
Every input is dirty or pure based on whether value was updated (or not, yet).
On each input we can define
- validator - Input's value must satisfy validation to be valid input.
- translateError - If there are validation errors, function for error translations can be provided.
- inputKey - For debug purposes and dependencies, each input can have unique name for simple identification.
- dependencies - Each input can depend on another inputs for validation.
- stringTovalueConverter - If input is used by TextField and
Tis not aString, value converter should be provided. - valueComparator - Sometimes it is handy to provied
initialValuewhich will be never updated after input is mutated.valueComparatorshould be provided to compareinitialValueandvalueifTis not comparable type by default. - valueTransform - transform
Tvalue into differentTvalue. An example of usage can be sanitazation of string input (trim(),...). - defaultTranslation - If error's translations are simple, the default translation settings can be set instead of custom
translateErrormethod. - textEditingController - It is possible to provide custom instance of controller instead of default one.
Most of the time, input is created with .create() factory with defined validation, translation and other properties.
An overview how each input's value is updated. If needed it is converted from string into T, then transformed via valueTransform (if provided), after that new value is set.
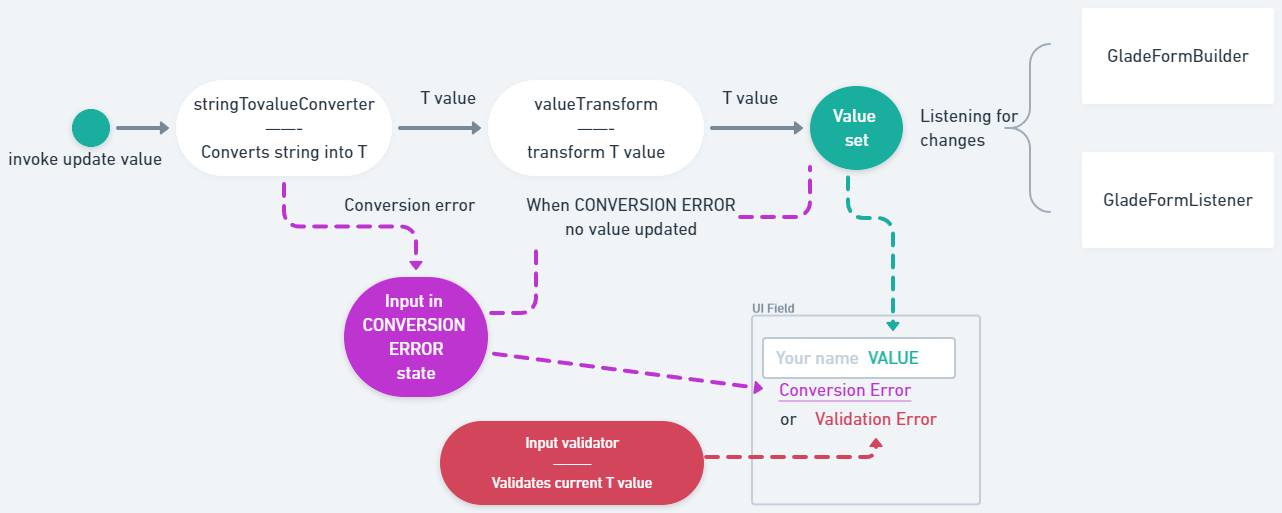
StringInput
StringInput is specialized variant of GladeInput
Validation #
Validation is defined through part methods on ValidatorFactory such as notNull(), satisfy() and other parts.
Each validation rule defines
- value validation, e.g
notNull()defines that value can not be null.satisfy()defines a predicate which has to be true to be valid etc. - devErrorMessage - a message which will be displayed if no translation is not provided.
- key - Validation error's identification. Usable for translation.
This example defines validation that int value has to be greater or equal to 18.
ageInput = GladeInput.create(
validator: (v) => (v
..notNull()
..satisfy(
(value, extra, dependencies) {
return value >= 18;
},
devError: (_, __) => 'Value must be greater or equal to 18',
key: _ErrorKeys.ageRestriction,
))
.build(),
value: 0,
valueConverter: GladeTypeConverters.intConverter,
);
The order of each validation part matters. By default, the first failing part stops validation. Pass stopOnFirstError: false on .build() to validate all parts simultaneously.
Fields connected with textFormFieldInputValidator will automatically call validator and validation error (if any) is passed down to fields. By default devError is used unless translation is specified. See below.
Using validators without GladeInput
It is possible to use GladeValidator without associated GladeInput.
Just create instance of GladeValidator (or StringValidator) and use it.
final validator = (StringValidator()..notEmpty()).build();
final result = validator.validate(null);
GladeModel #
GladeModel is base class for Form's model which holds all inputs together. It is useful for cases where you want to sum up validations at once, like disabling save button until all inputs are valid.
GladeModel is ChangeNotifier so all dependant widgets will be rebuilt.
There are several rules how to define models
- Each input has to be mutable and
latefield - Model has to override
initializemethod where each input field is created - In the end of
initializemethod,super.initialize()must be called to wire-up inputs with model.
⚠️ Without wiring-up model, model will not be updated appropiately
and properties such as isValid or formattedErrors will not work.
For updating input call either updateValueWithString(String?) to update T value with string (will be converted if needed) or set value directly (via setter).
Flutter widgets
GladeModelProvider is predefined widget to provide GladeModel to widget's subtreee.
GladeFormBuilder allows to listen to model's changes and rebuilts its child.
GladeFormListener allows to listen to model's changes and react to it. Useful for invoking side-effects such as showing dialogs, snackbars etc. listener provides lastUpdatedKeys which is list of last updated input keys.
GladeFormConsumer combines GladeFormBuilder and GladeFormListener together.
Edit multiple inputs at once
With each update of input, via update or setting .value directly, listeners (if any) are triggered. Sometimes it is needed to edit multiple inputs at once and triggering listener in the end.
For editing multiple values use groupEdit(). It takes void callback to update inputs.
An example
class FormModel extends GladeModel {
late GladeInput<int> age;
late GladeInput<String> name;
// ....
groupEdit(() {
age.value = 18;
name.value = 'default john',
});
}
After that listener will contain lastUpdatedKeys with keys of age and name inputs.
Dependencies #
Input can have dependencies on other inputs to allow dependent validation. Define input's dependencies with dependencies.
inputKey must be specified on inputs to be used as dependencies.
In validation, translation or in onChange(), just call dependencies.byKey() to get dependent input.
Note that byKey() will throw if no input is found. This is by design to provide immediate indication of error.
For example, we want to restrict "Age input" to be at least 18 when "VIP Content" is checked.
ageInput = GladeInput.create(
validator: (v) => (v
..notNull()
..satisfy(
(value, extra, dependencies) {
final vipContentInput = dependencies.byKey<bool>('vip-input');
if (!vipContentInput.value) {
return true;
}
return value >= 18;
},
devError: (_, __) => 'When VIP enabled you must be at least 18 years old.',
key: _ErrorKeys.ageRestriction,
))
.build(),
value: 0,
dependencies: () => [vipInput], // <--- Dependency
valueConverter: GladeTypeConverters.intConverter,
inputKey: 'age-input',
translateError: (error, key, devMessage, dependencies) {
if (key == _ErrorKeys.ageRestriction) return LocaleKeys.ageRestriction_under18.tr();
if (error.isConversionError) return LocaleKeys.ageRestriction_ageFormat.tr();
return devMessage;
},
);
vipInput = GladeInput.create(
validator: (v) => (v..notNull()).build(),
value: false,
inputKey: 'vip-input',
);

Controlling other inputs #
Sometimes, it can be handy to update some input's value based on the changed value of another input.
Each input has onChange() callback where these reactions can be created.
An example could be automatically update Age value based on checked VIP Content input (checkbox).
// In vipContent input
onChange: (info, dependencies) {
final age = dependencies.byKey<int>('age-input');
if (info.value && age.value < 18) {
age.value = 18;
}
}
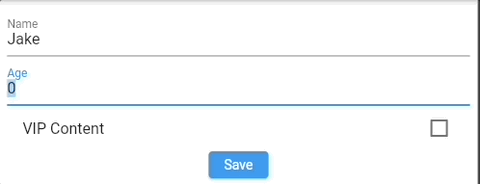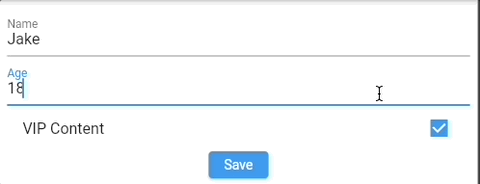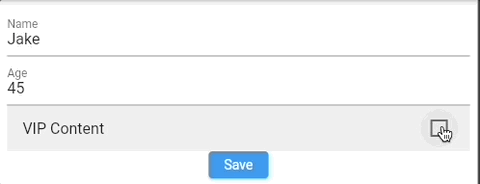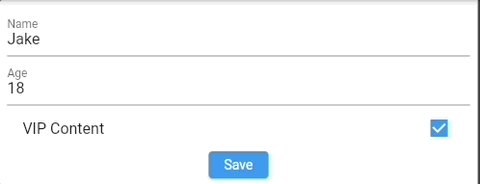
Translation #
Each validation error (and conversion error if any) can be translated. Provide translateError function which accepts:
error- Error to translatekey- Error's identification if anydevMessage- ProvideddevErrorfrom validatordependencies- Input's dependencies
Age example translation (LocaleKeys are generated translations from easy_localization package)
translateError: (error, key, devMessage, {required dependencies}) {
if (key == _ErrorKeys.ageRestriction) return LocaleKeys.ageRestriction_under18.tr();
if (error.isConversionError) return LocaleKeys.ageRestriction_ageFormat.tr();
return devMessage;
}
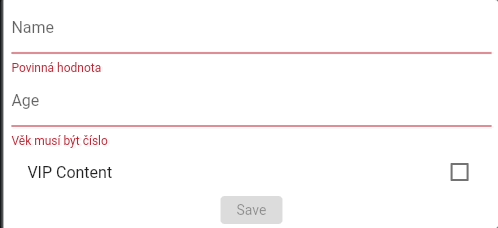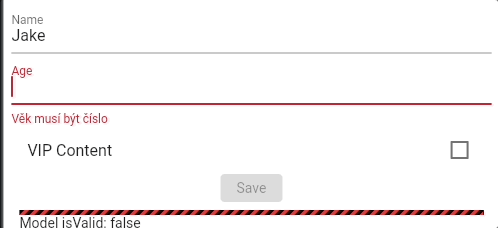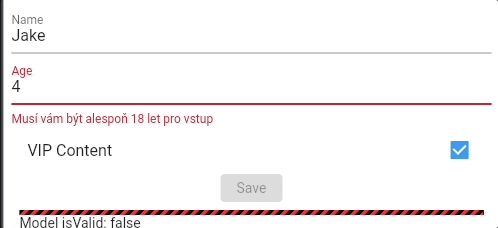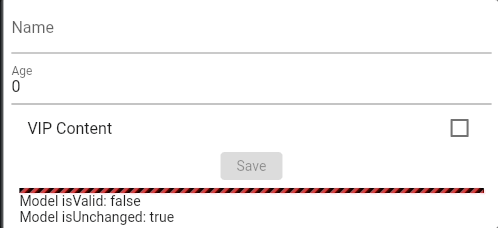
Converters #
As noted before, if T is not a String, a converter from String to T has to be provided.
GladeForms provides some predefined converters such as IntConverter and more. See GladeTypeConverters for more.
Debugging #
There are some getters and methods on GladeInput / GladeModel which can be used for debugging.
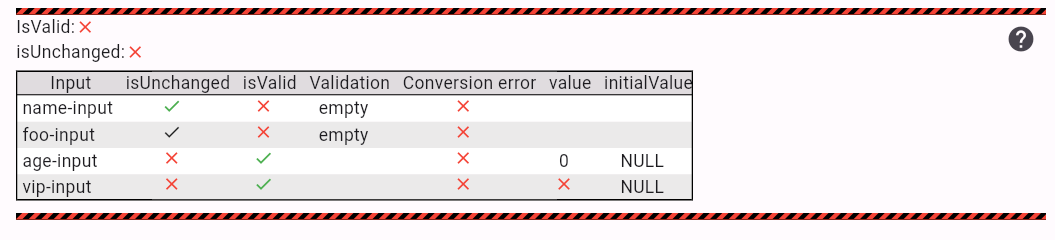
Use model.formattedValidationErrors to get all input's error formatted for simple debugging.
There is also GladeModelDebugInfo widget which displays table of all model's inputs
and their properties such as isValid or validation error.
👏 Contributing #
Your contributions are always welcome! Feel free to open pull request.



