flutter_mediator 1.1.1  flutter_mediator: ^1.1.1 copied to clipboard
flutter_mediator: ^1.1.1 copied to clipboard
Flutter mediator is a MVC state management package base on the InheritedModel with automatic aspect management to make them simpler, easier, and intuitive to use.
Flutter Mediator #
Flutter mediator is a MVC state management package base on the InheritedModel with automatic aspect management to make them simpler, easier, and intuitive to use.
By providing automatic generated aspects and management, flutter mediator makes you feel comfortable using the InheritedModel just like the InheritedWidget and rebuild widgets only when necessary.
Features #
- Easy and simple - Automatically make things work only by a few steps. Dependency injection, IoC, Proxy to make the state management much easier.
- Efficiency and Performance - Use InheritedModel as the underlying layer, rebuild widgets only when necessary.
- Lightweight - Small package size.
- Flexible - Provide both automatic and manual publish.
- Intuitive - Three main classes:
Pub,Subscriber,Host
Pub- to publish aspects
Subscriber- to subscribe aspects
Host- to dispatch aspects
Flutter Widget of the Week: InheritedModel explained #
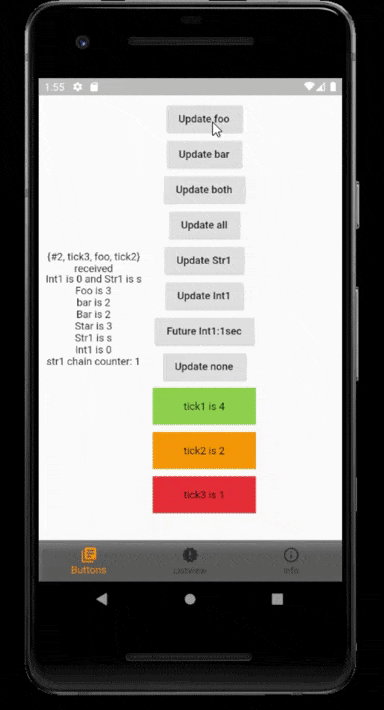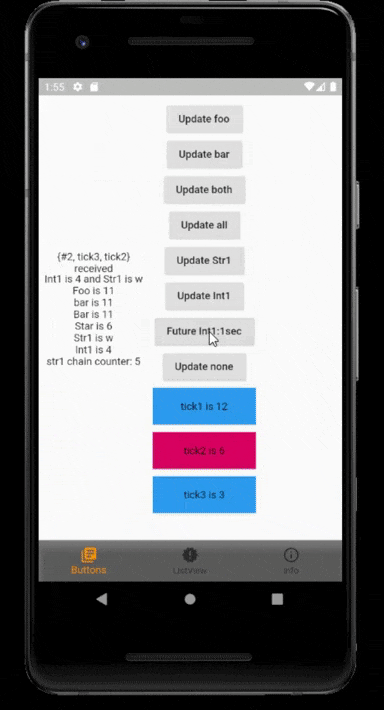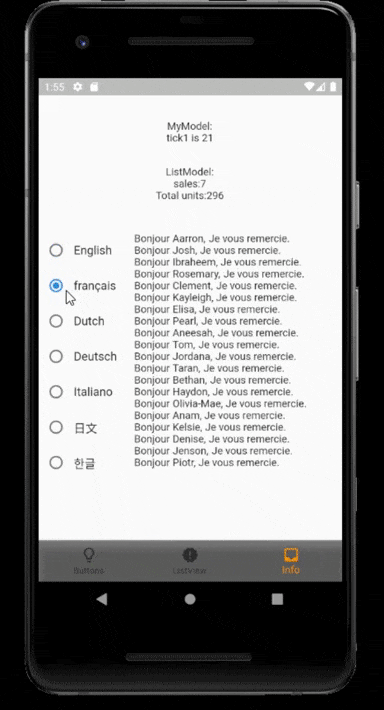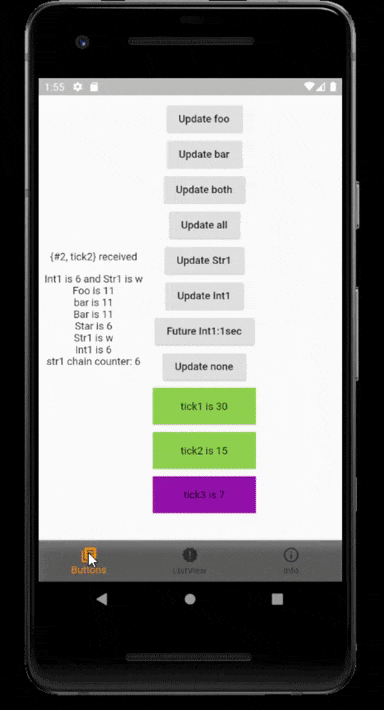
InheritedModel provides an aspect parameter to its descendants to indicate which fields they care about to determine whether that widget needs to rebuild. InheritedModel can help you rebuild its descendants only when necessary.
Key contepts #
Subscribe and Publish
A widget subscribes with aspects and will rebuild whenever a model controller publishs any of those aspects.
Rx Variable
A proxy object, by design pattern, proxy provides a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
Variables in the model can turn into a proxy object by denoting .rx
Widget Aspects
Aspects denote what the widget is interested in. That widget will rebuild whenever any of those aspects is published.
Rx Related Widget
When subscribing a widget, any rx variables used inside the create method will rebuild the widget automatically when updated.
Rx Automatic Aspect
By using rxSub<Model> to subscribe a widget, the package will generate aspects for the widget automatically, provides there is at least one rx variable used or use model.rxVar.touch() inside the create method to activate rx automatic aspect. (and so this widget is a rx related widget)
View Map
View map consists of two maps of create methods, Subscriber and Controller, that build upon rx automatic aspect and try to go one step further to make the UI view cleaner.
Setting up #
Add the following dependency to pubspec.yaml of your flutter project:
dependencies:
flutter_mediator: "^1.1.1"
Import flutter_mediator in files that will be used:
import 'package:flutter_mediator/mediator.dart';
For help getting started with Flutter, view the online documentation.
Getting Started Quick Steps #
Host, Model, View, Controller: #
1. Model: #
1-1. Implement the model by extending from Pub
1-2. Use .rx to turn model variables into rx variables, which will automatically rebuild the rx related widget when updated.
1-3. Implement the controller method of that variable.
For example,
/// my_model.dart
class MyModel extends Pub {
/// `.rx` make the var automatically rebuild the rx related widget when updated
var int1 = 0.rx;
void updateInt1() {
/// since int1 is a rx variable,
/// it will automatically rebuild the aspect-realted-widget when updated
int1 += 1;
}
}
Then, later, get the model by
Pub.getModel<Model>()
Note that you don't need
contextto get the model, this provides you the flexibility to do things anywhere.
2. Host: #
Register the models to the Host, and place it at the top level of the widget tree.
MultiHost.create1 to MultiHost.create9 are provided by the package, use it with the number of the amount of models.
For example, register 2 models, MyModel and ListModel, to the host.
void main() {
runApp(
MultiHost.create2(
MyModel(updateMs: 1000), // model extends from Pub
ListModel(updateMs: 500),// model extends from Pub
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
Or, use the generic form.
MultiHost.create( // Generic form
[
Host<MyModel>(model: MyModel(updateMs: 1000)),
Host<ListModel>(model: ListModel(updateMs: 500)),
],
child: MyApp(),
),
3. View: Subscribe widgets #
There are two ways to subscribe a widget:
-
rx automatic aspect: (Recommend)
- The package will generate aspects for the widget automatically, provides there is at least one rx variable used or use
model.rxVar.touch()inside the create method to activate rx automatic aspect. (and so this widget is a rx related widget)
rxSub<Model>((context, model) {/*create method*/})
- The package will generate aspects for the widget automatically, provides there is at least one rx variable used or use
-
specific aspect:
- Subscribe an aspect:
aspect.subModel<Model>((context, model) {/*create method*/}) - Subscribe multiple aspects: (Place aspects in a list)
[a1, a2].subModel<Model>((context, model) {/*create method*/}) - Broadcast to all aspects of the model: (Subscribe with
nullaspect to broadcast)
null.subModel<Model>((context, model) {/*create method*/})
- Subscribe an aspect:
Place that Subscriber in the widget tree then any rx variables used inside the create method will automatically rebuild the related widget when updated. (triggered by getter and setter)
For example, subscribes a widget with model class <MyModel>
- Case 1: Use rx automatic aspect.
rxSub<MyModel>((context, model) => Text('Int1 is ${model.int1}'))
- Case 2: With specific aspect
'int1'.
'int1'.subModel<MyModel>((context, model) => Text('Int1 is ${model.int1}'))
- Case 3: When using rx automatic aspect, but the create method does not use any rx variables, then you can use
model.rxVar.touch()which the widget depends on thatrxVarto activate rx automatic aspect.
For example, when changing locale, the create method doesn't have to display the value of the locale, then you can usemodel.locale.touch()to activate rx automatic aspect.
rxSub<MyModel>((context, model) {
model.locale.touch();
final hello = 'app.hello'.i18n(context);
return const Text('$hello');
})
4. Controller: #
Place the controller in the widget tree.
For example, to get the model class <MyModel> and execute its controller method within a RaisedButton.
Controller<MyModel>(
create: (context, model) => RaisedButton(
child: const Text('Update Int1'),
onPressed: () => model.updateInt1(), // or simplely, `model.int1++`
),
)
Or implement a controller function of MyModel.updateInt1(), then place it in the widget tree.
Widget int1Controller() {
return Controller<MyModel>(
create: (context, model) => RaisedButton(
child: const Text('Update Int1'),
onPressed: () => model.updateInt1(), // or simplely, `model.int1++`
),
);
}
5. Works automatically! #
Then whenever the rx variable updates, the related widgets will rebuild automatically!
Access the underlying value of rx variables #
Sometimes, an operation of a rx variable can not be done, then you need to do that with the underlying value by denoting .value .
For example,
/// my_model.dart
var int1 = 0.rx; // turn int1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
var str1 = 'A'.rx; // turn str1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
void updateInt1() {
// int1 *= 5; // can not do this (dart doesn't support operator*= to override)
int1.value *= 5; // need to do that with the underlying value
// str1 = 'B'; // can not do this
str1.value = 'B'; // need to do that with the underlying value
}
Visual Studio Code snippets #
These are code snippets, for example, for visual studio code to easy using the package.
To add these code snippets in visual studio code, press
control+shift+p => Preferences: Configure user snippets => dart.json
Then add the content of vscode_snippets.json to the dart.json.
Now you can type these shortcuts for code templates to easy using the package:
mmodel- Generate a Model Boilerplate Code of Flutter Mediatorgetmodel- Get the Model of Flutter Mediator
View Map shortcuts: (See View Map)
addsub- Add a Creator to the Subscriber Map of the Model.addcon- Add a Creator to the Controller Map of the Model.pubsub- Create a Subscriber Widget from the Subscriber Map of the Model.pubcon- Create a Controller Widget from the Controller Map of the Model.
Shortcuts:
controller- Create a Flutter Mediator Controller Function.subscriber- Create a Flutter Mediator Subscriber Function with Aspect.rxfun- Create a Flutter Mediator Subscriber Function with RX Automatic Aspect.submodel- Create a Flutter Mediator Subscriber with Aspect.rxsub- Create a Flutter Mediator Subscriber with RX Automatic Aspect.
View Map - one step further of dependency injection #
View map consists of two maps of create methods, Subscriber and Controller, which build upon rx automatic aspect and try to go one step further to make the UI view cleaner.
First, let's see what's the difference by an original view and after using the view map.
Original View
/// Original view
class LocalePanel extends StatelessWidget {
const LocalePanel({Key key}) : super(key: key);
Widget txt(BuildContext context, String name) {
return SizedBox(
width: 250,
child: Row(
children: [
rxSub<ListModel>(
(context, model) {
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final hello = 'app.hello'.i18n(context);
return Text('$hello ');
},
),
Text('$name, '),
rxSub<ListModel>(
(context, model) {
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final thanks = 'app.thanks'.i18n(context);
return Text('$thanks.');
},
),
],
),
);
}
/// ...
After using the View Map
/// After using the View Map
class LocalePanel extends StatelessWidget {
const LocalePanel({Key key}) : super(key: key);
Widget txt(BuildContext context, String name) {
return SizedBox(
width: 250,
child: Row(
children: [
Pub.sub<ListModel>('hello'), // use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate
Text('$name, '),
Pub.sub<ListModel>('thanks'), // use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate
],
),
);
}
/// ...
Isn't it cleaner.
Here's how to use View Map. #
- Add these code into the model and change
<Model>to the class name of the model.Use the code snippet shortcut,
mmodel, to generate these boilerplate code.
/// some_model.dart
void addSub(Object key, CreatorFn<Model> sub) => regSub<Model>(key, sub);
void addCon(Object key, CreatorFn<Model> con) => regCon<Model>(key, con);
@override
void init() {
// addSub('', (context, model) {
// return Text('foo is ${model.foo}');
// });
// addCon('', (context, model) {
// return RaisedButton(child: const Text('Update foo'),
// onPressed: () => model.increaseFoo(),);
// });
super.init();
}
- Use the
addsuboraddconshortcut to add create methods ofSubscriberorControllerin theinit()method.'hello'and'thanks'are the keys to the map, later, you can use these keys to create corresponding widgets.
/// in the init() of some_model.dart
// use `addsub` shortcut to generate boilerplate code
addSub('hello', (context, model) {
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final hello = 'app.hello'.i18n(context);
return Text('$hello ');
});
// use `addsub` shortcut to generate boilerplate code
addSub('thanks', (context, model) {
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final thanks = 'app.thanks'.i18n(context);
return Text('$thanks.');
});
- Then use the
pubsubshortcut to place theSubscriberwidget in the widget tree.Change
<Model>to the class name of the model.
/// in the widget tree
child: Row(
children: [
Pub.sub<Model>('hello'), // use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate
Text('$name, '),
Pub.sub<Model>('thanks'),// use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate
],
),
Done.
Now you just need to use these shortcuts, or commands, to do state management.
mmodel- Generate a Model Boilerplate Code.addsub- Add a Creator to the Subscriber Map of the Model.addcon- Add a Creator to the Controller Map of the Model.pubsub- Create a Subscriber Widget from the Subscriber Map of the Model.pubcon- Create a Controller Widget from the Controller Map of the Model.
Plus with,
.rx- Turn model variables into rx variables, thus, you can use rx automatic aspect.rxVar.touch()- Used when the create method doesn't have to display the value of that rx variable, then youtouch()that rx variable to activate rx automatic aspect.getmodel- Get the model. (Note thatcontextis not needed to get the model.)
Happy Coding!
Use Case - explain how the package works #
This use case explains how the package works, you can skip it. There is an use case for i18n with View Map, which is much more straight forward to use.
First of all, implement the Model and place the Host at the top level of the widget tree,
/// my_model.dart
class MyModel extends Pub {
var int1 = 0.rx; // turn int1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
var star = 0.rx; // turn str1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
var m = 0; // ordinary variable
/// controller function for case 1
void ifUpdateInt1({bool update = true}) {
if (update == true) {
int1 += 1; // int1 is a rx variable, will rebuild the related widget when updated.
} else {
int1.touch(); // `touch()` to activate rx automatic aspect, will also rebuild the related widget.
}
}
/// controller function for case 2
void increaseStar() => star++; // star is a rx variable, will rebuild the related widget when updated.
/// controller function for case 3
void increaseManual(Object aspect) {
m++;
publish(aspect); // m is an ordinary variable, needs to publish the aspect manually.
}
}
/// main.dart
void main() {
runApp(
MultiHost.create1(
MyModel(updateMs: 1000), // model extends from Pub
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
Case 1: use rx automatic aspect
Implement the Subscriber and Controller functions, and place them in the widget tree.
/// main.dart
/// Subscriber function
Widget rxAAInt1Subscriber() {
return rxSub<MyModel>((context, model) {
return Text('int1: ${model.int1}');
});
}
/// Controller function
Widget rxAAInt1Controller() {
return Controller<MyModel>(
create: (context, model) => RaisedButton(
child: const Text('ifInt1'),
onPressed: () => model.ifUpdateInt1(),
),
);
}
/// widget tree
Widget mainPage() {
return Column(
children: [
rxAAInt1Subscriber(),
rxAAInt1Controller(),
],
);
}
Case 2: with specific aspect
Specific an aspect, for example, 'star', then implement the Subscriber and Controller functions for that aspect, and place them in the widget tree.
/// main.dart
/// Subscriber function
Widget starSubscriber() {
return 'star'.subModel<MyModel>((context, model) {
return Text('star: ${model.star}');
});
}
/// Controller function
Widget starController() {
return Controller<MyModel>(
create: (context, model) => RaisedButton(
child: const Text('update star'),
onPressed: () => increaseStar(), // or simplely model.star++,
),
);
}
/// widget tree
Widget mainPage() {
return Column(
children: [
starSubscriber(),
starController(),
],
);
}
Case 3: manual publish aspect
Specific an aspect, for example, 'manual', then implement the Subscriber and Controller functions for that aspect, and place them in the widget tree, and do publish the aspect in the controller function.
/// main.dart
/// Subscriber function
Widget manualSubscriber() {
return 'manual'.subModel<MyModel>((context, model) {
return Text('manual: ${model.manual}');
});
}
/// Controller function
Widget manualController() {
return Controller<MyModel>(
create: (context, model) => RaisedButton(
child: const Text('update manual'),
onPressed: () => increaseManual('manual'),
),
);
}
/// widget tree
Widget mainPage() {
return Column(
children: [
manualSubscriber(),
manualController(),
],
);
}
Use Case - i18n with View Map #
For example, to write an i18n app using flutter_i18n with View Map.
These are all boilerplate code, you may just need to look at the lines with comments, that's where to put the code in.
- Edit
pubspec.yamlto use flutter_i18n and flutter_mediator.
dependencies:
flutter_i18n: ^0.20.0
flutter_mediator: ^1.1.0
flutter:
assets:
- assets/flutter_i18n/
- Create the i18n folder
asserts/flutter_i18nand edit the locale files, see folder.
For example, anen.jsonlocale file.
{
"app": {
"hello": "Hello",
"thanks": "Thanks",
"~": ""
}
}
-
Create a folder
modelsthen new a filesetting_model.dartin the folder and usemmodelshortcut to generate a model boilerplate code with the class nameSetting. -
Add an
i18nextension to thesetting_model.dart.
//* i18n extension
extension StringI18n on String {
String i18n(BuildContext context) {
return FlutterI18n.translate(context, this);
}
}
- Add the
localevariable and make it a rx variable along with thechangeLocalefunction, then add create methods to theSettingmodel. (in theinit()method)
Add theSettingEnumto represent the map keys of the view map.
/// setting_model.dart
enum SettingEnum {
hello,
thanks,
}
class Setting extends Pub {
//* member variables
var locale = 'en'.rx;
//* controller function
Future<void> changeLocale(BuildContext context, String countryCode) async {
final loc = Locale(countryCode);
await FlutterI18n.refresh(context, loc);
locale.value = countryCode;
// locale is a rx variable, will rebuild related widget when updated.
}
//* View Map:
// ...
@override
void init() {
addSub(SettingEnum.hello, (context, model) { // SettingEnum.hello is the map key
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final hello = 'app.hello'.i18n(context); // app.hello is the json field in the locale file
return Text('$hello ');
});
addSub(SettingEnum.thanks, (context, model) { // SettingEnum.thanks is the map key
model.locale.touch(); // to activate rx automatic aspect
final thanks = 'app.thanks'.i18n(context); // app.thanks is the json field in the locale file
return Text('$thanks.');
});
//...
- Setup
main.dart.
Import files, addSettingmodel to the host, i18n stuff and sethometoinfoPage().
/// main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_i18n/flutter_i18n.dart';
import 'package:flutter_i18n/loaders/decoders/json_decode_strategy.dart';
import 'package:flutter_localizations/flutter_localizations.dart';
import 'package:flutter_mediator/mediator.dart';
import 'models/setting_model.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MultiHost.create1(
Setting(), // add `Setting` model to the host
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Mediator Demo',
theme: ThemeData(primarySwatch: Colors.blue),
// add flutter_i18n support, i18n stuff
localizationsDelegates: [
FlutterI18nDelegate(
translationLoader: FileTranslationLoader(
decodeStrategies: [JsonDecodeStrategy()],
),
missingTranslationHandler: (key, locale) {
print('--- Missing Key: $key, languageCode: ${locale.languageCode}');
},
),
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
],
home: infoPage(), // set `infoPage` as home page
);
}
}
- Implement
infoPage()with View Map.These are boilerplate code, just look at the lines with comments, that's where to put the code in.
/// main.dart
Widget infoPage() {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(
children: [
SizedBox(height: 50),
Container(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: const [
RadioGroup(),
LocalePanel(),
],
),
),
],
),
);
}
class LocalePanel extends StatelessWidget {
const LocalePanel({Key key}) : super(key: key);
Widget txt(BuildContext context, String name) {
return SizedBox(
width: 250,
child: Row(
children: [
Pub.sub<Setting>(SettingEnum.hello), // Use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate, SettingEnum.hello is the map key.
Text('$name, '),
Pub.sub<Setting>(SettingEnum.thanks), // Use `pubsub` shortcut for boilerplate, SettingEnum.thanks is the map key.
],
),
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: [for (final name in names) txt(context, name)],
);
}
}
class RadioGroup extends StatefulWidget {
const RadioGroup({
Key key,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
_RadioGroupState createState() => _RadioGroupState();
}
class _RadioGroupState extends State<RadioGroup> {
final locales = ['en', 'fr', 'nl', 'de', 'it', 'zh', 'jp', 'kr']; // locale values
final languages = [ // the language options to let the user to select, need to be corresponded with the locale values
'English',
'français',
'Dutch',
'Deutsch',
'Italiano',
'中文',
'日文',
'한글',
];
Future<void> _handleRadioValueChange1(String value) async {
final model = Pub.getModel<Setting>(); // use `getmodel` shortcut to get the model
await model.changeLocale(context, value); // change the locale
setState(() {
/// model.locale.value = value; // changed in model.changeLocale
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final model = Pub.getModel<Setting>(); // use `getmodel` shortcut to get the model
final _radioValue1 = model.locale.value; // get the locale value back to maintain state
Widget panel(int index) {
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Radio(
value: locales[index],
groupValue: _radioValue1,
onChanged: _handleRadioValueChange1,
),
Text(
languages[index],
style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 16.0),
),
],
);
}
return Container(
width: 130,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: [for (var i = 0; i < locales.length; i++) panel(i)],
),
);
}
}
final names = [
'Aarron',
'Josh',
'Ibraheem',
'Rosemary',
'Clement',
'Kayleigh',
'Elisa',
'Pearl',
'Aneesah',
'Tom',
'Jordana',
'Taran',
'Bethan',
'Haydon',
'Olivia-Mae',
'Anam',
'Kelsie',
'Denise',
'Jenson',
'Piotr',
];
- Work completed. Now you get an app with i18n support.
Example #
You can find the example in the example folder.
Try it once, you will see it's simple and easy to use.
These steps can help you in most situations. The following details explain the package one step further, you can skip it.
Detail #
- Single model - host
- Multiple models - host
- Automatically rebuild the widget whenever the rx variable updates - Pub
- Access the underlying value of rx variables - Pub
- Update the rx variables by call style - Pub
- Manually publish an aspect - Pub
- Manually publish multiple aspects - Pub
- Broadcast to the model - Pub
- Publish aspects of a rx variable - Pub
- Future publish - Pub
- Rebuild only once per frame for the same aspect - Pub
- Writing model extension - Pub
- Get the model - Controller and Subscriber
- Subscribe with rx automatic aspect - rx automatic aspect - Subscriber
- Touch the rx variable - rx automatic aspect - Subscriber
- Subscribe an aspect - specific aspect - Subscriber
- Subscribe multiple aspects - specific aspect - Subscriber
- Subscribe all aspects - specific aspect - Subscriber
- Subscribe with enum aspects - specific aspect - Subscriber
- Manage rx aspects - Chain react aspects - advance topic
- Implement custom rx class - advance topic
- Aspect type - terminology
1. Single model #
Register a model to the Host, and place it at the top level of the widget tree.
/// main.dart
void main() {
runApp(
Host(
model: AppModel(), // model extends from Pub
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
2. Multiple models #
Register multiple models to the Host, and place it at the top level of the widget tree.
MultiHost.create1 to MultiHost.create9 are provided by the package, use it with the number of the amount of models.
/// main.dart
void main() {
runApp(
MultiHost.create2(
MyModel(updateMs: 1000), // model extends from Pub
ListModel(updateMs: 500), // model extends from Pub
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
Or, use the generic form.
MultiHost.create( // Generic form
[
Host<MyModel>(model: MyModel(updateMs: 1000)),
Host<ListModel>(model: ListModel(updateMs: 500)),
],
child: MyApp(),
),
3. Automatically rebuild the widget whenever the rx variable updates #
Denoting .rx turns a variable of the model into a rx variable, a proxy object, which will automatically rebuild the related widget when updated. For Example,
rx int:
/// my_model.dart
class MyModel extends Pub {
/// `.rx` turn the var into a rx variable(i.e. a proxy object)
/// and rebuild the related widget when updated.
var int1 = 0.rx;
void updateInt1() {
int1 += 1; // automatically update the rx related widget
}
rx list:
/// list_model.dart
class ListModel extends Pub {
/// `.rx` turn the var into a rx variable(i.e. a proxy object)
/// and rebuild the related widget when updated
final data = <ListItem>[].rx;
void updateListItem() {
// get new item data...
final newItem = ListItem(itemName, units, color);
data.add(newItem); // automatically update the rx related widget
}
rx variable of type int, double, num, string, bool, list, map, set are provided by the package.
See also RxInt class,
RxList class,
RxList.add
4. Access the underlying value of rx variables #
Sometimes, you can not do an operation with the rx variable, then you need to do that with the underlying value by denoting .value, for example,
/// my_model.dart
var int1 = 0.rx; // turn int1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
var str1 = 'A'.rx; // turn str1 into a rx variable (i.e. a proxy object)
void updateInt1() {
// int1 *= 5; // can not do this (dart doesn't support operator*= to override)
int1.value *= 5; // need to do that with the underlying value
// str1 = 'B'; // can not do this
str1.value = 'B'; // need to do that with the underlying value
}
5. Update the rx variables by call style #
Dart provides a call(T) to override, you can use rxVar(value) to update the underlying value.
/// my_model.dart
var _foo = 1.rx;
set foo(int value) {
_foo(value); // update the rx variable by call() style
/// is the same as
// _foo = value;
/// is the same as
// _foo.value = value;
}
6. Manually publish an aspect #
Use the publish() method of the model to manually publish an aspect.
/// my_model.dart
int manuallyInt = 0;
void manuallyPublishDemo(int value) {
manuallyInt = value;
publish('manuallyInt'); // manually publish aspect of 'manuallyInt'
}
7. Manually publish multiple aspects #
Place aspects in a list to publish multiple aspects.
/// my_model.dart
int _foo = 0;
int _bar = 0;
void increaseBoth() {
_foo += 1;
_bar += 1;
publish(['foo', 'bar']); // manually publish multiple aspects
}
8. Broadcast to the model #
Publish null value to broadcast to all aspects of the model.
/// my_model.dart
void increaseAll() {
//...
publish(); // broadcasting, publish all aspects of the model
}
9. Publish aspects of a rx variable #
Publish a rx variable to publish the aspects that rx variable attached.
/// my_model.dart
var int1 = 0.rx;
void publishInt1Related() {
//...
publish(int1); // publish the aspects that int1 attached
}
10. Future publish #
Use rx variables within an async method.
/// my_model.dart
int int1 = 0.rx;
Future<void> futureInt1() async {
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1));
int1 += 1; // int1 is a rx variable, it'll automatically update the rx related widget when updated
}
11. Rebuild only once per frame #
InheritedModel uses Set to accumulate aspects thus the same aspect only causes the related widget to rebuild once per frame for the same aspect.
The following code only causes the rx related widget to rebuild once.
/// my_model.dart
int int1 = 0.rx;
void incermentInt1() async {
int1 += 1; // int1 is a rx variable, it'll automatically update the rx related widget when updated
publish('int1'); // manually publish 'int1'
publish('int1'); // manually publish 'int1', again
// only cause the aspected-related-widget to rebuild once per frame
}
12. Writing model extension #
You can write model extensions to simplified the typing. For example,
Use shortcut
mmodelwill generate these extensions automatically.
/// MyModel extension
MyModel getMyModel(BuildContext context) => Pub.getModel<MyModel>();
Subscriber<MyModel> subMyModel(CreatorFn<MyModel> create,
{Key key, Object aspects}) {
return Subscriber<MyModel>(key: key, aspects: aspects, create: create);
}
extension MyModelExtT<T> on T {
Subscriber<MyModel> subMyModel(CreatorFn<MyModel> create,
{Key key}) {
return Subscriber<MyModel>(key: key, aspects: this, create: create);
}
}
/// ListModel extension
ListModel getListModel(BuildContext context) => Pub.getModel<ListModel>();
Subscriber<ListModel> subListModel(CreatorFn<ListModel> create,
{Key key, Object aspects}) {
return Subscriber<ListModel>(key: key, aspects: aspects, create: create);
}
extension ListModelExtT<T> on T {
Subscriber<ListModel> subListModel(CreatorFn<ListModel> create,
{Key key}) {
return Subscriber<ListModel>(key: key, aspects: this, create: create);
}
}
See also mediator_extension.dart for package extension.
13. Get the model #
To get the model, for example, getting MyModel,
Note that you don't need
contextto get the model, this provides you the flexibility to do things anywhere.
- original form
final model = Pub.getModel<MyModel>();
- with user extension
final model = getMyModel();
Get current triggered frame aspects of the model. See also allSubscriber@main.dart.
final model = Pub.getModel<MyModel>();
final aspects = model.frameAspects;
14. Subscribe with rx automatic aspect #
By using rxSub<Model> to subscribe a widget, the package will generate aspects for the widget automatically, provides there is at least one rx variable used or use model.rxVar.touch() inside the create method to activate rx automatic aspect. (and so this widget is a rx related widget)
For example,
/// my_model.dart
int tick1 = 0.rx;
/// main.dart
rxSub<MyModel>((context, model) {
return Text('tick1 is ${model.tick1}');
}),
15. Touch the rx variable #
When using rx automatic aspect, but the create method does not use any rx variables, then you can use model.rxVar.touch() which the widget depends on that rxVar to activate rx automatic aspect.
For example, when changing locale, the create method doesn't have to display the value of the locale, then you can use model.locale.touch() to activate rx automatic aspect.
rxSub<MyModel>((context, model) {
model.locale.touch();
final hello = 'app.hello'.i18n(context);
return const Text('$hello');
})
16. Subscribe an aspect #
For example, subscribe to a String aspect 'int1' of class <MyModel>.
- simple form
'int1'.subModel<MyModel>((context, model) => Text('Int1 is ${model.int1}')),
- original form
Subscriber<MyModel>(
aspects: 'int1',
create: (context, model) {
return Text('Int1 is ${model.int1}');
},
),
- with user extension
'int1'.subMyModel((context, model) => Text('Int1 is ${model.int1}')),
17. Subscribe multiple aspects #
Place aspects in a list to subscribe multiple aspects.
- simple form
['int1', 'star'].subModel<MyModel>(
(context, model) => Text(
'Int1 is ${model.int1} and Star is ${model.star}',
softWrap: true,
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
),
- original form
Subscriber<MyModel>(
aspects: ['int1', 'star'],
create: (context, model) {
return Text(
'Int1 is ${model.int1} and Star is ${model.star}',
softWrap: true,
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
);
},
),
- with user extension
['int1', 'star'].subMyModel(
(context, model) => Text(
'Int1 is ${model.int1} and Star is ${model.star}',
softWrap: true,
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
),
18. Subscribe all aspects #
Provide no aspects parameter, or use null as aspect to subscribe to all aspects of the model.
See also allSubscriber@main.dart.
- simple form
null.subModel<MyModel>( // null aspects means broadcasting to the model
(context, model) {
final aspects = model.frameAspects;
final str = aspects.isEmpty ? '' : '$aspects received';
return Text(str, softWrap: true, textAlign: TextAlign.center);
},
),
- original form
Subscriber<MyModel>(
// aspects: , // no aspects parameter means broadcasting to the model
create: (context, model) {
final aspects = model.frameAspects;
final str = aspects.isEmpty ? '' : '$aspects received';
return Text(str, softWrap: true, textAlign: TextAlign.center);
},
),
- with user extension
null.subMyModel( // null aspects means broadcasting to the model
(context, model) {
final aspects = model.frameAspects;
final str = aspects.isEmpty ? '' : '$aspects received';
return Text(str, softWrap: true, textAlign: TextAlign.center);
},
),
19. Subscribe with enum aspects #
You can use enum as aspect.
For example, first, define the enum.
/// list_model.dart
enum ListEnum {
ListUpdate,
}
Then everything is the same as String aspect, just to replace the String with enum.
See also cardPage@main.dart.
- simple form
ListEnum.ListUpdate.subModel<ListModel>((context, model) {
/* create method */
}),
- original form
Subscriber<ListModel>(
aspects: ListEnum.ListUpdate,
create: (context, model) {
/* create method */
}),
- with user extension
ListEnum.ListUpdate.subMyModel((context, model) {
/* create method */
}),
20. Manage rx aspects - Chain react aspects #
Chain react aspects: #
Supposed you need to rebuild a widget whenever a model variable is updated, but it has nothing to do with the variable. Then you can use chain react aspects.
For example, to rebuild a widget whenever str1 of class <MyModel> is updated, and chained by the aspect 'chainStr1'.
/// my_model.dart
final str1 = 's'.rx..addRxAspects('chainStr1'); // to chain react aspects
/// main.dart
int httpResCounter = 0;
Future<int> _futureHttpTask() async {
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 0));
return ++httpResCounter;
}
//* Chain subscribe binding myModel.str1 with aspect 'chainStr1'.
Widget chainReactSubscriber() {
return 'chainStr1'.subModel<MyModel>((context, model) {
return FutureBuilder(
future: _futureHttpTask(),
initialData: httpResCounter,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
Widget child;
if (snapshot.hasData) {
child = Text('str1 chain counter: $httpResCounter');
} else {
child = Text('str1 init counter: $httpResCounter');
}
return Center(child: child);
},
);
});
}
Then whenever str1 of class <MyModel> updates, the widget rebuild automatically.
Manage rx aspects: #
-
Add aspects to the rx variable:
- add an aspect:
rxVar.addRxAspects('chained-aspect') - add multiple aspects:
rxVar.addRxAspects(['chained-as1', 'chained-as2']) - add aspects from another rx variable:
rxVar.addRxAspects(otherRxVar) - broadcast to the model:
rxVar.addRxAspects()
- add an aspect:
-
Remove aspects from the rx variable:
- remove an aspect:
rxVar.removeRxAspects('chained-aspect') - remove multiple aspects:
rxVar.removeRxAspects(['chained-as1', 'chained-as2']) - remove aspects from another rx variable:
rxVar.removeRxAspects(otherRxVar) - don't broadcast to the model:
rxVar.removeRxAspects()
- remove an aspect:
-
Retain aspects in the rx variable:
- retain an aspect:
rxVar.retainRxAspects('chained-aspect') - retain multiple aspects:
rxVar.retainRxAspects(['chained-as1', 'chained-as2']) - retain aspects from another rx variable:
rxVar.retainRxAspects(otherRxVar)
- retain an aspect:
-
Clear all rx aspects:
rxVar.clearRxAspects()
21. Implement custom rx class #
If you need to write your own rx class, see custom_rx_class.dart for example.
Or you can manipulate the underlying value directly. For example,
/// some_model.dart
final someClassRx = someClass.rx;
void updateSomeClass() {
someClassRx.value.counter++;
someClassRx.publishRxAspects();
}
By the extension method, package can turn anything into a rx variable.
22. Aspect type #
- Widget aspects - aspects denotes what the widget is interested in.
- Frame aspects - aspects that will update the related widgets in the next UI frame.
- Registered aspects - aspects of the model that has been registered.
- RX aspects - aspects that the rx variable is attached. Once the rx variable updated, it will rebuild the related widgets.
Changelog #
Please see the Changelog page.
License #
Flutter mediator is distributed by MIT license.