flutter_event_component_system 0.0.5  flutter_event_component_system: ^0.0.5 copied to clipboard
flutter_event_component_system: ^0.0.5 copied to clipboard
Powerful Event-Component-System state management for Flutter. Promotes clean architecture, testability, and includes visual debugging with Inspector
Flutter Event Component System (ECS) #
A powerful and flexible Event-Component-System architecture pattern implementation for Flutter applications. This package provides a reactive state management solution that promotes clean architecture, separation of concerns, and scalable application development.
NOTICE This library is not a data-oriented ECS. It does not optimize for memory layout or CPU cache efficiency. Instead, it uses events, components, and systems as a conceptual model for structuring complex, event-driven domain logic in Flutter applications. Events and components are modeled as entities with explicit lifecycle and state, enabling deterministic, inspectable, and testable workflows.
📌 Why Choose This Over Other State Management Libraries #
Clear Separation of Data, Logic, and Events #
Instead of coupling state and logic inside widgets, notifiers, or bloc classes, this system splits:
- Components: containers for state with history tracking
- Events: explicit triggers for actions
- Systems: pure logic reacting to changes and events
This separation makes business logic easier to reason about, test, and maintain as the application grows.
Features as Self Contained Modules** #
Your app can be structured into features that encapsulate related entities, events, and systems together. This enables:
- Easy removal or addition of features
- Clear boundaries between domains modular testing
This modularity isn’t easy to achieve with classic state management methods.
Deterministic and Testable Logic #
Systems in this architecture are pure and stateless functions of components and events. This makes them:
- predictable
- Easy to unit test in isolation
- Easy to mock
- Easy to reason about without widget scaffolding
Testing flows or business rules does not require spinning up widget trees or provider scopes.
Explicit Event Handling #
Instead of implicit streams, callbacks, or passing dispatch functions through widget trees, events in this library are first-class entities that can carry data and trigger reactions explicitly. This gives you:
- Traceable workflows
- Easier debugging
behavior that is visible and inspectable This contrasts with the invisible event flow in many pub-sub systems.
Built-In Inspector Devtools Extension #
Because the architecture has explicit entities, events, and systems, you can build tooling to inspect the runtime structure including logs, entity state, and dependency graphs; something that most state libs don’t provide out of the box.
Scalability Without Coupling #
As your app grows:
- You don’t end up with tangled notifier hierarchies.
- UI logic doesn’t leak into business workflows.
- Systems can evolve independently.
This makes large and complex applications easier to evolve than with shared state or global providers.
📚 Articles & Resources #
- Flutter ECS: Rethinking State Management for Flutter Apps
- Flutter ECS: Mastering Async Operations and Complex Workflows
- Flutter ECS: Testing Strategies That Actually Work
🌟 Features #
Core Architecture #
- 🏗️ Entity-Component-System Pattern: Clean separation between data (Components), behavior (Systems), and events
- ⚡ Reactive Programming: Automatic UI updates when components change
- 🔄 Event-Driven: Decoupled communication through events and reactive systems
- 🎯 Type-Safe: Full type safety with Dart generics
- 🧩 Modular Design: Organize code into reusable features
Advanced Capabilities #
- 🔍 Built-in Inspector: Real-time debugging and visualization tools
- 📊 Flow Analysis: Detect circular dependencies and cascade flows
- 📈 Performance Monitoring: Track system interactions and entity changes
- 🌐 Graph Visualization: Interactive dependency graphs
- 📝 Comprehensive Logging: Detailed system activity tracking
Developer Experience #
- 🛠️ Widget Integration: Seamless Flutter widget integration
- 🎨 Reactive Widgets: Automatic rebuilds on component changes
- 🔧 Debugging Tools: Visual inspector with filtering and search
- 📋 Cascade Analysis: Understand data flow and dependencies
- ⚙️ Hot Reload Support: Full development workflow integration
🚀 Quick Start #
Installation #
Add this package to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
flutter_event_component_system: any
Basic Usage #
1. Define Components and Events
// Components hold state data
class CounterComponent extends ECSComponent<int> {
CounterComponent([super.value = 0]);
}
// Events trigger actions
class IncrementEvent extends ECSEvent {
IncrementEvent();
}
2. Create Reactive Systems
// Systems define behavior and reactions
class IncrementCounterSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
IncrementCounterSystem();
@override
Set<Type> get reactsTo => {IncrementEvent};
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {CounterComponent};
@override
void react() {
final counter = getEntity<CounterComponent>();
counter.update(counter.value + 1);
}
}
3. Organize into Features
class CounterFeature extends ECSFeature {
CounterFeature() {
// Add components
addEntity(CounterComponent());
addEntity(IncrementEvent());
// Add systems
addSystem(IncrementCounterSystem());
}
}
4. Setup ECS Scope
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ECSScope(
features: {
CounterFeature(),
},
child: MaterialApp(
home: CounterPage(),
),
);
}
}
5. Create Reactive Widgets
class CounterPage extends ECSWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ECSContext ecs) {
final counter = ecs.watch<CounterComponent>();
final incrementEvent = ecs.get<IncrementEvent>();
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Counter')),
body: Center(
child: Text('Count: ${counter.value}'),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: incrementEvent.trigger,
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
🏛️ Architecture Overview #
Core Concepts #
Entities
Base building blocks that can be either Components or Events:
- Components: Hold state data with automatic change notification
- Events: Trigger actions and system reactions
Systems
Define behavior and business logic:
- InitializeSystem: Setup tasks on feature initialization
- ExecuteSystem: Frame-based continuous execution
- ReactiveSystem: React to entity changes
- CleanupSystem: Cleanup tasks after each frame
- TeardownSystem: Cleanup on feature disposal
Features
Organize related entities and systems into cohesive modules:
class UserAuthFeature extends ECSFeature {
UserAuthFeature() {
// Components
addEntity(AuthStateComponent());
addEntity(LoginCredentialsComponent());
// Events
addEntity(LoginEvent());
addEntity(LogoutEvent());
// Systems
addSystem(LoginUserReactiveSystem());
addSystem(LogoutUserReactiveSystem());
}
}
Manager
Central coordinator that:
- Manages all features and their lifecycles
- Coordinates system execution
- Handles entity change notifications
- Provides entity lookup and access
System Lifecycle #
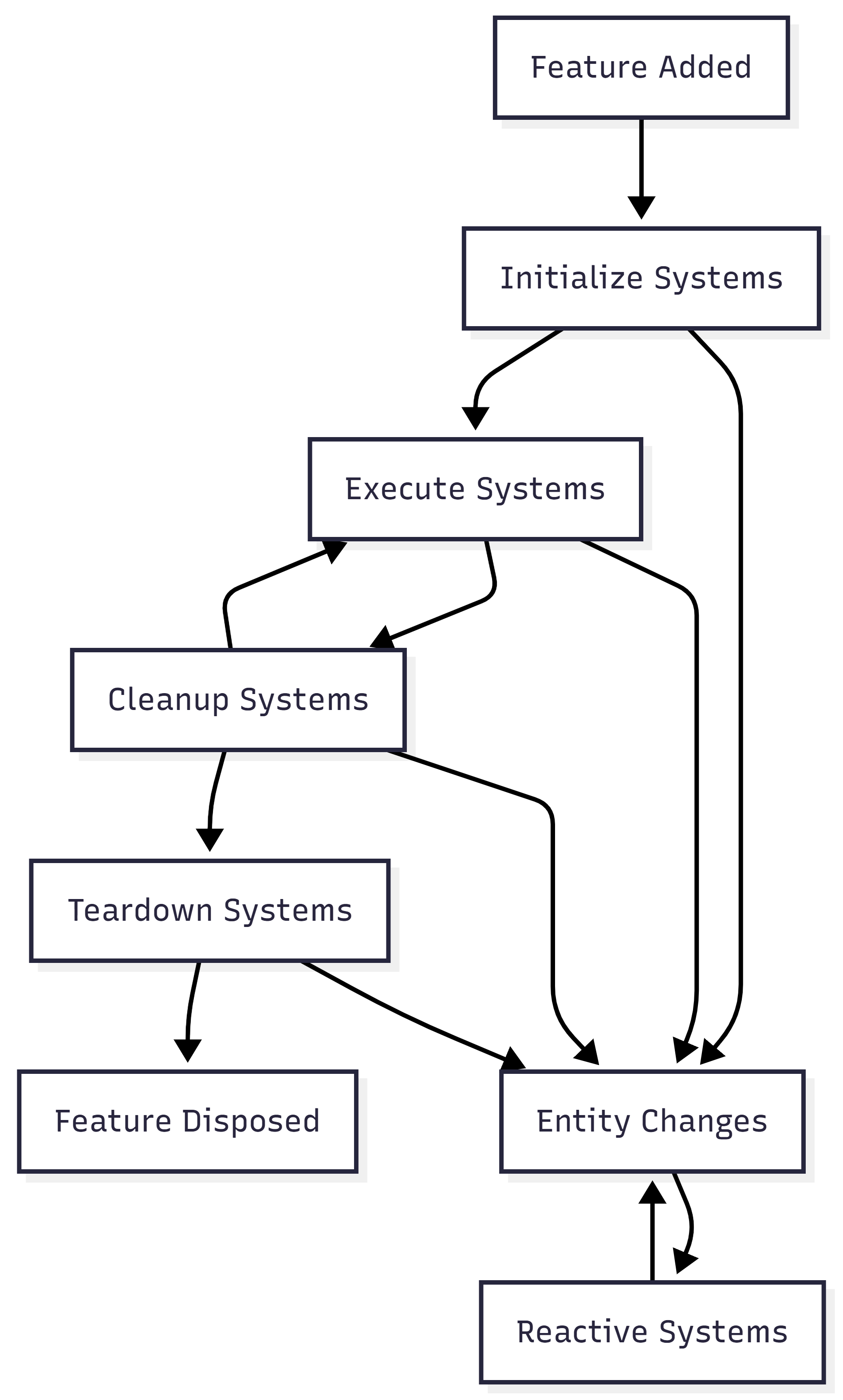
🎯 Advanced Features #
Reactive Widget Integration #
ECSWidget
Automatically rebuilds when watched components change:
class ProfileWidget extends ECSWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ECSContext ecs) {
final user = ecs.watch<UserComponent>();
final auth = ecs.watch<AuthStateComponent>();
return Column(
children: [
Text('Welcome ${user.value.name}'),
Text('Status: ${auth.value}'),
],
);
}
}
ECSBuilder
Functional approach for simple reactive widgets:
ECSBuilder<UserComponent>(
builder: (context, ecs) {
final user = ecs.watch<UserComponent>();
return Text('Hello ${user.value.name}');
},
)
ECSStatefulWidget
For complex widgets requiring local state:
class ComplexWidget extends ECSStatefulWidget {
@override
ECSState<ComplexWidget> createState() => _ComplexWidgetState();
}
class _ComplexWidgetState extends ECSState<ComplexWidget> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final data = ecs.watch<DataComponent>();
return YourComplexWidget(data: data.value);
}
}
Event Handling and Listeners #
Direct Event Listening
class NotificationWidget extends ECSWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ECSContext ecs) {
// Listen to specific entity
ecs.listen<ErrorComponent>((entity) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text(entity.value.message)),
);
});
return YourWidget();
}
}
Lifecycle Callbacks
class LifecycleWidget extends ECSWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ECSContext ecs) {
ecs.onEnter(() {
print('Widget entered ECS context');
});
ecs.onExit(() {
print('Widget exited ECS context');
});
return YourWidget();
}
}
System Types and Usage #
Reactive Systems
Respond to entity changes:
class ValidationSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
ValidationSystem();
@override
Set<Type> get reactsTo => {FormDataComponent};
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {ValidationStateComponent};
@override
bool get reactsIf => true; // Conditional reactions
@override
void react() {
final formData = getEntity<FormDataComponent>();
final validation = getEntity<ValidationStateComponent>();
// Validate form data
final isValid = validateForm(formData.value);
validation.update(isValid);
}
}
Execute Systems
Continuous frame-based execution:
class TimerSystem extends ExecuteSystem {
TimerSystem();
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {TimerComponent};
@override
executesIf => true; // Conditional executions
@override
void execute(Duration elapsed) {
final timer = getEntity<TimerComponent>();
timer.update(timer.value + elapsed.inMilliseconds);
}
}
Initialize/Teardown Systems
Setup and cleanup:
class DatabaseInitSystem extends InitializeSystem {
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {DatabaseComponent};
@override
void initialize() {
// Initialize database connection
print('Database initialized');
}
}
class DatabaseTeardownSystem extends TeardownSystem {
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {DatabaseComponent};
@override
void teardown() {
// Close database connection
print('Database closed');
}
}
📊 Real-World Example #
User Authentication System #
// Components
class AuthStateComponent extends ECSComponent<AuthState> {
AuthStateComponent() : super(AuthState.unauthenticated);
}
class LoginCredentialsComponent extends ECSComponent<LoginCredentials> {
LoginCredentialsComponent() : super(LoginCredentials.empty());
}
// Events
class LoginEvent extends ECSEvent {
LoginEvent();
}
class LogoutEvent extends ECSEvent {
LogoutEvent();
}
// Systems
class LoginUserReactiveSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
LoginUserReactiveSystem();
@override
Set<Type> get reactsTo => {LoginEvent};
@override
Set<Type> get interactsWith => {AuthStateComponent, LoginCredentialsComponent};
@override
void react() async {
final credentials = getEntity<LoginCredentialsComponent>();
final authState = getEntity<AuthStateComponent>();
try {
authState.update(AuthState.loading);
final user = await authenticateUser(credentials.value);
authState.update(AuthState.authenticated(user));
} catch (error) {
authState.update(AuthState.error(error.toString()));
}
}
}
// Feature
class UserAuthFeature extends ECSFeature {
UserAuthFeature() {
addEntity(AuthStateComponent());
addEntity(LoginCredentialsComponent());
addEntity(LoginEvent());
addEntity(LogoutEvent());
addSystem(LoginUserReactiveSystem());
addSystem(LogoutUserReactiveSystem());
}
}
// UI Integration
class LoginPage extends ECSWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ECSContext ecs) {
final authState = ecs.watch<AuthStateComponent>();
final credentials = ecs.get<LoginCredentialsComponent>();
final loginEvent = ecs.get<LoginEvent>();
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Login')),
body: Column(
children: [
if (authState.value.isLoading)
CircularProgressIndicator(),
TextField(
onChanged: (value) {
credentials.update(
credentials.value.copyWith(email: value)
);
},
decoration: InputDecoration(labelText: 'Email'),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: authState.value.isLoading ? null : loginEvent.trigger,
child: Text('Login'),
),
if (authState.value.hasError)
Text(
authState.value.error,
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red),
),
],
),
);
}
}
🧪 Testing #
Testing Components #
test('component notifies listeners on change', () {
final component = TestComponent();
bool notified = false;
component.addListener(TestListener(() => notified = true));
component.update(42);
expect(notified, isTrue);
expect(component.value, equals(42));
});
Testing Systems #
test('reactive system processes events', () {
final manager = ECSManager();
final feature = TestFeature();
final system = TestReactiveSystem();
feature.addEntity(TestEvent());
feature.addSystem(system);
manager.addFeature(feature);
manager.activate();
manager.getEntity<TestEvent>().trigger();
expect(system.reacted, isTrue);
});
Testing Features #
test('feature manages entities and systems', () {
final manager = ECSManager();
final feature = TestFeature();
final component = TestComponent();
final system = TestSystem();
feature.addEntity(component);
feature.addSystem(system);
manager.addFeature(feature);
manager.activate();
expect(feature.entities, contains(component));
expect(feature.reactiveSystems[TestEvent], contains(system));
});
Widget Testing #
testWidgets('ECS widget rebuilds on component change', (tester) async {
final feature = TestFeature();
await tester.pumpWidget(
ECSScope(
features: {feature},
child: TestECSWidget(),
),
);
final component = feature.getEntity<TestComponent>();
component.update(100);
await tester.pump();
expect(find.text('100'), findsOneWidget);
});
🎯 Best Practices #
1. Feature Organization #
// ✅ Good: Organized by domain
features/
user_auth_feature/
components/
events/
systems/
user_auth_feature.dart
// ❌ Avoid: Mixing concerns
features/
all_components.dart
all_events.dart
all_systems.dart
2. Component Design #
// ✅ Good: Immutable data structures
class UserComponent extends ECSComponent<User> {
UserComponent(super.value);
void updateName(String name) {
update(value.copyWith(name: name));
}
}
// ❌ Avoid: Mutable data
class UserComponent extends ECSComponent<User> {
UserComponent(super.value);
void updateName(String name) {
value.name = name; // Don't mutate directly
notifyListeners(); // Manual notification
}
}
3. System Granularity #
// ✅ Good: Single responsibility
class ValidateEmailSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
@override
Set<Type> get reactsTo => {EmailComponent};
@override
void react() {
// Only validate email
}
}
class ValidatePasswordSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
@override
Set<Type> get reactsTo => {PasswordComponent};
@override
void react() {
// Only validate password
}
}
// ❌ Avoid: Multiple responsibilities
class ValidateEverythingSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
@override
void react() {
// Validate email, password, phone, etc.
}
}
4. Error Handling #
// ✅ Good: Proper error handling
class LoginSystem extends ReactiveSystem {
@override
void react() async {
try {
final result = await authService.login();
authState.update(AuthState.authenticated(result));
} catch (error) {
errorState.update(ErrorState.fromException(error));
}
}
}
Development Setup #
-
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/FlameOfUdun/flutter_event_component_system.git cd flutter_event_component_system -
Install dependencies
flutter pub get -
Run tests
flutter test -
Run example
cd example flutter run
Code Style #
This project follows the Dart Style Guide and uses flutter_lints for code analysis.
📄 License #
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.
Copyright 2025 Ehsan Rashidi
🙏 Acknowledgments #
- Inspired by the Entity-Component-System pattern from game development
- Built for the Flutter community with ❤️
📞 Support #
- Issues: GitHub Issues
- Discussions: GitHub Discussions
Made with ❤️ by FlameOfUdun



