flex_seed_scheme 2.0.0  flex_seed_scheme: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
flex_seed_scheme: ^2.0.0 copied to clipboard
A more flexible and powerful version of Flutter's ColorScheme.fromSeed. Use multiple seed colors, custom chroma and tone mapping.
FlexSeedScheme (FSS) #
A more flexible and powerful version of Flutter's ColorScheme.fromSeed.
Use this package like ColorScheme.fromSeed with the following additional capabilities:
- Use separate seed key colors to generate seed-based tonal palettes for primary and optionally secondary, tertiary as well as error, neutral and neutral variant colors in
ColorScheme. - Change the chroma limits and values used in the Material-3 default strategy for tonal palette generation in the new Google HCT (Hue-Chroma-Tone) color space.
- Get access to new Material-3 design
ColorSchemevariants likefidelityandmonochromethat do not yet exist in Flutter SDK v3.22, but will arrive in later versions. - Change which tones in the generated core tonal palettes are used by which
ColorSchemecolor. - Use
FlexPaletteType.extended, that gives access to all the new tones that are used in revised Material-3 design for surfaces and fixed main color. The new tones are used and supported by the standardColorSchemein Flutter 3.22 and later. It is recommended to useFlexPaletteType.extendedif creating new customFlexTones. In the package version 2.0.0 and later,FlexPaletteType.extendedis the default palette type. The older palette typeFlexPaletteType.commonis available for backwards compatibility, but should be avoided in Flutter 3.22 and later.
Getting Started #
Add the flex_seed_scheme package to pubspec.yaml:
dart pub add flex_seed_scheme or flutter pub add flex_seed_scheme
Usage #
Import the package to use it:
import 'package:flex_seed_scheme/flex_seed_scheme.dart';
Define seed key colors that will be used to compute your seed generated ColorScheme.
// Define your seed colors.
const Color primarySeedColor = Color(0xFF6750A4);
const Color secondarySeedColor = Color(0xFF3871BB);
const Color tertiarySeedColor = Color(0xFF6CA450);
With FlexSeedScheme you make a seed generated ColorScheme using SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds.
It works like ColorScheme.fromSeed, but instead of only accepting a single seed color, it can use
six key colors as seed colors. One for each main color (primary, secondary and tertiary) group
in ColorScheme. You can customize the error color, typically there is no need to do so, but
if your primary color is of a red hue, that conflicts with the error color, then adjusting the error
color is a possibility. You can also use custom key colors to seed generate the neutral and
neutral variant palettes, that are used to define all the surface and background colors in
ColorScheme. We recommend sticking to the default that uses primary key color's hue with very low
chroma.
Chroma limits that differ from Material 3 defaults for tonal palette generation, can also be
defined. Additionally, tone mapping, that defines which tone is used by what ColorScheme color,
can be customized. Both are done via FlexTones passed in to tones.
Typically, you should use the same key colors and tones setup to produce the ColorScheme for
light and dark theme mode. This guarantees that the light and dark theme use identical generated
tonal palettes, and only vary based on which tones are used for what color in light and dark mode.
This results in matching light and dark theme colors. This is just the norm though, feel free
to experiment.
// Make a light ColorScheme from the seeds.
final ColorScheme schemeLight = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
// Primary key color is required, like seed color ColorScheme.fromSeed.
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
// You can add optional own seeds for secondary and tertiary key colors.
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
// Tone chroma config and tone mapping is optional, if you do not add it
// you get the config matching Flutter's Material 3 ColorScheme.fromSeed.
tones: FlexTones.vivid(Brightness.light),
);
// Make a dark ColorScheme from the seeds.
final ColorScheme schemeDark = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.dark,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.vivid(Brightness.dark),
);
You can use separate key colors as seeds to generate the primary, secondary and tertiary tonal
palettes. If no key color for secondaryKey and/or tertiaryKey are provided, they use
primaryKey color as their seed color value.
If you only specify primaryKey color as seed, and no custom tones configuration, an identical
ColorScheme to ColorScheme.fromSeed is produced.
The default chroma limits in the HCT color space used for seed generated colors for secondary and
tertiary colors in ColorScheme.fromSeed have quite low chroma values. This makes the colors
fairly muted or pastel like. This is especially the case with secondary colors. This is by design
in the standard Material-3 color palette. You can tune this behavior by passing in a custom
FlexTones configuration to tones. There are pre-made configurations you can use, above
FlexTones.vivid was used. It is also easy to make custom configurations. Look in FlexTones
and use the pre-made definitions as inspiration for your own configs.
Using the above configuration, the following core palettes are generated, in order from top to bottom:
- Primary tonal palette
- Secondary tonal palette
- Tertiary tonal palette
- Error tonal palette
- Neutral tonal palette
- Neutral variant tonal palette
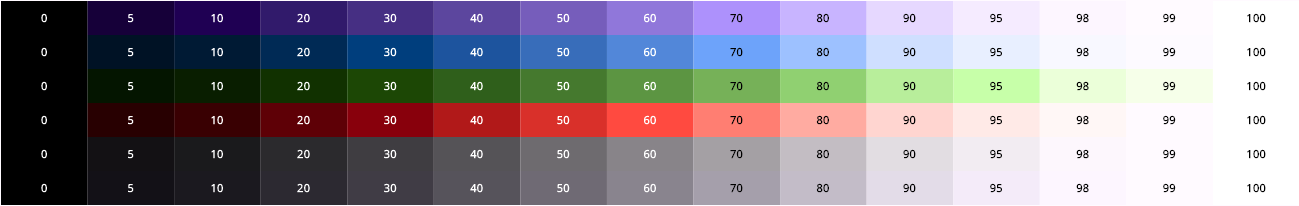
The color tones in the above palettes are then mapped to ColorScheme colors. Mapping is
different for light and dark theme mode to create a color scheme with suitable contrast.
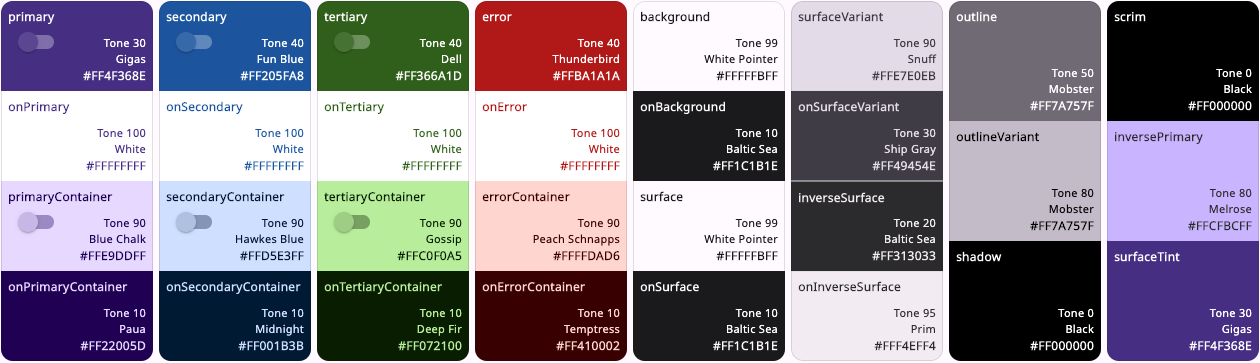
With the example FlexTones.vivid setup used in tones, the light ColorScheme is mapped as
shown below:
And the dark ColorScheme becomes:
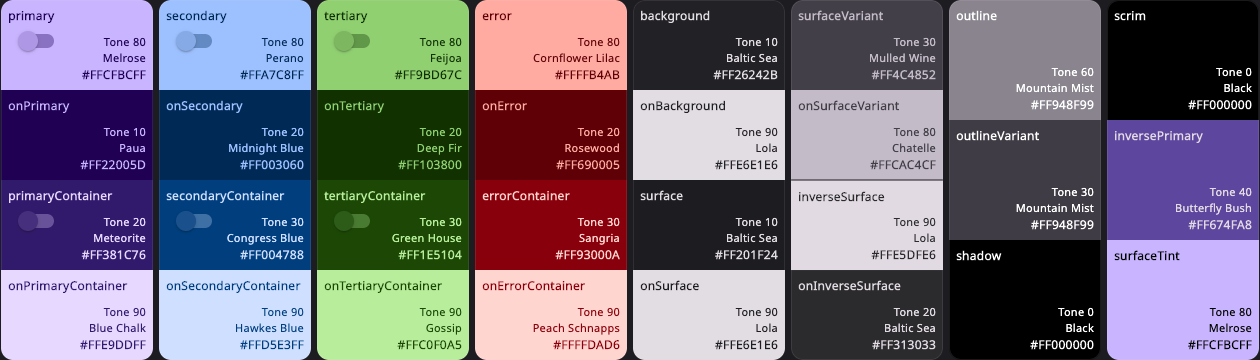
We can, for example, see that in light mode, the primary tone 30, is assigned to ColorScheme.primary
color and tone 90 to primaryContainer. In dark mode they get tones 80 and 20. Similar assignments
are repeated for secondary, tertiary, error colors and all the surface and background colors.
It is this mapping that FlexTones gives you control over.
Variants #
If you want to access the ColorScheme variants that Flutter SDK will provide in a future version, most likely in the next stable version after Flutter 3.22, then use SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds with the variant property of enum type FlexSchemeVariant.
If the variant FlexSchemeVariant style is one that is also provided by Flutter SDK, it has FlexSchemeVariant property isFlutterScheme set to true. In that case, all other key colors except primaryKey are ignored. This is because the Flutter SDK ColorScheme variant system only supports one seed color. The FlexSchemeVariant also include the predefined FlexTone based variants. You can use the variant option as a way to select ColorScheme seed generation variant that is based on both new (coming) Flutter SDK options and the FlexSeedScheme predefined FlexTones tones based seed generation options.
// Make a light ColorScheme from a seeds using variant style fidelity.
// This is a variant that is not yet available in Flutter SDK, but will be after 3.22.x stable.
final ColorScheme schemeLight = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
variant: FlexSchemeVariant.fidelity,
);
// Make a dark ColorScheme from a seeds using variant style fidelity.
final ColorScheme schemeDark = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.dark,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
variant: FlexSchemeVariant.fidelity,
);
Define ThemeData #
In your MaterialApp you then define your light and dark mode themes using the seed
generated ColorSchemes just as you would with any other ColorScheme. For example:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds Demo',
themeMode: ThemeMode.system,
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: schemeLight,
useMaterial3: true,
),
darkTheme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: schemeDark,
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: HomePage(),
);
}
Override Color Values #
All colors in the seed produced ColorScheme can be overridden by providing each ColorScheme
color property in SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds a given color value. This feature is equivalent to
ColorScheme.fromSeed.
This is typically used to assign a given color value to primary color, which is often used as app
brand color. When the brand color is used as primaryKey seed color, it typically does
not end up as the primary color in the seed generated ColorScheme. Having a given brand color as
primary color is often desired. To get the seed color as your primary brand color, assign the
color used as primaryKey to primary color as well.
// Make a light ColorScheme from the seeds.
final ColorScheme schemeLight = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
// Use a "brand" seed color as primary color in the result.
primary: primarySeedColor,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
//
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.vivid(Brightness.light),
);
This strategy works well for the light mode ColorScheme, since the prominent brand color a company
has defined is typically intended to be printed on white paper. If you have secondary brand colors
that are to be used, using them as seeds for secondaryKey and tertiaryKey will work too.
How well they will fit and match the Material 3 color system, if assigned to
secondary and tertiary directly as colors in SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds, will vary depending
on what colors they are.
If your brand color(s) for light mode are light, so that they require dark text for good contrast,
instead of light or white text, you will also have to override the contrast colors for them if you
overrode them by giving the seed colors to primary, secondary and tertairy. You then have to
manually also assign suitable contrast colors to onPrimary, onSecondary and onTertairy.
Companies rarely have brand colors suited for good contrast in dark theme mode. In that case
prefer only using the same light mode brand colors as key colors to seed the dark mode
ColorScheme. If they do have dark mode specifications, and the colors are of same hue as
light mode, consider still using the light mode colors as the seed source, and only applying the
appropriate dark mode colors to primary, secondary and tertiary as needed.
If there is a spec that calls for completely different main colors in dark mode, with different
hues, then seeding from them and also setting primary, secondary and tertiary to these
color values is appropriate.
ColorScheme Generation Strategy #
In the above example, we used a predefined tone mapping and chroma setup ColorScheme generation strategy
called FlexTones.vivid. There are currently eleven predefined configurations available:
FlexTones.material, default and same as Flutter SDK M3 setup in Flutter 3.22.0 and later.FlexTones.material3Legacy, same as Flutter SDK M3 default setup in Flutter before 3.22.0.FlexTones.soft, softer and earthier tones than M3 FlexTones.material.FlexTones.vivid, more vivid colors, uses chroma as defined by each given key color.FlexTones.vividSurfaces, likevivid, but with more color tint in surfaces and backgrounds.FlexTones.highContrast, can be used for more color-accessible themes.FlexTones.ultraContrast, for a very high-contrast theme version.FlexTones.jolly, for a more "jolly" and colorful theme.FlexTones.vividBackground, likevividSurfaces, but tone mapping forsurfaceandbackgroundare swapped.FlexTones.oneHue, a balanced chromatic setup. It is called oneHue because When only primary color is used as seed, it does not rotate its hue value to make a computed hue for tertiary tonal palettes, but uses the same hue. This makes it possible to make seed-generated color schemes from a single color. In such themes, all colors are based on the same hue, but using different chroma and tones.FlexTones.canyPop, A high contrast color scheme, useful for accessible themes, with colors that pop like candy. Keeps the background and surface white in light mode, and only a slight tint in dark mode. Neutrals have very low chroma.FlexTones.chroma, use it to create a color scheme that follows chroma of each used seed color. Useful for manual control of pop or low chromacity. It uses low surface tint and neutrals with medium chroma.
You can also define custom tones mapping and chroma limitation setups with FlexTones. Prefer using
the FlexTones.light and FlexTones.dark constructors as base for custom definitions. By using
them, you only need to override defaults that you want to change.
// Example definition of light custom tones config.
const FlexTones myLightTones = FlexTones.light(
primaryTone: 30, // Default is 40.
onPrimaryTone: 96, // Default is 100
onSecondaryTone: 96, // Default is 100
onTertiaryTone: 96, // Default is 100
onErrorTone: 96, // Default is 100
primaryMinChroma: 55, // Default is 36
secondaryChroma: 25, // Default is 16
tertiaryChroma: 40, // Default is 24
neutralChroma: 5, // Default is 6, avoid very high values in light mode.
neutralVariantChroma: 10, // Default is 8
paletteType: FlexPaletteType.extended, // Use extended palette type
);
// Example definition of dark custom tones config.
const FlexTones myDarkTones = FlexTones.dark(
primaryTone: 70, // Default is 80.
onPrimaryTone: 6, // Default is 20
onSecondaryTone: 6, // Default is 20
onTertiaryTone: 6, // Default is 20
onErrorTone: 6, // Default is 20
primaryMinChroma: 55, // Default is 36
secondaryChroma: 25, // Default is 16
tertiaryChroma: 40, // Default is 24
neutralChroma: 7, // Default is 6, you can go higher in dark mode than light.
neutralVariantChroma: 14, // Default is 8
paletteType: FlexPaletteType.extended, // Use extended palette type
);
Extended Palette #
By using paletteType with value FlexPaletteType.extended, you can create seed generated ColorSchemes that use and access new color tones that exists in the late 2022 revised ColorScheme for surface colors and even more colors for fixed and fixedDim main colors that arrived in the Material-3 design during later half of 2023.
The ColorScheme colors that use these new tones are now finally also available in Flutter 3.22 or later. For more information and the latest updates, see Material-3 color-roles specification.
The updated Material-3 color system adds tones [4, 6, 12, 17, 22, 24], they are used for new dark mode surfaces in revised Material-3 dark surface colors. Likewise, the added tones [87, 92, 94, 96, 98] are for light mode surfaces in the updated Material-3 color system. By default paletteType of FlexTones.extended is now used to enable support for the tones in the updated specification and also adding three more custom tone [2, 5, 97]. The paletteType with value FlexPaletteType.extended is now default, it produces 27 tones [0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 17, 20, 22, 24, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 87, 90, 92, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100].
To use the older classic setup you can still use FlexTones.common. It produces the legacy M3 tones with its own two additions [5] and [98] resulting in 15 tones [0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 95, 98, 99, 100]. Flutter versions before 3.22 do not yet use these new tones in its standard ColorScheme.
For backwards compatibility, when using type FlexPaletteType.common the chroma of high tones, meaning higher or equal to 90, are limited to maximum chroma of 40. This keeps the chromacity of tones 90 to 100 lower than or equal to 40. If the source seed color has higher chromacity than 40, there may be a sudden jump in chroma reduction at tone 90. This is the standard behavior for the original Material-3 tonal palette computation. The FlexPaletteType.common type is intended to be used when there is a need to follow the M3's original palette design.
When using the FlexPaletteType.extended type tones, there are not only new tones, but the chroma limit of tones >= 90 is also removed. This increases fidelity of higher tone when high chromacity is used.
Accessibility #
You can use FlexTones to create a seed generated ColorScheme, that is based on same colors
as your standard theme's light and dark scheme colors, but uses a chroma configuration and tone
mapping setup that increases contrast further from standard light and dark theme setup.
There are two high contrast FlexTones configuration pre-made for this. They are called
FlexTones.highContrast, a colorful high-contrast version, and FlexTones.ultraContrast, a less
colorful version, a more dark on light in light theme mode, and light on dark in dark mode.
The FlexTones.canyPop also creates very high contrast theme, with colors that are vibrant and pop, it can also be used for high contrast themes. Depending on seed color input values and its chroma value, FlexTones.chroma can also be very vibrant and high contrast. It can also be monochromatic, i.e. gray-scale if input seed colors have chroma value zero.
// Make a high contrast light ColorScheme from the seeds.
final ColorScheme schemeLightHc = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.highContrast(Brightness.light),
);
// Make a ultra contrast dark ColorScheme from the seeds.
final ColorScheme schemeDarkHc = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.dark,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.ultraContrast(Brightness.dark),
);
If you then define equivalent ThemeData based on those schemes as your standard MaterialApp,
theme and darkTheme definitions, but assign them to highContrastTheme and
highContrastDarkTheme, you get more accessible themed colors that are based on same colors,
but with higher contrast, that are activated when users select high-contrast theme in device
accessibility system settings. Changing to accessibility theme based on device system setting
automatically, by using theme data defined on MaterialApp properties highContrastTheme and
highContrastDarkTheme, is only supported on iOS devices in the current version of Flutter SDK.
For other platforms, you need to use a user setting and toggle themes based on it.
// Define accessibility high contrast versions using same color base.
//
highContrastTheme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: schemeLightHc,
useMaterial3: true,
),
highContrastDarkTheme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: schemeDarkHc,
useMaterial3: true,
),
Black and White Contrast #
Another way to modify FlexTones configurations for contrast and accessibility, is by forcing all
main contrasting on colors and all surfaces on colors to only use black and white contrasting colors.
If we remove the Material-3 guide used color system's colored contrasting colors, we can improve
color accessibility and contrast on any FlexTones configuration.
Note
If you use the variant property to the seed generated ColorScheme you cannot
use the below presented tones modifiers, as they are modifiers used only on the input FlexTones configurations provided in tones. In the package example app you can find a demonstration of how to instead use tones as input for FlexTones based variants and variant being effective only when using variants that are Flutter SDK based.
We can do this with the FlexTones modifying methods onMainsUseBW(), for main on colors and
with onSurfacesUseBW() for the surface on colors. These modifiers automatically make their
corresponding contrasting colors black or white, depending on if the source color is light or dark.
The main colors are:
primary,primaryContainersecondary,secondaryContainertertiary,tertiaryContainererror,errorContainer
The on colors made black or white by onMainsUseBW() are:
onPrimary,onPrimaryContaineronPrimaryFixed,onPrimaryFixedVariantonSecondary,onSecondaryContaineronSecondaryFixed,onSecondaryFixedVariantonTertiary,onTertiaryContaineronTertiaryFixed,onTertiaryFixedVariantonError,onErrorContainer
The surface on colors made black or white by onSurfacesUseBW() are:
onBackground(deprecated)onSurfaceonSurfaceVariantonInverseSurface
The surface colors made black by surfacesUseBW() are:
background(deprecated in Flutter 3.22)surface
Here is a usage example, using both these modifiers. You cna use them individually too, and you don't have to use them in both light and dark mode.
// Make a Material 3 seeded light ColorScheme,
// but with always black and white contrasting onColors.
final ColorScheme schemeLightOnBW = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.material(Brightness.light)
.onMainsUseBW()
.onSurfacesUseBW(),
);
// Make a Vivid dark ColorScheme,
// but with always black and white contrasting onColors.
final ColorScheme schemeDarkOnBW = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.dark,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.vivid(Brightness.dark)
.onMainsUseBW()
.onSurfacesUseBW(),
);
Another FlexTones modifier is surfacesUseBW(). This modifier will make the surface and
background colors plain white in light mode and true black in dark mode.
This modifier can be used for great effect in light mode, as you can remove the colored
background surfaces from any of the FlexTones seeding strategies. Some designs may prefer
plain white, for backgrounds in light mode, for a more platform-agnostic design.
In dark mode surfacesUseBW() can be used create seeded color schemes with true black
background and surface colors, but you may prefer to keep the primary seed color based
slightly primary color tinted backgrounds in dark mode.
// Make a Material 3 seeded light ColorScheme, but with always
// black and white contrasting onColors and ensure that background
// and surface colors are always white.
final ColorScheme schemeLightOnBW = SeedColorScheme.fromSeeds(
brightness: Brightness.light,
primaryKey: primarySeedColor,
secondaryKey: secondarySeedColor,
tertiaryKey: tertiarySeedColor,
tones: FlexTones.material(Brightness.light)
.onMainsUseBW()
.onSurfacesUseBW()
.surfacesUseBW(), // Make light surface and background white
);
Example Application #
The included example application uses above color seeding and custom tone mapping. You can also choose any of the built-in pre-configured tone mappings as used seeding strategy. When you select seeding strategy, basic info about is displayed.
You can try a web version of this example for version 2 of FSS here in V2 demo. The older demo for version 1 of FSS is still available here in V1 demo.
You can choose to use secondary and primary seed colors as additional keys to generate the color schemes. You can also toggle keeping contrasting onColors black & white, or force background and surface colors to be white in light mode and true black in dark mode. You can change the seed colors with a color picker by tapping on the seed colors. You can also modify the default error seed color.
With the app we can compare results from FlexSeedScheme.fromSeeds, to using the single seed color
based ColorScheme.fromSeed seed generated default Material-3 ColorScheme available in Flutter.
Both use the same key color as their primary seed color, but ColorScheme.fromSeed can only use it as its single seed color, we cannot use hues from our secondary and tertiary key colors for the seed produced tonal palettes, nor change how and its tones are mapped to the generated ColorScheme.
With ColorScheme.fromSeed we can also not customize the colorfulness (chromacity) of its seed generated secondary and tertiary colors. Like we can with FlexSeedScheme.fromSeeds, demonstrated here by choosing different FlexTones configurations. The tonal palette tones to ColorScheme color mappings can also not be modified, like we can do with FlexSeedScheme.fromSeeds and its different mappings in each FlexTones seeding strategy.
The seed generated tonal palettes are also displayed in the example application. You can toggle it to show the default FlexPaletteType.common or the FlexPaletteType.extended version. Only FlexTones.candyPop and chroma, as well as the custom mappings used in the example custom FlexTones` in the example app, use the extended tones. More schemes might use the extended tones later when Flutter SDK also starts using them.
Scheme Generation Strategies #
Below some example color schemes made with FlexSeedScheme using SeedColorScheme.fromSeed using different FlexTones seed generation strategies.
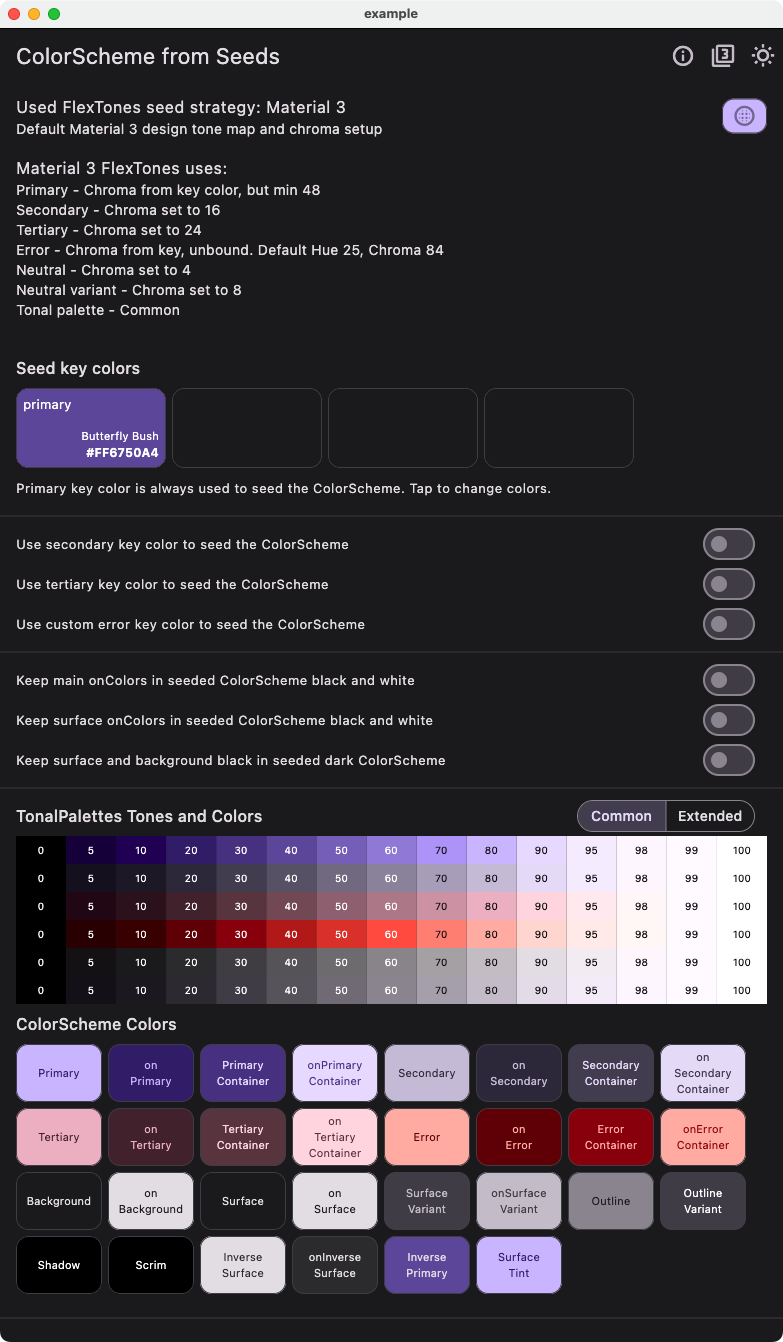
Default Strategy Material-3 Theme #
This example shows how to recreate the default Material-3 theme using a single primary seed color and the default tones strategy FlexTones.material. This is no different from using Flutter's default ColorScheme.fromSeed, it is shown here for comparison. In the package, there are also tests to ensure that this strategy produces the same result.
| Light from single seed - Material 3 tones | Dark from single seed - Material 3 tones |
|---|---|
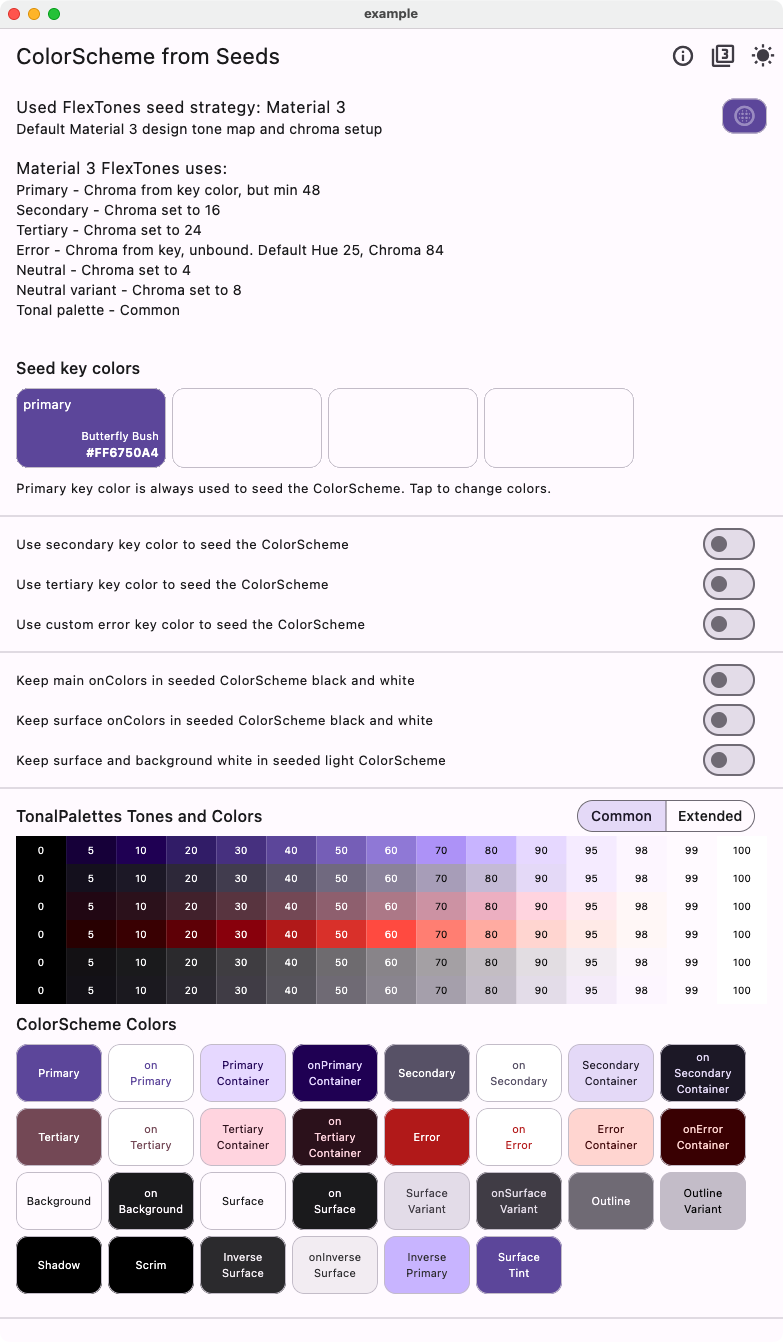 |
 |
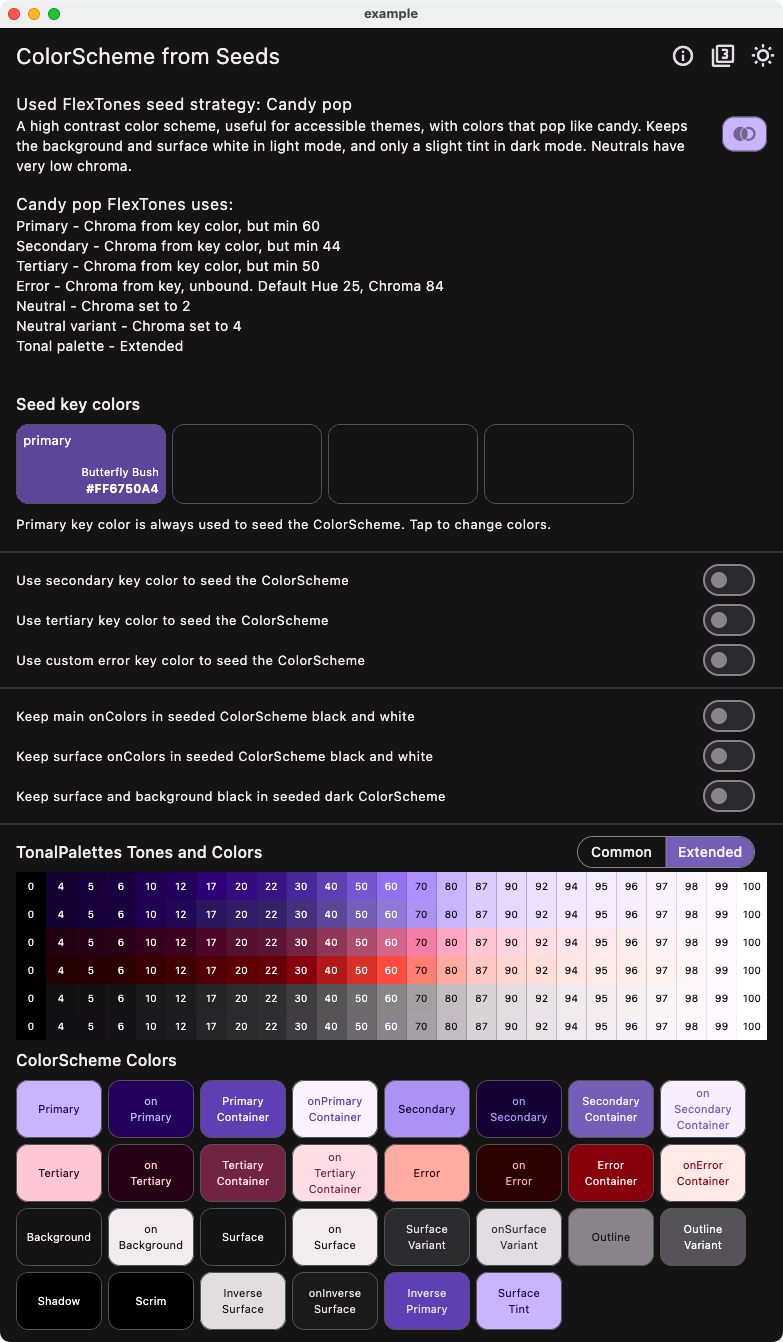
Candy Pop Strategy with One Seed Color #
This example using tones strategy FlexTones.candyPop shows the difference when using the same single seed color, as in the above case with the default Material-3 seed strategy. We can observe that the colors are brighter and more candy like.
| Light from single seed - Candy pop tones | Dark from single seed - Candy pop tones |
|---|---|
 |
 |
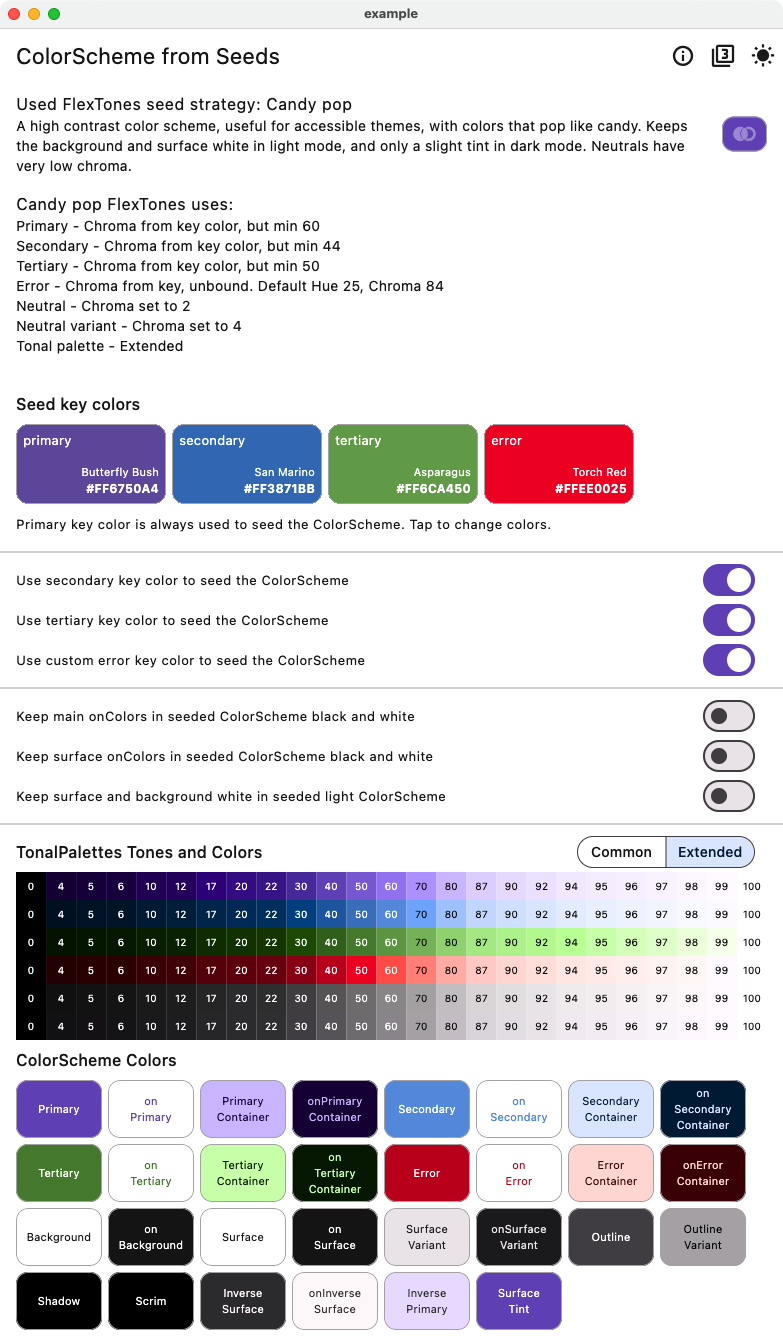
Candy Pop Strategy with Four Seed Colors #
This example shows how to use four seeds colors, including a custom error seed color, using the same CandyPop seed strategy.
| Light from four seeds - Candy pop tones | Dark from four seeds - Candy pop tones |
|---|---|
 |
 |
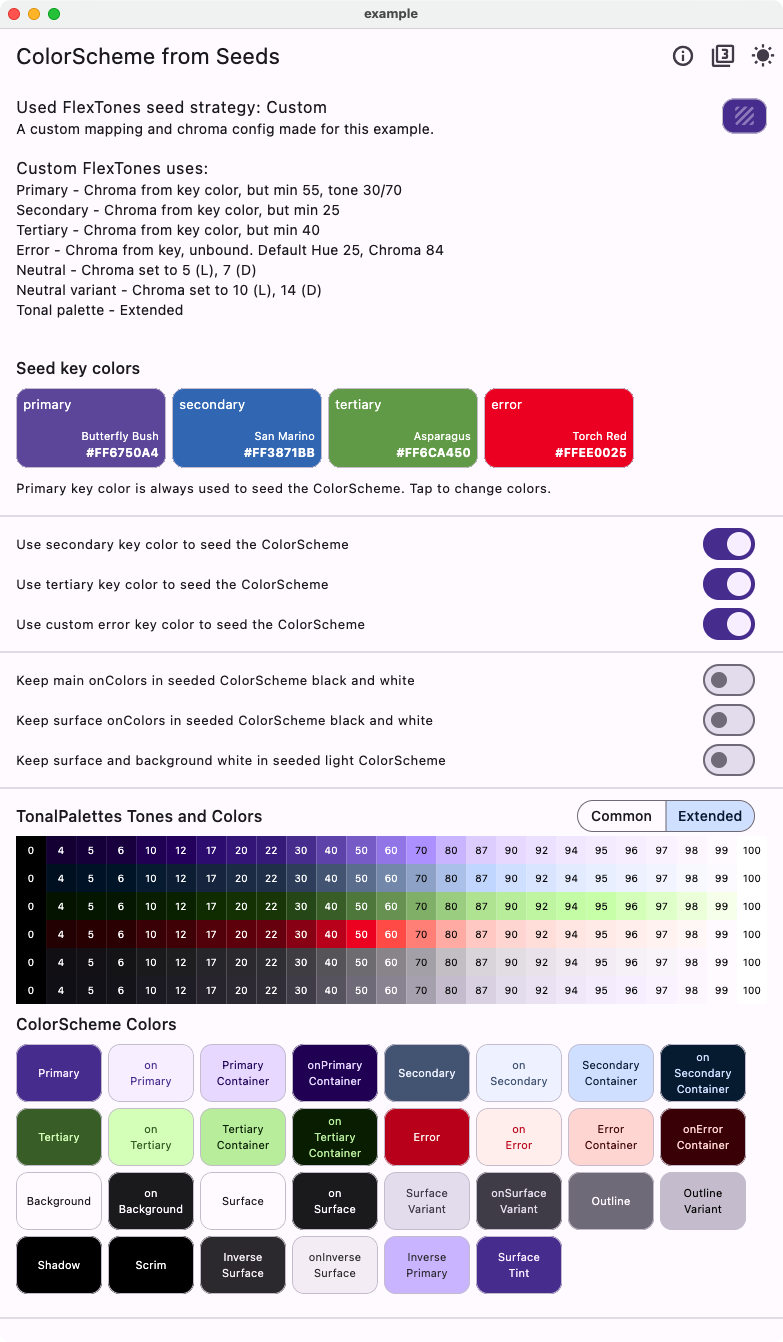
Custom Strategy #
This shows the light and dark version of the tones strategy with the custom FlexTones we defined earlier in myLightTones and myDarkTones in the example.
| Light from seeds - Custom tones | Dark from seeds - Custom tones |
|---|---|
 |
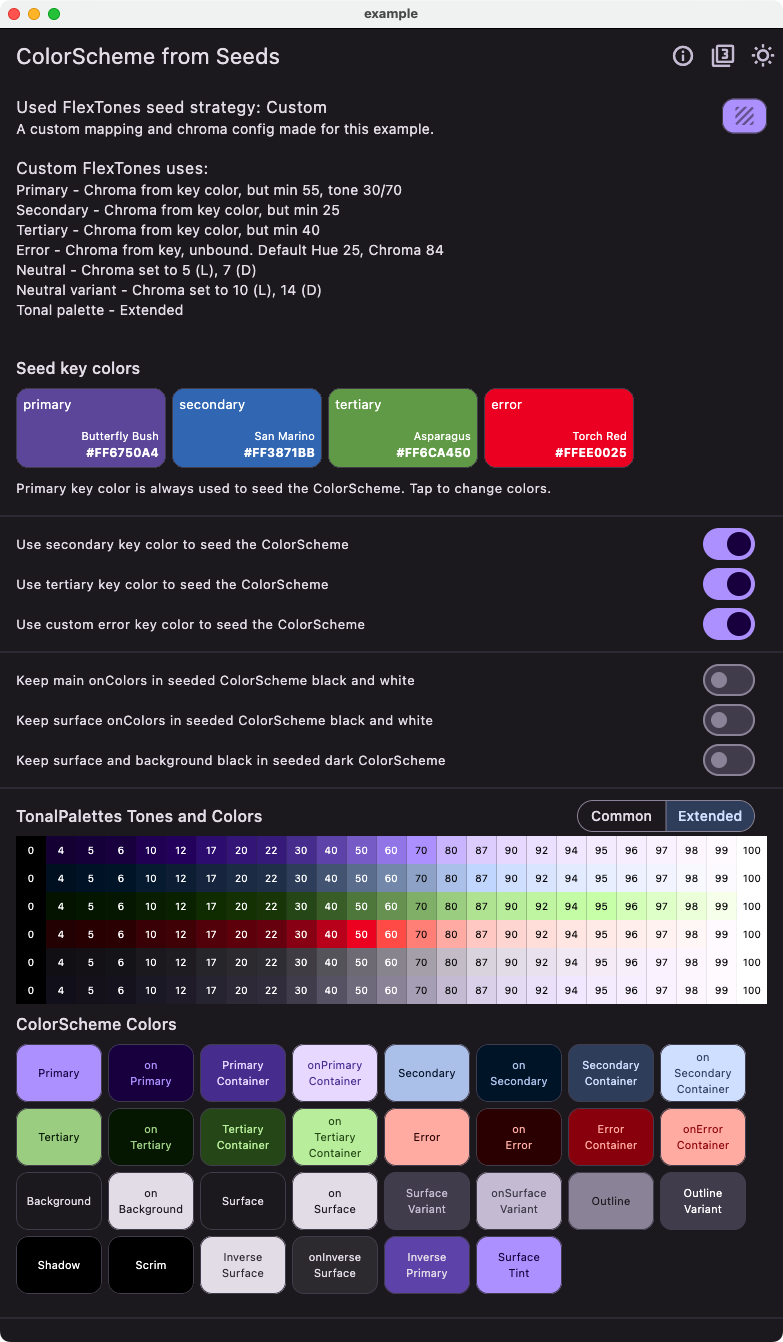 |
Comparing Styles #
Below an example of Material widgets using the theme created using the tones strategy with the custom FlexTones we defined.
| Light from seeds - Custom tones Widget | Dark from seeds - Custom tones Widget |
|---|---|
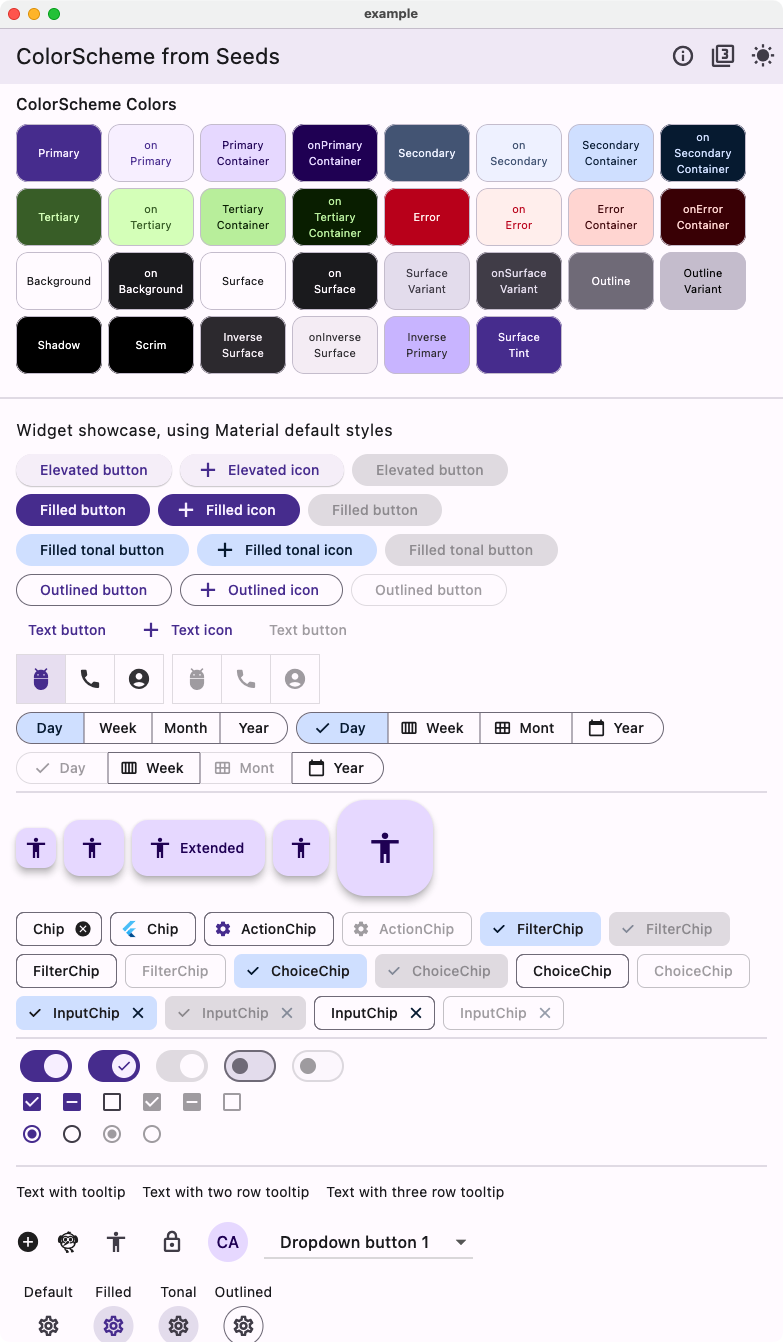 |
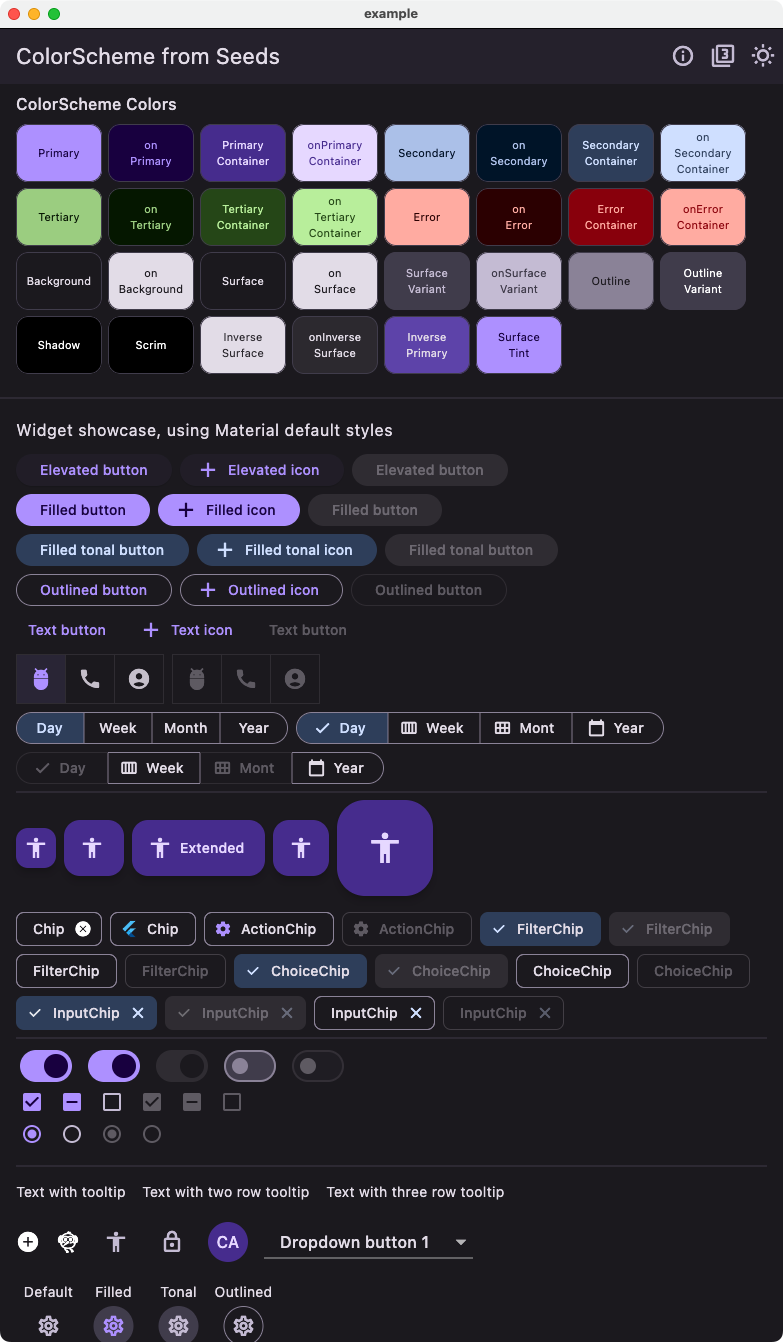 |
Here we can compare it to an example of Material widgets using the theme created using the earlier above tones strategy FlexTones.candyPop with four seed colors.
| Light from four seeds - Candy pop tones Widgets | Dark from four seeds - Candy pop tones Widget |
|---|---|
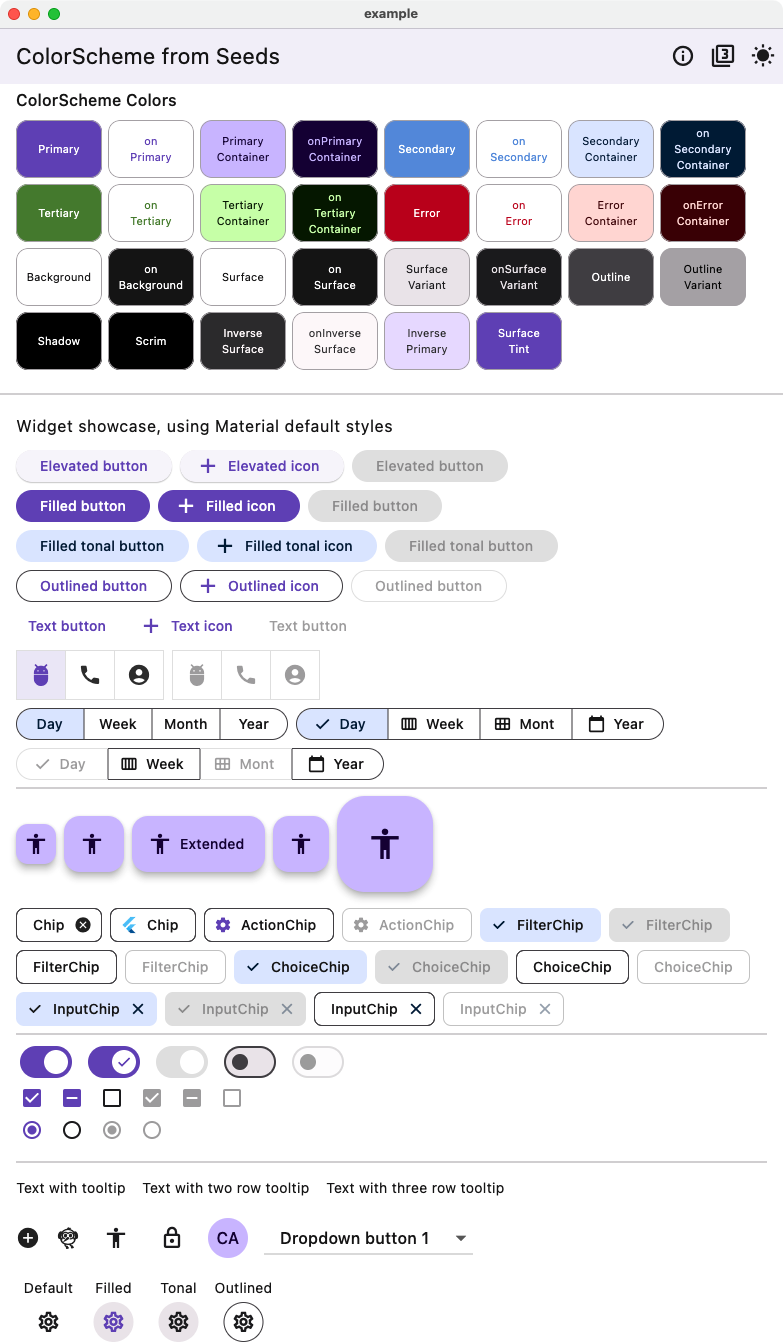 |
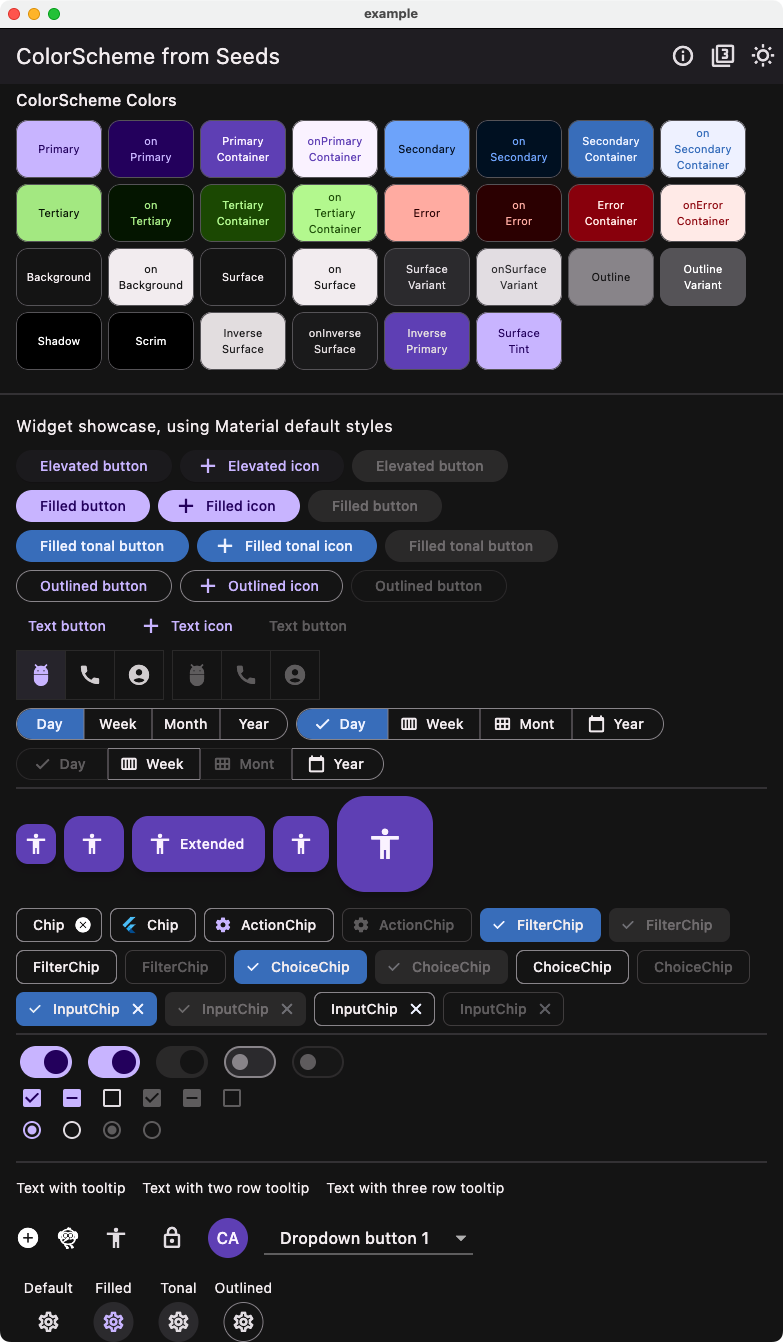 |
Package Background #
This package was extracted from the customizable color scheme seeding engine in the FlexColorScheme package to its own package.
This allows developers to use the same customizable ColorScheme seeding algorithms used by
FlexColorScheme, without using the FlexColorScheme package.
Starting with FlexColorScheme version 6 and later, it depends on this package instead.
If you use FlexColorScheme version 6 or later, you do not need to add FlexSeedScheme to use its features, FlexColorScheme exports its API as well. If you use FlexColorScheme you typically do not even need to use FlexSeedScheme directly, its usage is baked in and used based on how you configure FlexColorScheme.


