GeofenceEvent class
Event-object provided to BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((GeofenceEvent event) {
print('[geofence] ${event.identifier}, ${event.action}');
});
Geofencing Guide
The Background Geolocation SDK implements the native iOS and Android Geofencing APIs.
ℹ️ Note:
- Native iOS & Android API support only circular geofences, however the plugin does implement a custom mechanism for handling Polygon Geofences; see Geofence.vertices.
- The minimum reliable Geofence.radius is
200meters. - The native geofencing API for both iOS and Android require the user authorize GeoConfig.locationAuthorizationRequest
Always—When in Usewill not work.
Adding Geofences
Adding a single geofence with BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence(Geofence(
identifier: "Home",
radius: 200,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
notifyOnExit: true,
extras: {
"route_id": 1234
}
)).then((bool success) {
print('[addGeofence] success');
}).catchError((dynamic error) {
print('[addGeofence] FAILURE: $error');
});
Adding multiple geofences with BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofences.
Example
await BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofences([Geofence(
identifier: "Home",
radius: 200,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
), Geofence(
identifier: "Work",
radius: 200,
latitude: 45.61921927,
longitude: -73.71678582,
notifyOnEntry: true
)]);
print('[addGeofences] success');
ℹ️ Note: Adding a geofence having an Geofence.identifier which already exists within the SDK's geofence database will cause the previous record to be destroyed and the new one inserted.
Listening for Geofence Events
Listen to geofence events with BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence.
Example
// Listen for geofence events.
BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((GeofenceEvent event) {
print('[geofence] ${event.identifier}, ${event.action}');
});
Polygon Geofencing
The Background Geolocation SDK supports Polygon Geofences (Geofences of any shape). See API docs Geofence.vertices. ℹ️ Polygon Geofencing is sold as a separate add-on (fully functional in DEBUG builds).

Infinite Geofencing
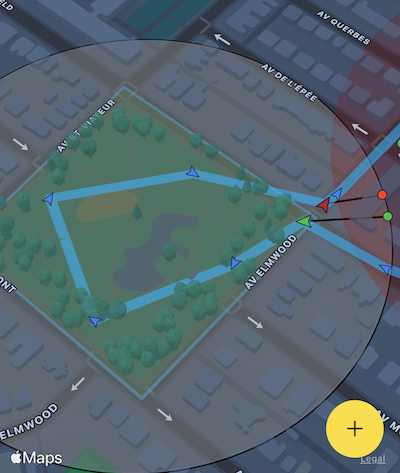
The Background Geolocation SDK contains unique and powerful Geofencing features that allow you to monitor any number of circular geofences you wish (thousands even), in spite of limits imposed by the native platform APIs (20 for iOS; 100 for Android).
The SDK achieves this by storing your geofences in its database, using a geospatial query to determine those geofences in proximity (GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius), activating only those geofences closest to the device's current location (according the limit imposed by the corresponding platform).
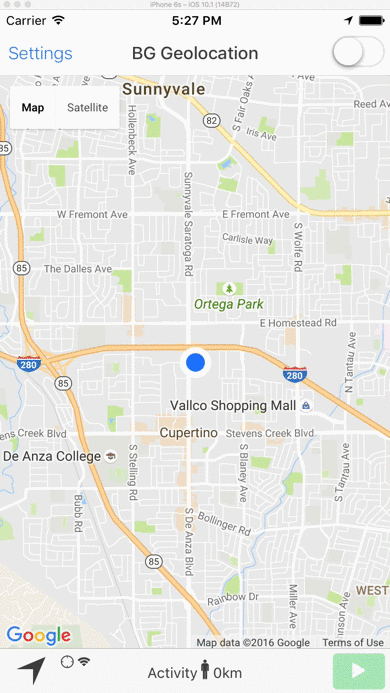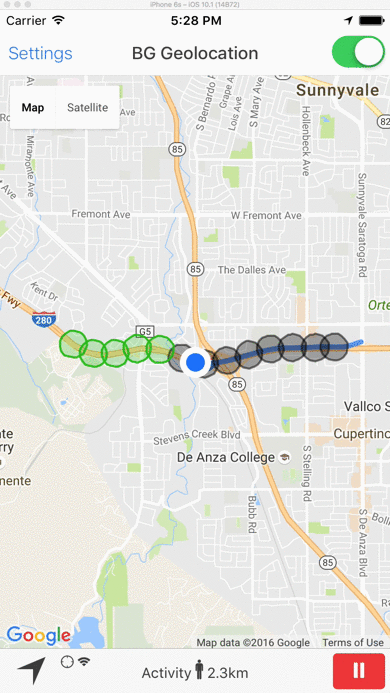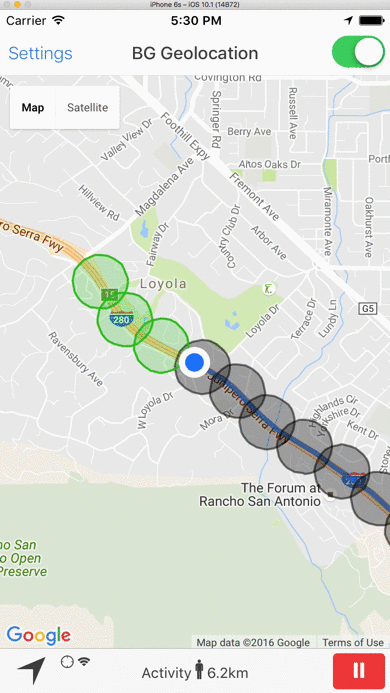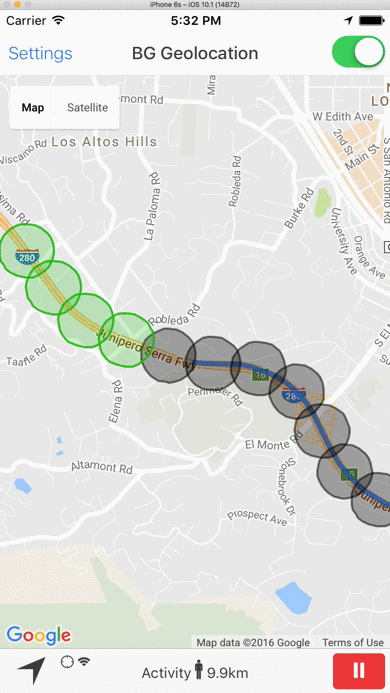
- When the device is determined to be moving, the plugin periodically queries for geofences within the GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius (eg. every minute) using the latest recorded location. This geospatial query is very fast, even with tens-of-thousands geofences in the database.
- The SDK enforces a minimum GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius of
1000meters. - In the following image, the green geofences within GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius are actively monitored. The grey geofences outside GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius still exist within the SDK's database but are not actively being monitored.

Listening for changes in the actively-monitored set-of-geofences.
As the SDK periodically queries for geofences within the GeoConfig.geofenceProximityRadius, you can listen for changes in the actively-monitored geofences using the event BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofencesChange. This event will let you know those geofences which have begun to be actively monitored (GeofencesChangeEvent.on) in addition to those which just ceased to be actively monitored (GeofencesChangeEvent.off).
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofencesChange((GeofencesChangeEvent event) {
// Create map circles
event.on.forEach((Geofence geofence) {
createGeofenceMarker(geofence)
});
// Remove map circles
event.off.forEach((String identifier) {
removeGeofenceMarker(identifier);
});
});
⚠️ Note:
- When all geofences have been removed, the GeofencesChangeEvent will provide empty lists for both GeofencesChangeEvent.on & GeofencesChangeEvent.off.
Removing Geofences
Once a geofence has been inserted into the SDK's database using BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence or BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofences, they will be monitored forever (as long as the plugin remains State.enabled == true). If you've configured AppConfig.stopOnTerminate false and AppConfig.startOnBoot true, geofences will continue to be monitored even if the application is terminated or device rebooted.
To cease monitoring a geofence or geofences, you must remove them from the SDK's database (or call BackgroundGeolocation.stop).
Removing a single geofence by Geofence.identifier:
BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofence('HOME').then((bool success) {
print('[removeGeofence] success');
});
Removing all geofences with BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofences:
BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofences().then((bool success) {
print('[removeGeofences] all geofences have been destroyed');
});
Querying Geofences
Use the method BackgroundGeolocation.geofences property to retrieve the entire Array of Geofence stored in the SDK's database:
List<Geofence> geofences = await BackgroundGeolocation.geofences;
print('[getGeofences: $geofences');
Or fetch a single geofence by Geofence.identifier with BackgroundGeolocation.getGeofence :
Geofence geofence = await BackgroundGeolocation.getGeofence("home");
print('[getGeofence] $geofence');
Monitoring only geofences
The BackgroundGeolocation SDK allows you to optionally monitor only geofences without constant location-tracking. To engage geofences-only mode, use the method BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences instead of BackgroundGeolocation.start.
Use option GeoConfig.geofenceModeHighAccuracy:true to improve the responsiveness of geofence events.
BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((GeofenceEvent event) {
print('[geofence]: ' + event.toString());
});
BackgroundGeolocation.ready(Config(
url: 'http://your.server.com/geofences',
autoSync: true,
geofenceModeHighAccuracy: true // <-- consumes more power; default is false.
)).then((State state) {
// engage geofences-only mode:
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();
});
Toggling between tracking-modes BackgroundGeolocation.start and BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences:
The SDK can easily be toggled between State.trackingMode simply by executing the corresponding BackgroundGeolocation.start or BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences methods.
// Listen to geofence events
BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((GeofenceEvent event) {
print('[geofence] ' + event.toString());
if (event.identifier == 'DANGER_ZONE') {
if (event.action == 'ENTER') {
// Entering the danger-zone, we want to aggressively track location.
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
} else if (event.action == 'EXIT') {
// Exiting the danger-zone, we resume geofences-only tracking.
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();
}
}
});
// Add a geofence.
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence(Geofence(
identifier: "DANGER_ZONE",
radius: 1000,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
notifyOnExit: true,
));
// Ready the plugin.
BackgroundGeolocation.ready(Config(
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
url: 'http://your.server.com/locations',
autoSync: true
)).then((State state) {
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();
});
Constructors
- GeofenceEvent(Map params)
Properties
- action ↔ String
-
The transition event that caused the geofence to fire (ENTER | EXIT | DWELL).
getter/setter pair
- extras ↔ Map?
-
Optional Geofence.extras
getter/setter pair
- geofence ↔ Geofence
-
The Geofence which fired this event.
getter/setter pair
- hashCode → int
-
The hash code for this object.
no setterinherited
- identifier ↔ String
-
Geofence.identifier of the Geofence which fired.
getter/setter pair
- location ↔ Location
-
The Location where this geofence triggered.
getter/setter pair
- runtimeType → Type
-
A representation of the runtime type of the object.
no setterinherited
- timestamp ↔ String
-
The device system time when the Geofence event was received by the OS. Note: this can differ from the timestamp of the triggering location responsible for the geofence (the triggering location can be from the past).
getter/setter pair
Methods
-
noSuchMethod(
Invocation invocation) → dynamic -
Invoked when a nonexistent method or property is accessed.
inherited
-
toString(
) → String -
String representation of
GeofenceEventforprintto logs.override
Operators
-
operator ==(
Object other) → bool -
The equality operator.
inherited