Align class
A widget that aligns its child within itself and optionally sizes itself based on the child's size.
For example, to align a box at the bottom right, you would pass this box a tight constraint that is bigger than the child's natural size, with an alignment of Alignment.bottomRight.
This widget will be as big as possible if its dimensions are constrained and widthFactor and heightFactor are null. If a dimension is unconstrained and the corresponding size factor is null then the widget will match its child's size in that dimension. If a size factor is non-null then the corresponding dimension of this widget will be the product of the child's dimension and the size factor. For example if widthFactor is 2.0 then the width of this widget will always be twice its child's width.
{@tool snippet} The Align widget in this example uses one of the defined constants from Alignment, Alignment.topRight. This places the FlutterLogo in the top right corner of the parent blue Container.
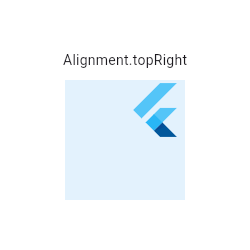
Center(
child: Container(
height: 120.0,
width: 120.0,
color: Colors.blue[50],
child: const Align(
alignment: Alignment.topRight,
child: FlutterLogo(
size: 60,
),
),
),
)
{@end-tool}
How it works
The alignment property describes a point in the child's coordinate system
and a different point in the coordinate system of this widget. The Align
widget positions the child such that both points are lined up on top of
each other.
{@tool snippet} The Alignment used in the following example defines two points:
- (0.2 * width of FlutterLogo/2 + width of FlutterLogo/2, 0.6 * height of FlutterLogo/2 + height of FlutterLogo/2) = (36.0, 48.0) in the coordinate system of the FlutterLogo.
- (0.2 * width of Align/2 + width of Align/2, 0.6 * height of Align/2 + height of Align/2) = (72.0, 96.0) in the coordinate system of the Align widget (blue area).
The Align widget positions the FlutterLogo such that the two points are on top of each other. In this example, the top left of the FlutterLogo will be placed at (72.0, 96.0) - (36.0, 48.0) = (36.0, 48.0) from the top left of the Align widget.

Center(
child: Container(
height: 120.0,
width: 120.0,
color: Colors.blue[50],
child: const Align(
alignment: Alignment(0.2, 0.6),
child: FlutterLogo(
size: 60,
),
),
),
)
{@end-tool}
{@tool snippet} The FractionalOffset used in the following example defines two points:
- (0.2 * width of FlutterLogo, 0.6 * height of FlutterLogo) = (12.0, 36.0) in the coordinate system of the FlutterLogo.
- (0.2 * width of Align, 0.6 * height of Align) = (24.0, 72.0) in the coordinate system of the Align widget (blue area).
The Align widget positions the FlutterLogo such that the two points are on top of each other. In this example, the top left of the FlutterLogo will be placed at (24.0, 72.0) - (12.0, 36.0) = (12.0, 36.0) from the top left of the Align widget.
The FractionalOffset class uses a coordinate system with an origin in the top-left corner of the Container in difference to the center-oriented system used in the example above with Alignment.

Center(
child: Container(
height: 120.0,
width: 120.0,
color: Colors.blue[50],
child: const Align(
alignment: FractionalOffset(0.2, 0.6),
child: FlutterLogo(
size: 60,
),
),
),
)
{@end-tool}
See also:
- AnimatedAlign, which animates changes in alignment smoothly over a given duration.
- CustomSingleChildLayout, which uses a delegate to control the layout of a single child.
- Center, which is the same as Align but with the alignment always set to Alignment.center.
- FractionallySizedBox, which sizes its child based on a fraction of its own size and positions the child according to an Alignment value.
- The catalog of layout widgets.
- Inheritance
- Implementers
Constructors
Properties
- alignment → AlignmentGeometry
-
How to align the child.
final
- child → Widget?
-
The widget below this widget in the tree.
final
- hashCode → int
-
The hash code for this object.
no setterinherited
- heightFactor → double?
-
If non-null, sets its height to the child's height multiplied by this factor.
final
- key → Key?
-
Controls how one widget replaces another widget in the tree.
finalinherited
- runtimeType → Type
-
A representation of the runtime type of the object.
no setterinherited
- widthFactor → double?
-
If non-null, sets its width to the child's width multiplied by this factor.
final
Methods
-
build(
BuildContext context) → Widget -
Describes the part of the user interface represented by this widget.
override
-
createElement(
) → StatelessElement -
Creates a StatelessElement to manage this widget's location in the tree.
inherited
-
debugDescribeChildren(
) → List< DiagnosticsNode> -
Returns a list of DiagnosticsNode objects describing this node's
children.
inherited
-
debugFillProperties(
DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) → void -
Add additional properties associated with the node.
inherited
-
noSuchMethod(
Invocation invocation) → dynamic -
Invoked when a nonexistent method or property is accessed.
inherited
-
toDiagnosticsNode(
{String? name, DiagnosticsTreeStyle? style}) → DiagnosticsNode -
Returns a debug representation of the object that is used by debugging
tools and by DiagnosticsNode.toStringDeep.
inherited
-
toString(
{DiagnosticLevel minLevel = DiagnosticLevel.info}) → String -
A string representation of this object.
inherited
-
toStringDeep(
{String prefixLineOne = '', String? prefixOtherLines, DiagnosticLevel minLevel = DiagnosticLevel.debug, int wrapWidth = 65}) → String -
Returns a string representation of this node and its descendants.
inherited
-
toStringShallow(
{String joiner = ', ', DiagnosticLevel minLevel = DiagnosticLevel.debug}) → String -
Returns a one-line detailed description of the object.
inherited
-
toStringShort(
) → String -
A short, textual description of this widget.
inherited
Operators
-
operator ==(
Object other) → bool -
The equality operator.
inherited