Tilde enables to easily build Flutter Single-Page Application (SPA) using Component and imperative programming model.

Features
- Simplifies Flutter model by combining "widgets" into easy-to-use "components".
- Handles app route management.
Component
Component is like a flutter StatefullWidget but without much complexity. It gives the ~ operator to get the widget (Widget = ~Component) which is the project name (Tilde). It exposes setState function to rebuild the widget.
Extension
Tilde gives you extension that allows the creation of a component for any variable.
dynamic.component<T>(Widget Function(BuildContext, XComponent<T>) builder)
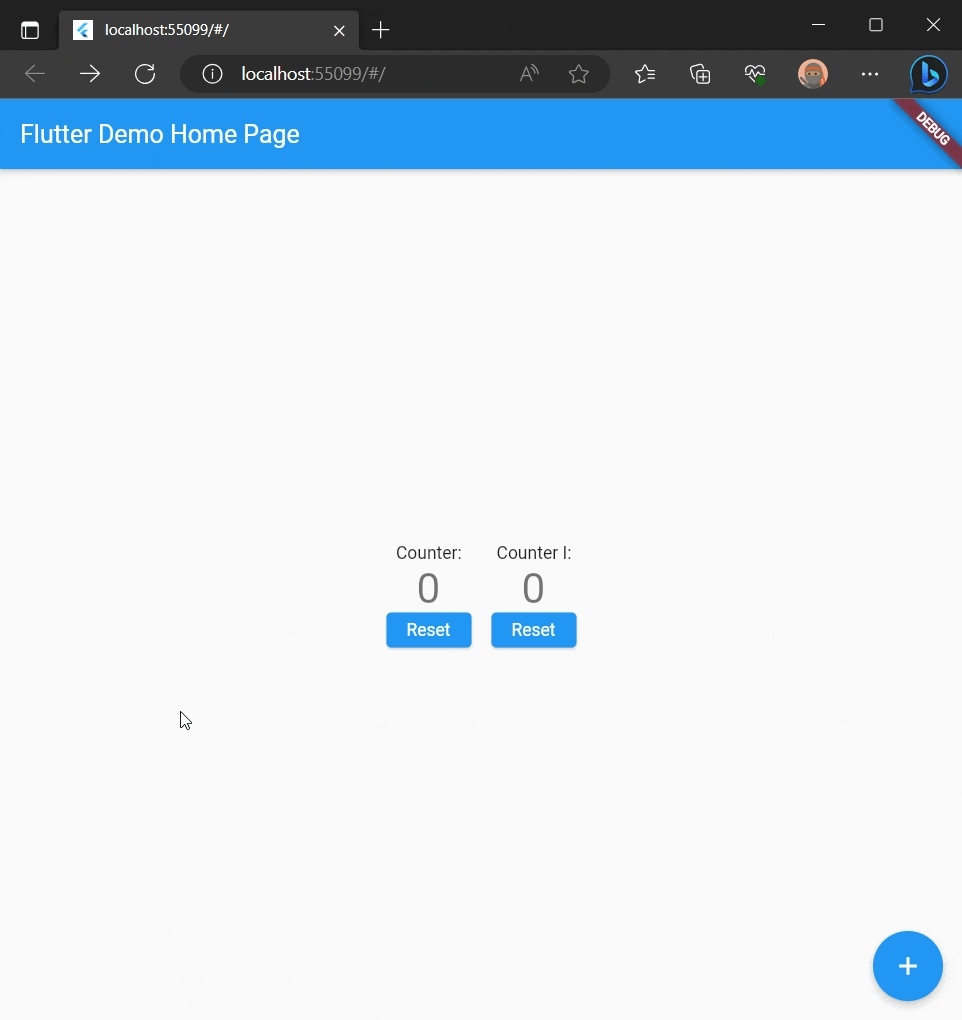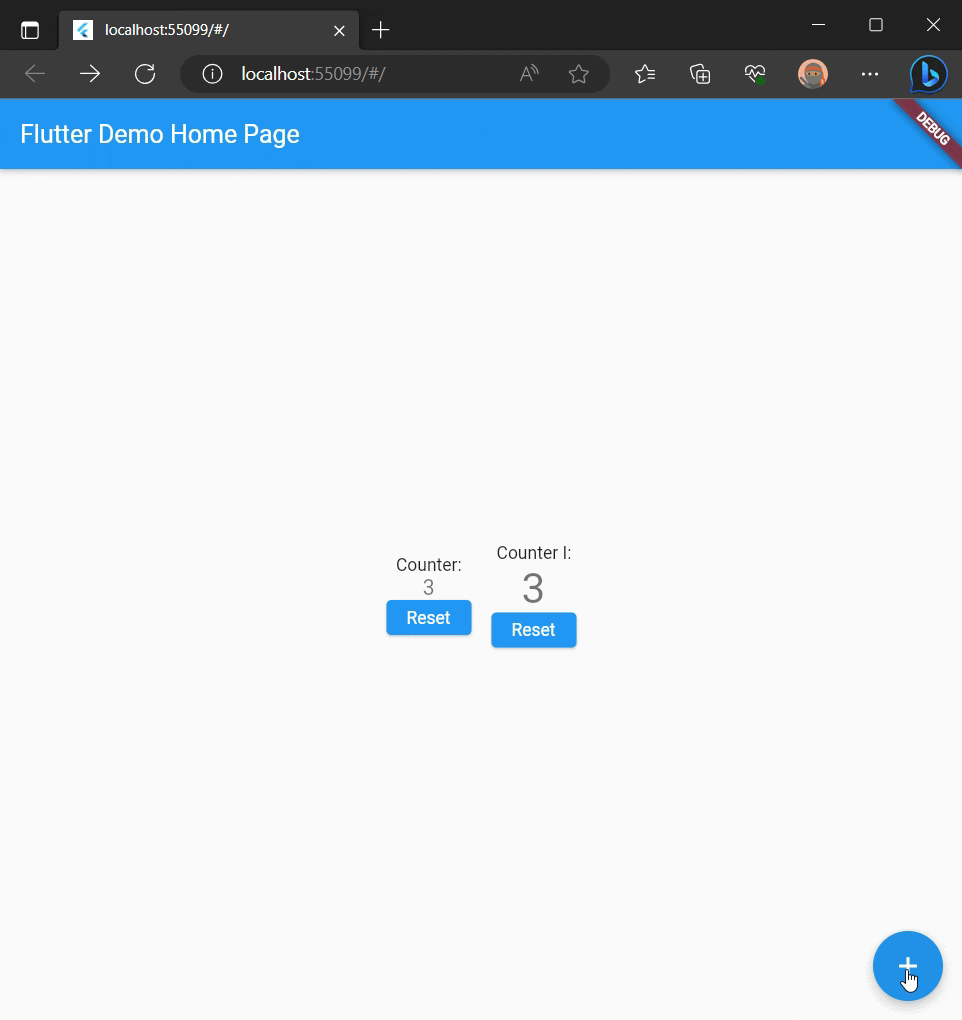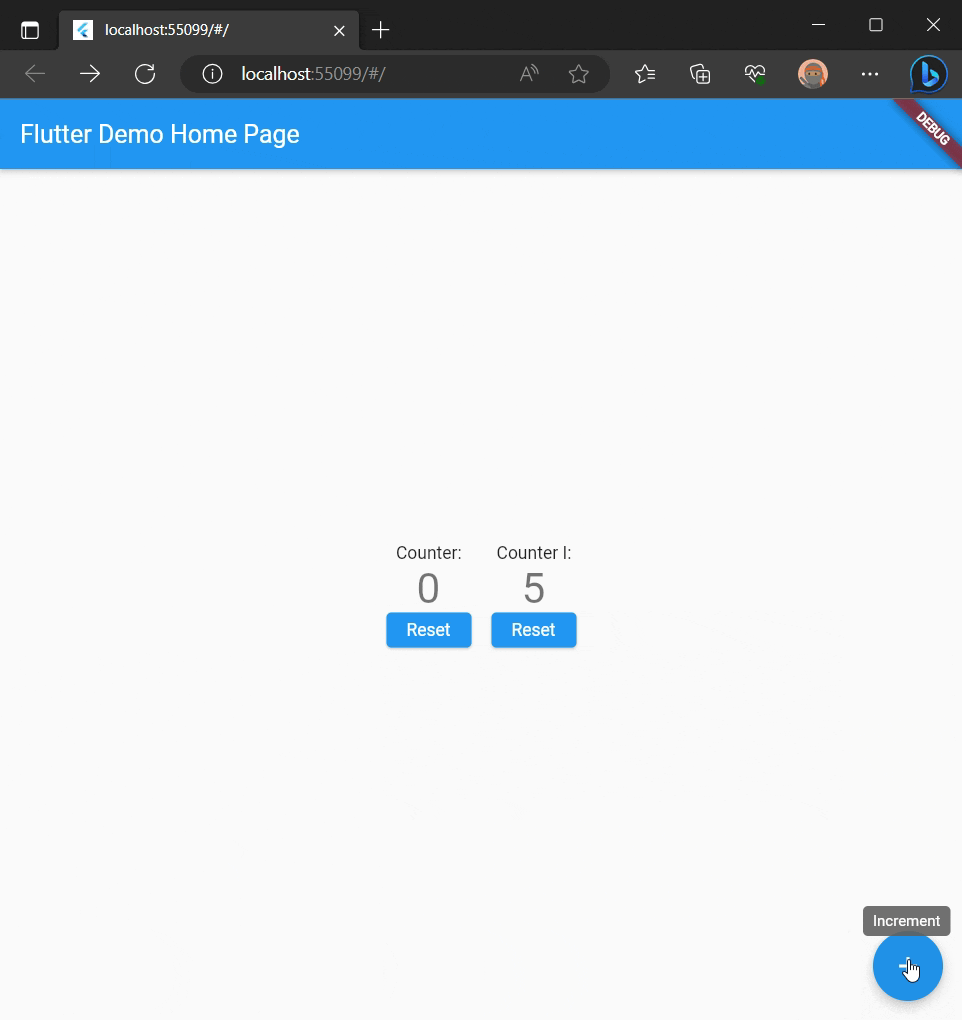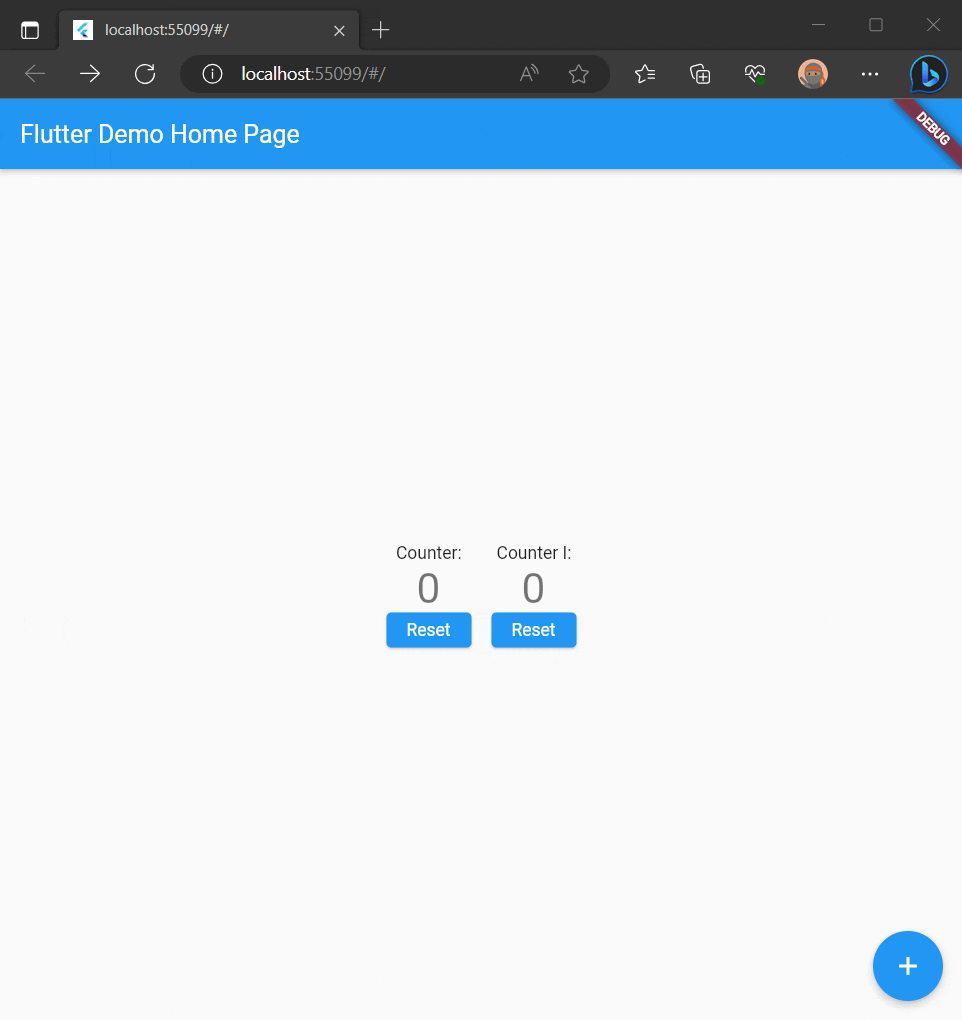
final _counter = 0.component<int>((ctx, self) => Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'Counter I:',
),
Text(
'${self.x}',
style: Theme.of(ctx).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => self.x = 0,
child: const Text('Reset'),
),
],
));
The extension method will returns a Component object with an x attribut that refers to the variable used by the extension.
Counter app
Here is a sample "Counter" app:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:tilde/tilde.dart';
void main() => runApp(MaterialApp(home: ~MyApp()));
class MyApp extends SPA {
final _counter = Counter();
final _counter1 = 0.component<int>((ctx, self) => Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'Counter I:',
),
Text(
'${self.x}',
style: Theme.of(ctx).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => self.x = 0,
child: const Text('Reset'),
),
],
));
@override
Widget onNavigate(BuildContext context) => Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Flutter Demo Home Page'),
),
body: Center(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
~_counter,
const Padding(padding: EdgeInsets.all(8)),
~_counter1,
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
_counter.increment();
_counter1.setState(() => _counter1.x++);
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
class Counter extends Component {
late Animation<double> _animation;
late AnimationController _controller;
int _count = 0;
Future<void> increment() async {
await _controller.reverse();
_count++;
await _controller.forward();
}
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
reverseDuration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
vsync: vsync);
_animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 1).animate(_controller)
..addListener(() => setState(() {}));
_controller.forward();
}
@override
void dispose() {
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget render(BuildContext context) => Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'Counter:',
),
Text(
'$_count',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
textScaleFactor: _animation.value,
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
_count = 0;
_controller.reset();
_controller.fling();
},
child: const Text('Reset'),
),
],
);
}
Navigation and routing
Navigation and routing is an essential feature of Single Page Applications (SPA) which allows organizing application user interface into virtual pages (views) and "navigate" between them while application URL reflects the current state of the app.
SPA class is used as a base class for application and will gives you many facilities:
-
Help to set the type of returned app (MaterialApp or CupertinoApp) by the
~operator,super.appTypeis set to material by default. -
Handle app route management by overriding these methods:
String get initialRouteoptional function that define the application initial route dynamically, return '/' by default.Widget onNavigate(BuildContext)function called every time the location is resolved to build the application widget.String onChanging(String newRoute)optional function that run every time the location is changed and before is resolved to protect or redirect routes. -
Access to the application any where in your code through the static method
SPA.of<T extends SPA>()but be aware of null. -
After getting the application instance you can get access to the route and getting the url query params.
Route management
Route is a portion of application URL after # symbol. Route reflects the current state of the app. Route management allows user interface views organization and controls navigation between them.
Initial application route, if not set in application constructor is /. Application route can be obtained by reading SPA.of()?.route property.
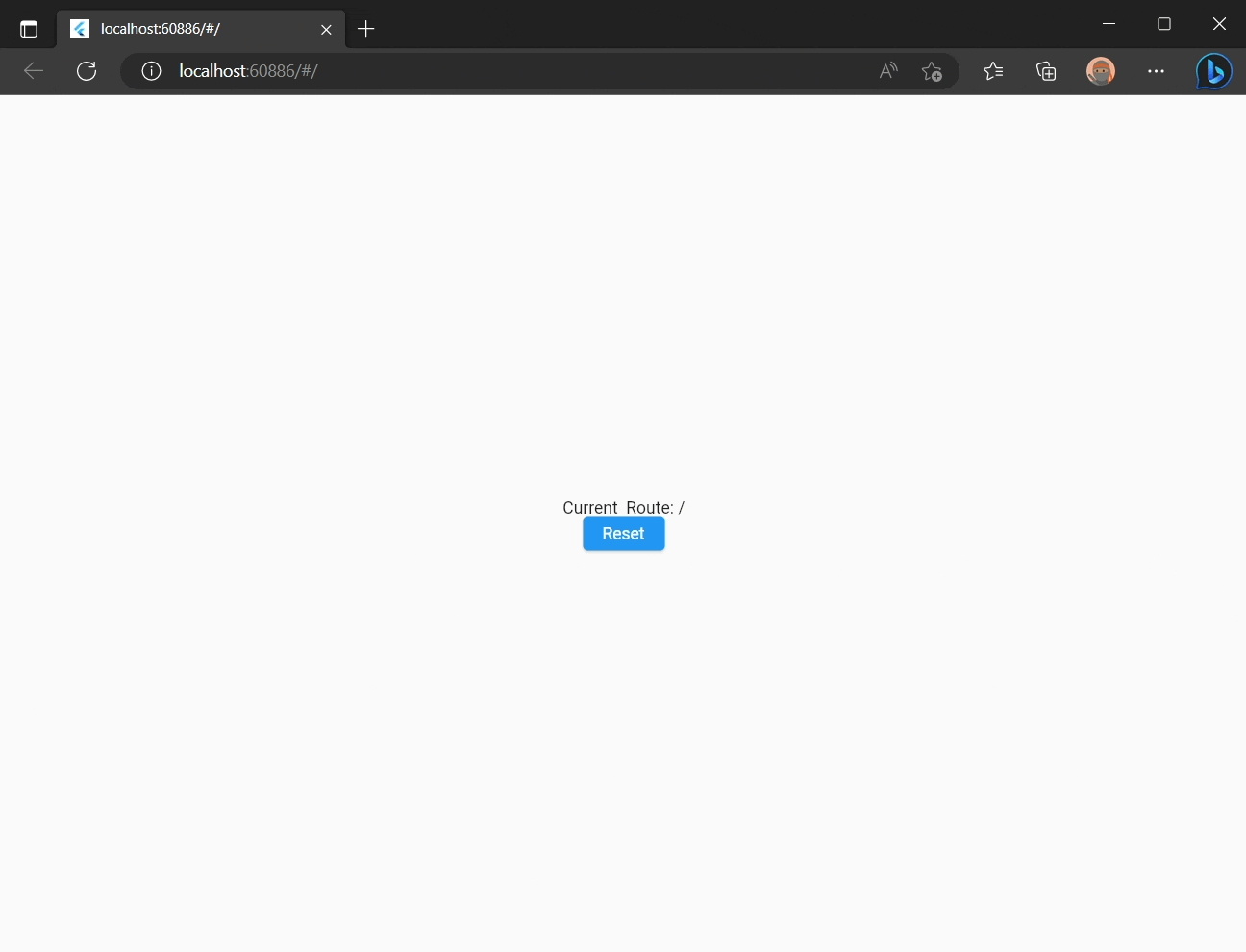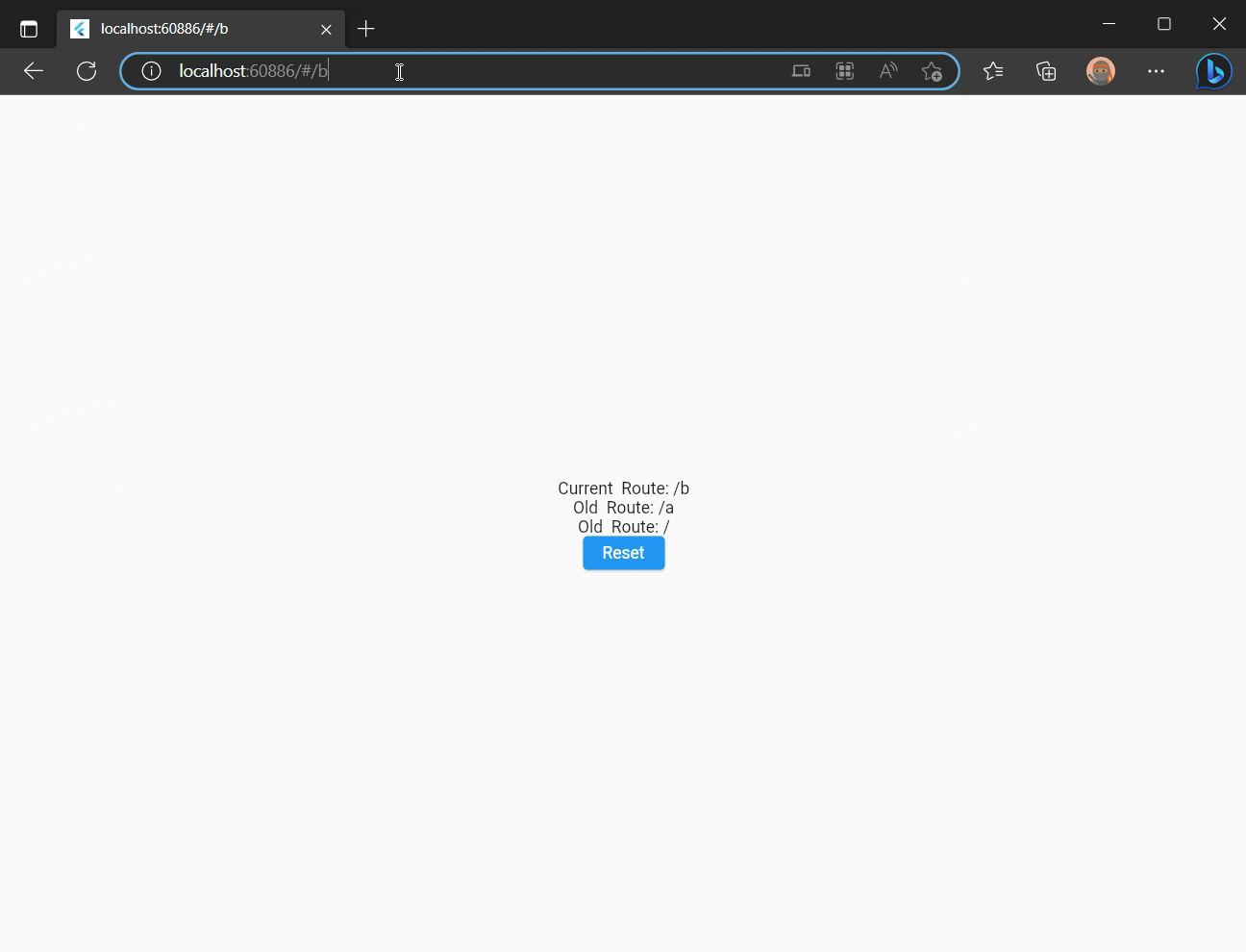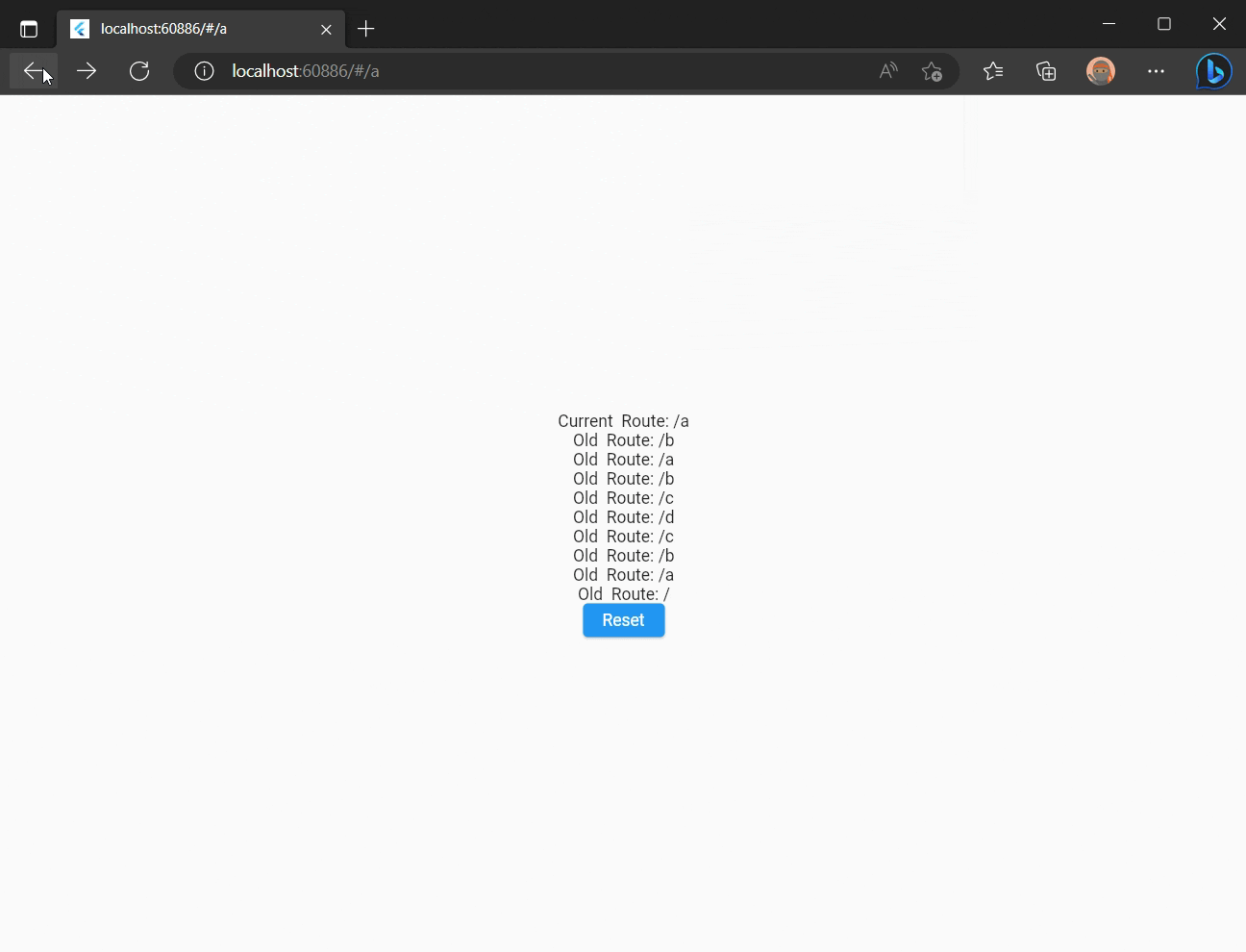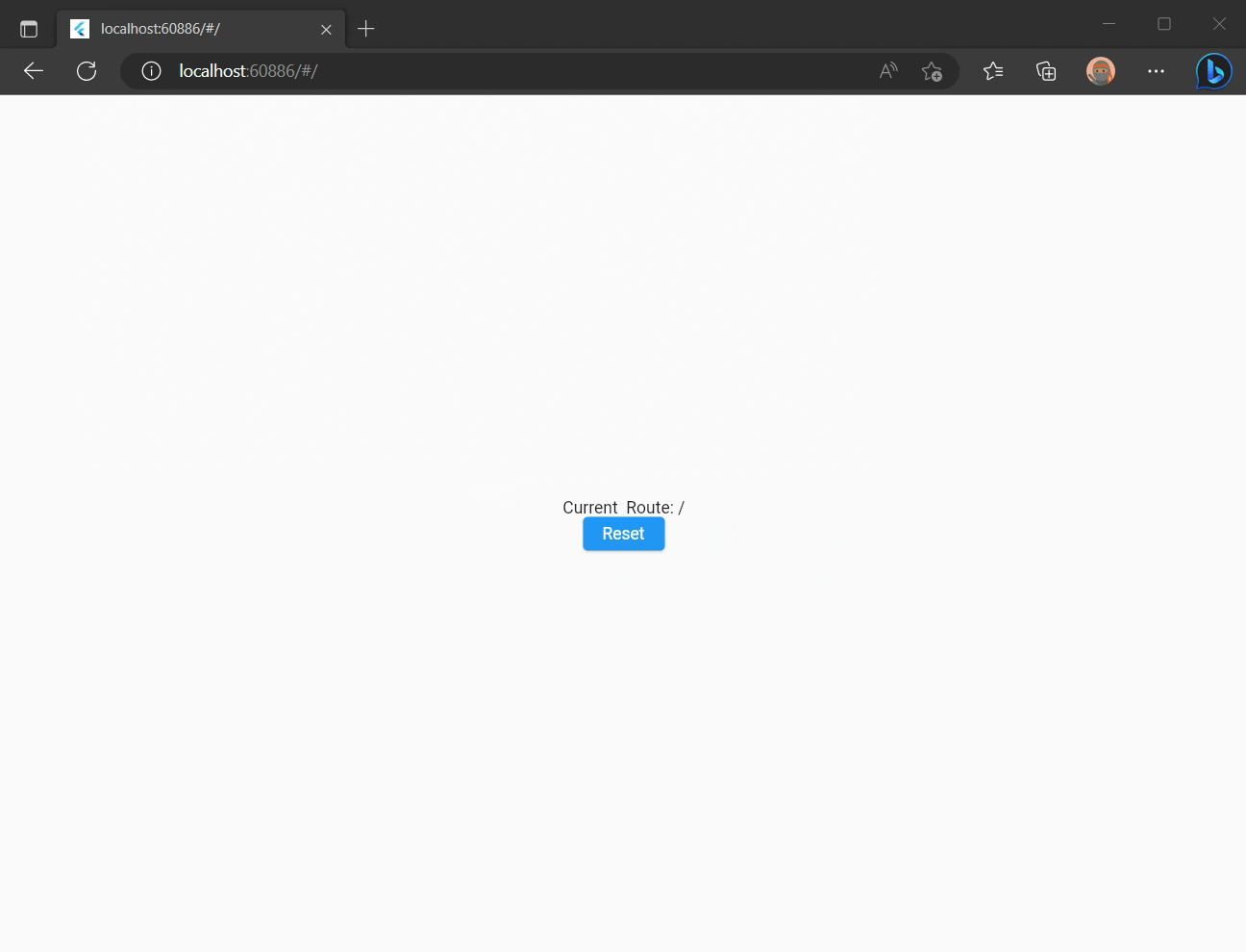
Every time the route in the URL is changed the Application Widget onNavigate(BuildContext context) function is called to return the corresponding view according to the current route. For example, let's add a new message showing the current route each time it changes:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:tilde/tilde.dart';
import 'package:velocity_x/velocity_x.dart';
class RoutesApp extends SPA {
final _routes = <String>[];
@override
Widget onNavigate(BuildContext context) {
if (route.isNotEmpty) _routes.add(route);
int i = 0;
return Scaffold(
body: _routes.reversed
.map<Widget>(
(_) {
i++;
return Text('${i == 1 ? 'Current' : 'Old'} Route: $_');
},
)
.toList()
.addT(
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
_routes.clear();
route = '/';
},
child: const Text('Reset'),
),
)
.column()
.centered(),
);
}
}
void main() {
final app = RoutesApp();
runApp(MaterialApp.router(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
routeInformationParser: app.routeInformationParser,
routerDelegate: app.routerDelegate,
));
}
Route can be changed programmatically, by updating SPA.of()?.route property.
Click "Reset" button and you'll see application Route is changed to / and a new item is pushed in a browser history.
You can use browser "Back" button to navigate to a previous route.
Try navigating between views programmatically using buttons, Back/Forward browser buttons, manually changing route in the URL - it works no matter what! :)
Other examples
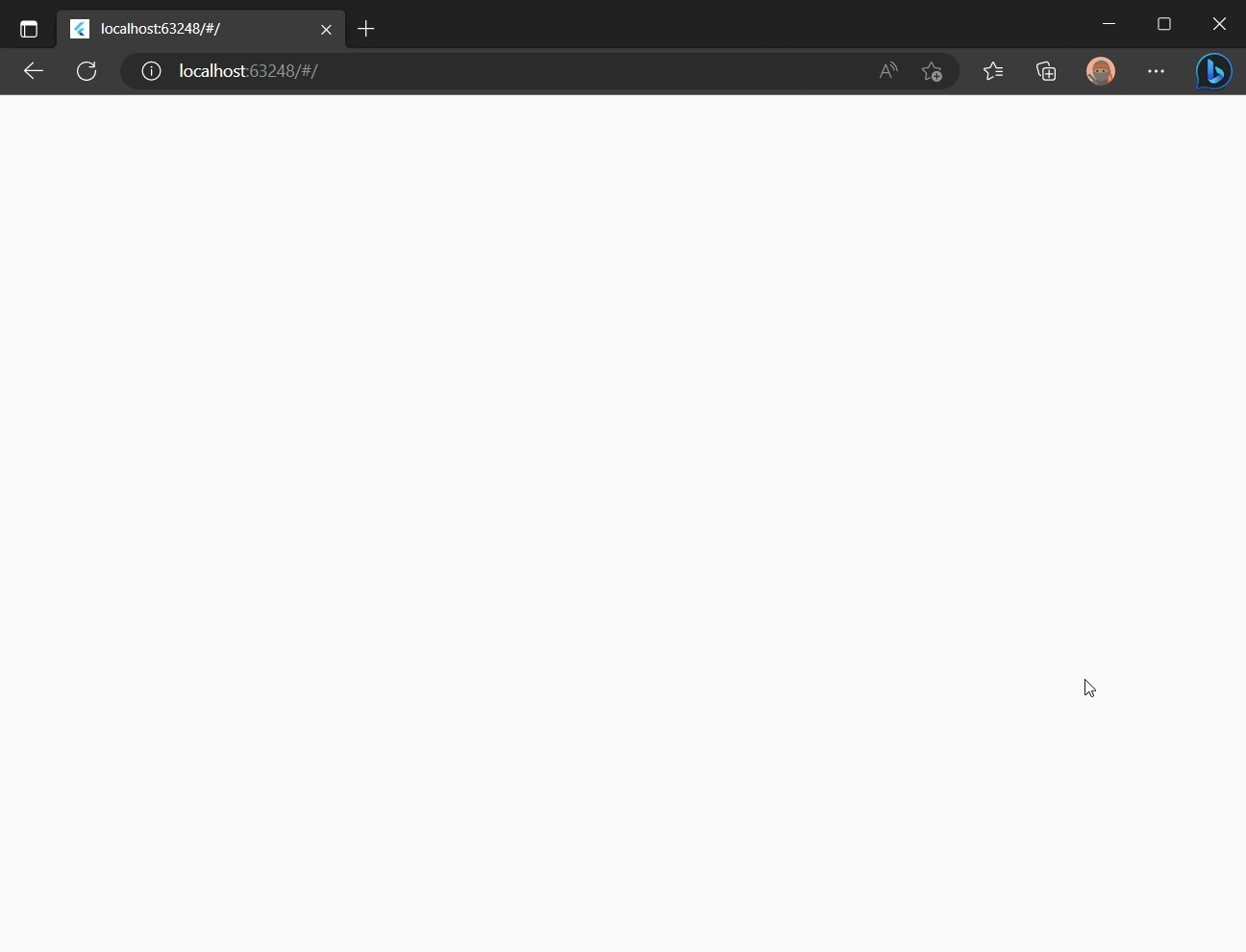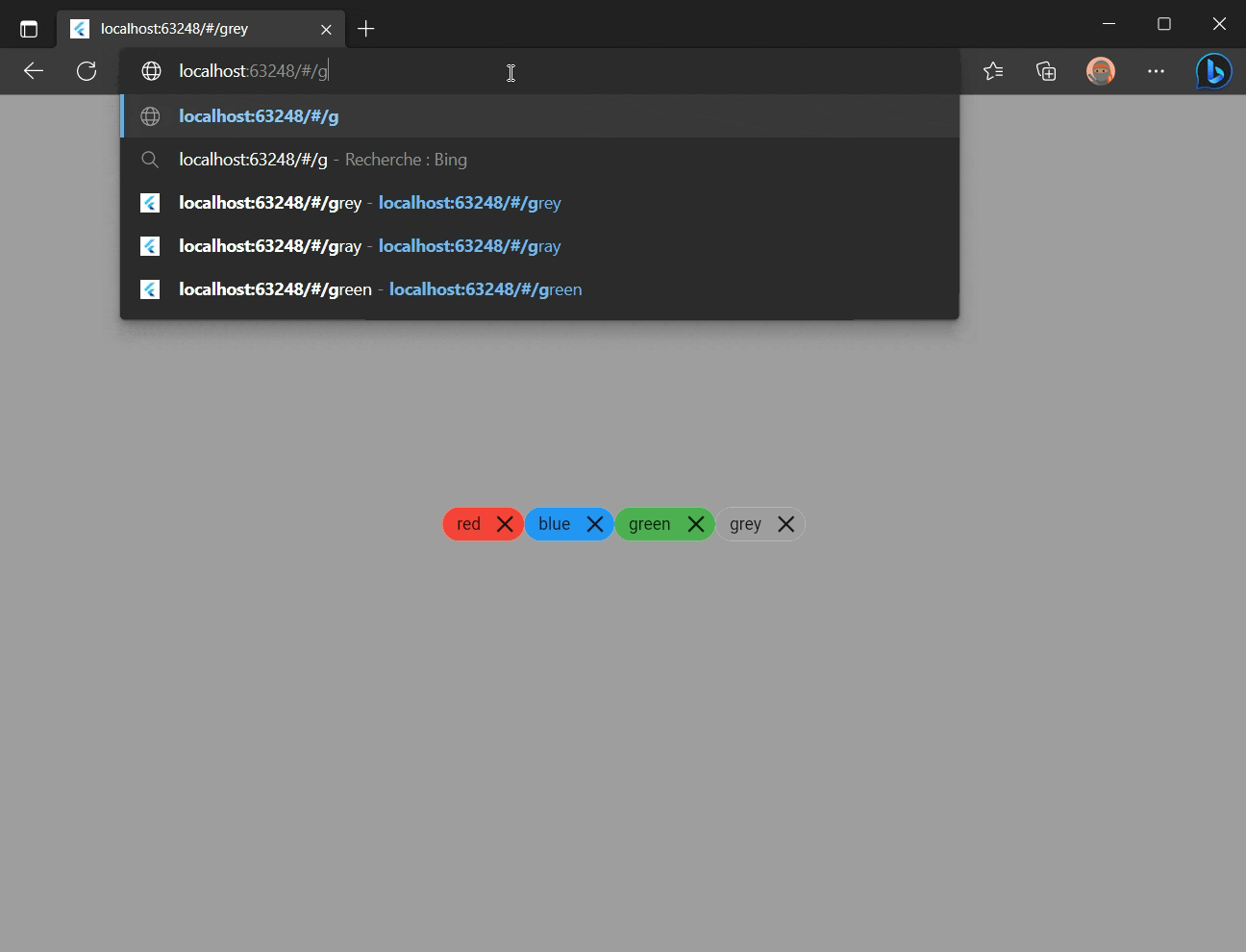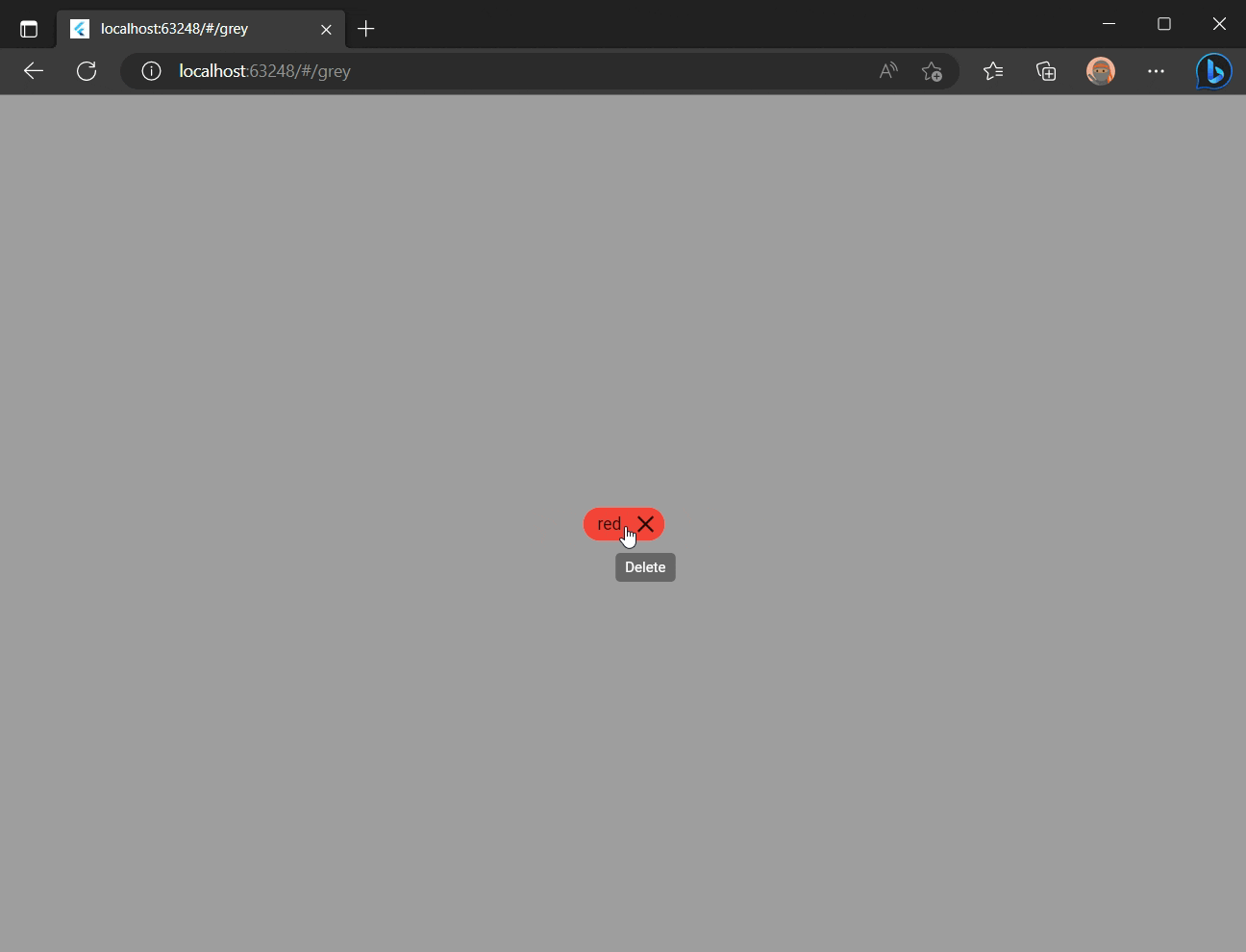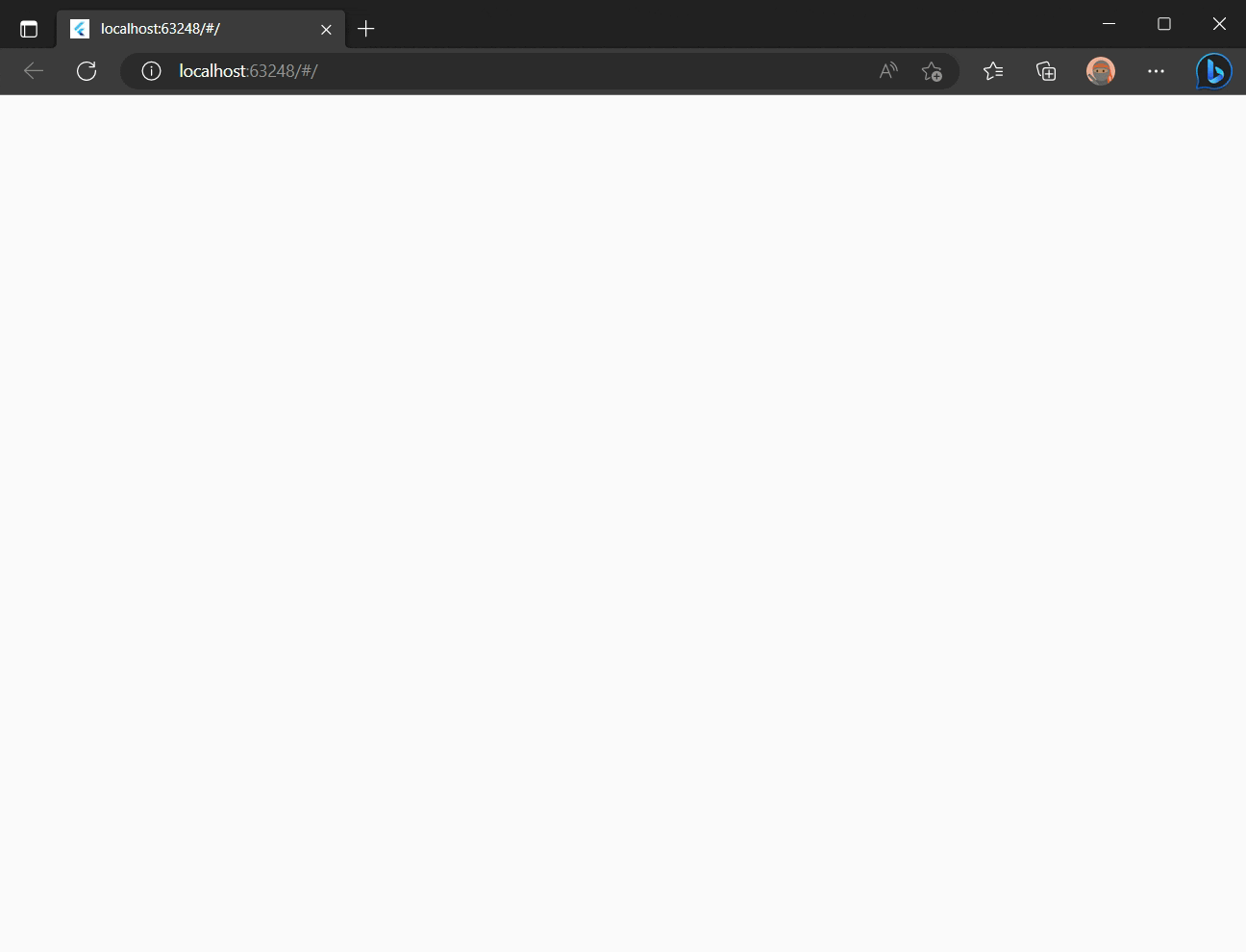
BG Color
A background color changer based on application route.
Shopping Cart
A simple shopping cart application containing a few screens, along with the functionality of adding and removing pre-listed items to and from the cart.
Todo List
A todo list app that allow user to add a new to-do item to the to-do list, to toggle the to-do item from active to complete and to delete the to-do items.