mu_state
Minimal Cubit-inspired state management using Flutter's built-in primitives. No external dependencies.
See my article From ValueNotifier to Cubit-inspired state management for more info
Overview
mu_state provides a lightweight alternative to Bloc/Cubit using Flutter's built-in ValueNotifier, ValueListenableBuilder and InheritedWidget. It follows the same patterns you know from Bloc but with zero dependencies and minimal boilerplate.
Key concepts:
MuLogic<S>- Your business logic (likeCubit)MuBuilder<S>- Rebuilds UI on state changes (likeBlocBuilder)MuListener<S>- Performs side effects (likeBlocListener)MuConsumer<S>- Combines builder and listener (likeBlocConsumer)MuProvider<T>- Provides values down the widget tree (likeProviderorBlocProvider)
Additional widgets are available for handling multiple states or providers: MuMultiBuilder, MuMultiListener, and MuMultiProvider. The MuComparable mixin is also available for state equality comparison. See the Components section for details.
Screenshots
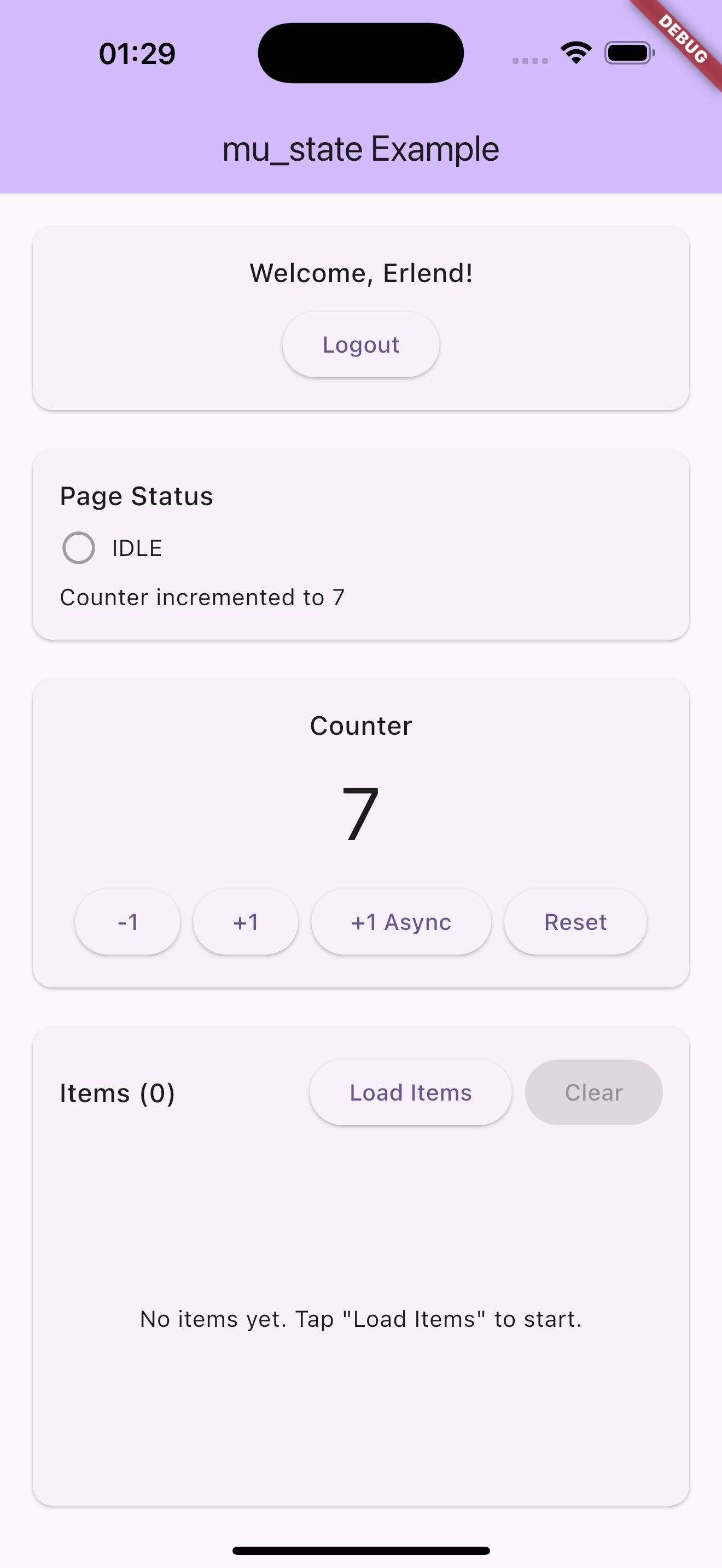
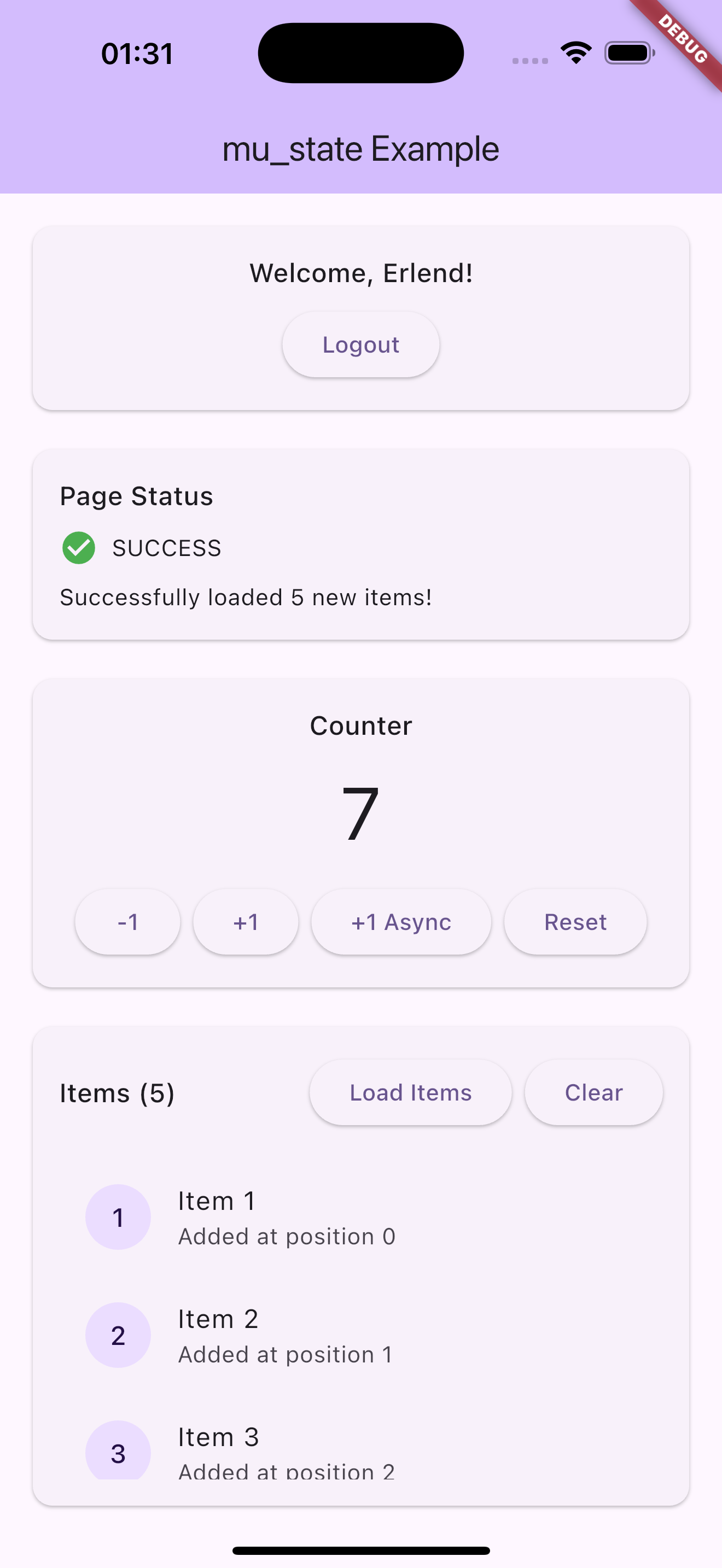
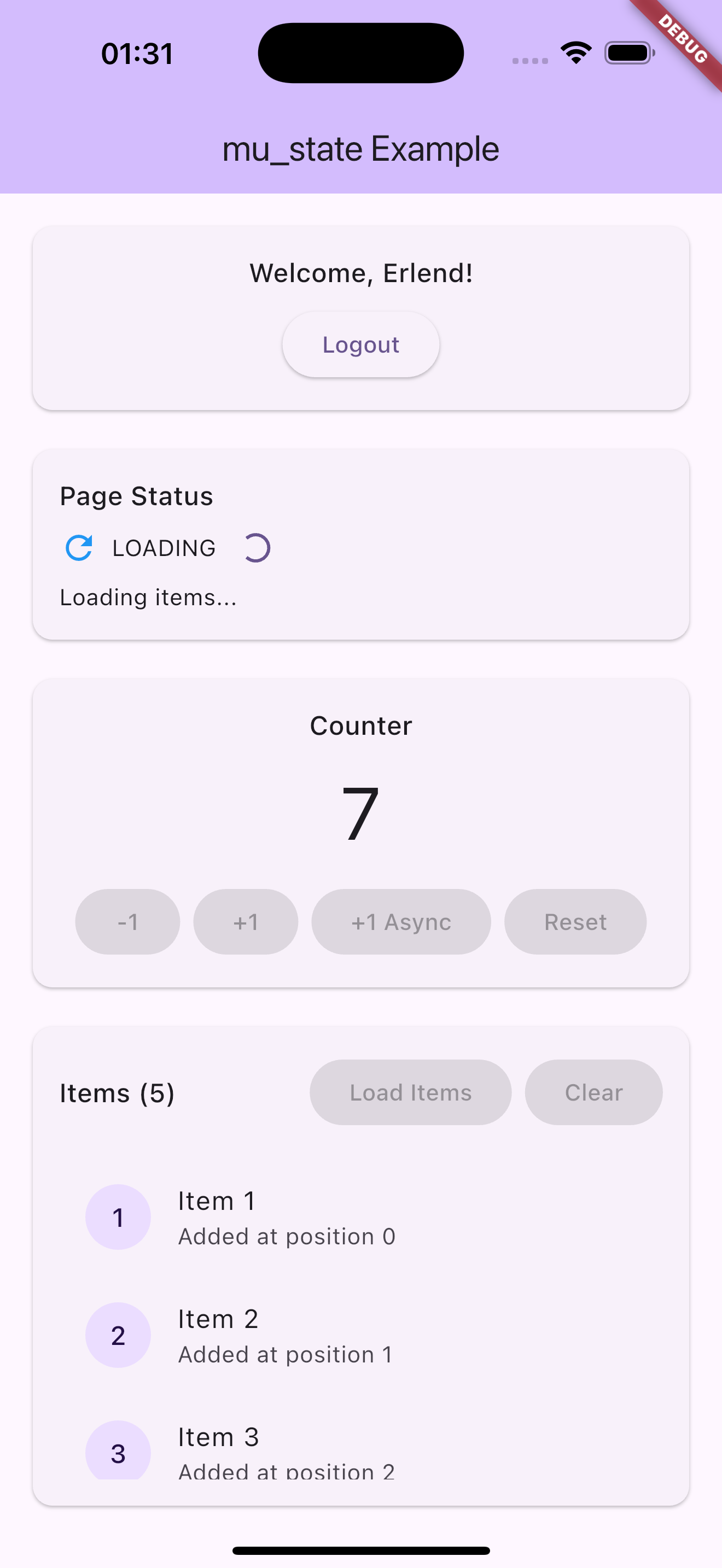
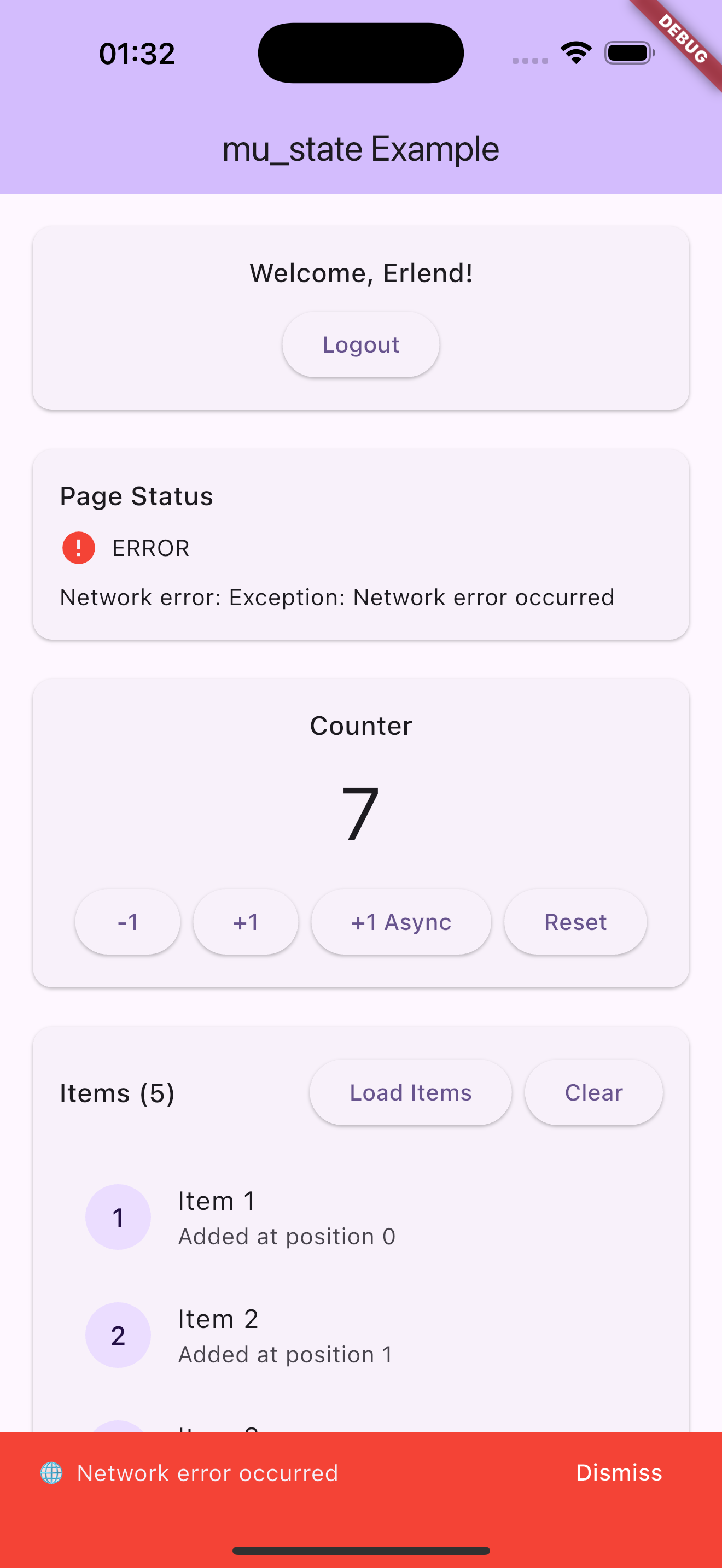
Usage
Let's create a simple counter to see how mu_state works:
counter_logic.dart
import 'package:mu_state/mu_state.dart';
class CounterState with MuComparable {
final int counter;
final bool isLoading;
final String? error;
const CounterState({required this.counter, required this.isLoading, this.error});
CounterState copyWith({int? counter, bool? isLoading, String? error}) {
return CounterState(
counter: counter ?? this.counter,
isLoading: isLoading ?? this.isLoading,
error: error ?? this.error,
);
}
@override
List<Object?> get props => [counter, isLoading, error];
}
class CounterLogic extends MuLogic<CounterState> {
CounterLogic() : super(const CounterState(counter: 0, isLoading: false));
void increment() {
value = value.copyWith(counter: value.counter + 1);
}
Future<void> incrementAsync() async {
value = value.copyWith(isLoading: true, error: null);
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1));
// Simulate random error
if (DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch % 3 == 0) {
value = value.copyWith(isLoading: false, error: 'Failed to increment');
} else {
value = value.copyWith(counter: value.counter + 1, isLoading: false);
}
}
}
main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:mu_state/mu_state.dart';
import 'counter_logic.dart';
void main() => runApp(CounterApp());
class CounterApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: MuProvider<CounterLogic>(
value: CounterLogic(),
child: CounterPage(),
),
);
}
}
counter_page.dart
class CounterPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final logic = context.logic<CounterLogic>();
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Counter')),
body: MuListener<CounterState>(
logic: logic,
listener: (context, state) {
if (state.error != null) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text('⚠️ ${state.error}')),
);
}
},
listenWhen: (prev, curr) => prev.error != curr.error && curr.error != null,
child: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
MuBuilder<CounterState>(
valueListenable: logic,
builder: (context, state, child) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('Counter: ${state.counter}', style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium),
if (state.isLoading) CircularProgressIndicator(),
],
);
},
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => logic.increment(),
child: Text('Increment'),
),
SizedBox(height: 8),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => logic.incrementAsync(),
child: Text('Async Increment'),
),
],
),
),
),
);
}
}
At this point we have successfully separated our presentational layer from our business logic layer. Notice that CounterPage knows nothing about what happens when a user taps the buttons. The widget simply notifies the CounterLogic that the user has pressed increment.
Alternative: You could also use
MuConsumerto combine the listener and builder functionality in a single widget. See the MuConsumer section below for details.
Components
MuLogic
MuLogic<S> is a typedef for ValueNotifier<S> that serves as the foundation for your business logic. It manages state and notifies listeners when the state changes. MuLogic is essentially an alias that makes the code more semantic for state management purposes.
class CounterLogic extends MuLogic<CounterState> {
CounterLogic() : super(const CounterState(counter: 0, isLoading: false));
void increment() {
value = value.copyWith(counter: value.counter + 1);
}
}
Since MuLogic extends ValueNotifier, you get all the familiar methods like addListener, removeListener, and the value property for getting and setting state.
MuBuilder
MuBuilder<S> is a typedef for ValueListenableBuilder<S> that rebuilds the widget when the state changes. It's essentially an alias that makes the code more semantic for state management, but underneath it's just Flutter's built-in ValueListenableBuilder.
See MuListener if you want to "do" anything in response to state changes such as navigation, showing a dialog, etc...
MuBuilder<CounterState>(
valueListenable: logic,
builder: (context, state, child) {
return Text('Counter: ${state.counter}');
}
)
MuComparable
MuComparable is a mixin that provides equality comparison for state classes. It's a lightweight alternative to packages like Equatable and helps MuBuilder and other listeners determine when to rebuild.
class CounterState with MuComparable {
final int counter;
final String? error;
const CounterState({required this.counter, this.error});
@override
List<Object?> get props => [counter, error];
}
The props list should include all properties that determine equality. When state changes, widgets will only rebuild if the new state is different from the previous state based on these properties.
MuListener
MuListener performs side effects in response to state changes - navigation, showing dialogs, etc. The listener is called once per state change and by default NOT on initial state (lazy: true). Set lazy: false to call the listener immediately with the current state.
MuListener<CounterState>(
logic: logic,
listener: (context, state) {
if (state.error != null) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text('Error: ${state.error}')),
);
}
},
listenWhen: (prev, curr) => prev.error != curr.error,
child: Container(),
)
MuProvider
MuProvider is a Flutter widget which provides any value to its children via dependency injection. While originally designed for MuLogic instances, it's now fully generic and can provide any type - making it perfect for injecting repositories, services, or other dependencies throughout your widget tree.
You provide the instance to MuProvider via the value parameter. MuProvider will automatically handle disposing the value when the provider is disposed (if it implements ChangeNotifier, which MuLogic does).
MuProvider<CounterLogic>(
value: CounterLogic(),
child: CounterPage(),
);
Access from anywhere in the subtree:
// For MuLogic instances
final logic = context.logic<CounterLogic>();
// For any type
final repo = context.read<AuthRepository>();
MuMultiProvider
MuMultiProvider is a Flutter widget that merges multiple MuProvider widgets into one. MuMultiProvider improves the readability and eliminates the need to nest multiple MuProviders. By using MuMultiProvider we can go from:
MuProvider<LogicA>(
value: LogicA(),
child: MuProvider<LogicB>(
value: LogicB(),
child: MuProvider<LogicC>(
value: LogicC(),
child: ChildA(),
)
)
)
to:
MuMultiProvider([
(child) => MuProvider<LogicA>(value: LogicA(), child: child),
(child) => MuProvider<LogicB>(value: LogicB(), child: child),
(child) => MuProvider<LogicC>(value: LogicC(), child: child),
], child: ChildA())
MuMultiBuilder
MuMultiBuilder is a Flutter widget which listens to multiple MuLogic instances and rebuilds when any of them change. This is useful when you need to build UI that depends on multiple state sources.
MuMultiBuilder(
listenables: [logicA, logicB],
builder: (context, values, child) {
final stateA = values[0] as StateA;
final stateB = values[1] as StateB;
return Text('A: ${stateA.value}, B: ${stateB.value}');
},
)
MuMultiListener
MuMultiListener is a Flutter widget that merges multiple MuListener widgets into one. MuMultiListener improves the readability and eliminates the need to nest multiple MuListeners. By using MuMultiListener we can go from:
MuListener<StateA>(
logic: logicA,
listener: (context, state) {
// handle state A changes
},
child: MuListener<StateB>(
logic: logicB,
listener: (context, state) {
// handle state B changes
},
child: ChildWidget(),
),
)
to:
MuMultiListener(
listeners: [
(child) => MuListener<StateA>(
logic: logicA,
listener: (context, state) {
// handle state A changes
},
child: child,
),
(child) => MuListener<StateB>(
logic: logicB,
listener: (context, state) {
// handle state B changes
},
child: child,
),
],
child: ChildWidget(),
)
MuConsumer
MuConsumer combines MuBuilder and MuListener functionality in a single widget.
MuConsumer<CounterState>(
logic: logic,
listener: (context, state) {
if (state.error != null) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text('Error: ${state.error}')),
);
}
},
builder: (context, state, child) {
return Text('Counter: ${state.counter}');
},
)
An optional listenWhen and buildWhen can be implemented for more granular control over when listener and builder are called. The listenWhen and buildWhen functions take the previous state and the current state and return a bool which determines whether or not the listener or builder function will be invoked.
MuConsumer<CounterState>(
logic: logic,
listenWhen: (previous, current) {
// return true/false to determine whether or not
// to invoke listener with state
return previous.error != current.error;
},
listener: (context, state) {
// do stuff here based on state
},
buildWhen: (previous, current) {
// return true/false to determine whether or not
// to rebuild the widget with state
return previous.counter != current.counter;
},
builder: (context, state, child) {
// return widget here based on state
return Text('Counter: ${state.counter}');
}
)
See the example project for a complete implementation with more features.