Heart
Extension methods for strings and lists, inspired by Haskell.
Alphabetical list of features: any, ascending, average, backwards, chr, chrs, concat, count, deepContains, deepEquals, descending, drop, dropWhile, elemIndices, every, filter, group, groupBy, head, inits, insertInOrder, intercalate, interleave, intersect, intersperse, isLowerCase, isUpperCase, last, letterCount, letters, nub, nums, product, removeWhitespace, replaceAll, replaceFirst, riffleIn, riffleOut, shuffled, splitAt, subtract, subtractAll, sum, tail, tails, toStringList, union, unwords, wordCount, words, zip, zip2, zip3, zip4, >, >=, <, <=, ^, *
(Strings are treated as lists in Haskell, and have many of the same functions.)
ascending, descending
Sort lists and strings:
List<int> l = [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].ascending(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
List<int> l2 = [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].descending(); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
String s = 'hello'.ascending(); // 'ehllo'
String s = 'hello'.descending(); // 'ollhe'
sum, product, average
Add or multiply numbers in a list:
int s = [1, 2, 3].sum(); // 6
int p = [4, 5, 6].product(); // 120
double a = [11, 2, 33, 55, 7, 2, 1].average(); // 15.857142857142858
// .average() works for Strings based on character codes
'abc'.average() // 'b'
count
Count occurrences in a list or string:
int c = [1, 2, 1, 3].count(1); // 2
// Works for nested iterables
[{1,2}, [1,3]].count({1,2}) // 1
'hello world'.count('l') // 3
'hello world'.count('ll') // 1
elemIndices
Find where element occurs in a list, or substring occurs in a string:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1].elemIndices(1); // [0, 2, 4]
// Works on nested iterables by using deepEquals function in this package
List<int> l2 = [[1,2], [1,2], [3,4]].elemIndices([1,2]); // [0, 1]
List<int> l3 = 'hello'.elemIndices('l'); // [2, 3]
List<int> l4 = 'hello'.elemIndices('ll'); // [2]
nub
Remove duplicates:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 1, 2].nub() // [1, 2]
String s = 'hello'.nub(); // 'helo'
Optional list or string parameter only looks at those elements:
[1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3].nub([1, 2]) // [1, 2, 3, 3]
'aaabbbcc'.nub('ab') // 'abcc'
backwards
Reverse a string or list:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].backwards(); // [3, 2, 1]
String s = 'hello'.backwards(); // 'olleh'
shuffled
Returns a shuffled list or string, with cryptographically secure option.
(Dart's shuffle method is void)
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].shuffled();
// or
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].shuffled(cryptographicallySecure: true);
String s = 'hello'.shuffled();
concat
Concatenate nested lists or strings:
List<int> l = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].concat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
String str = ['hello', 'world'].concat(); // 'helloworld'
intersperse
Inserts an item in between all other elements:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].intersperse(0); // [1, 0, 2, 0, 3]
String s = 'hello'.intersperse('-'); // 'h-e-l-l-o'
intercalate (in-TER-kuh-late)
Inserts a list between lists (or string between strings) and concatenates the result:
List<int> l = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].intercalate([0, 0]);
// [1, 2, 0, 0, 3, 4, 0, 0, 5, 6]
String s = ['hello', 'world'].intercalate('-');
// 'hello-world'
filter
Keep only elements that meet criteria:
// Keep where x^3 < 10:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4].filter((x) => pow(x, 3) < 10); // [1, 2]
Equivalent to .where().toList(), but also works on Strings:
// '<' operator defined in this package
String s = 'hello world'.filter((char) => char < 'j'); // 'he d'
any, every
(These already exist for lists)
bool b = 'hello'.any((char) => char == 'h'); // true
bool b2 = 'hello'.every((char) => char == 'h'); // false
drop, dropWhile
drop(n) removes first n elements. Similar to .sublist(n) or .substring(n) but doesn't throw exception for invalid n.
List<int> l = [0, 1, 2].drop(1); // [1, 2]
// Returns the same if n<=0
[0, 1, 2].drop(-1) // [0, 1, 2]
// Returns empty if n >= length
[0, 1, 2].drop(100) // []
'hello'.drop(2)
// 'llo'
dropWhile drops elements until they don't meet criteria, keeps everything after.
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1].dropWhile((x) => x < 3);
// [3, 2, 1]
// '<' operator defined in this package
String s = 'hello'.dropWhile((char) => char < 'i');
// 'llo'
replaceFirst, replaceAll
(These methods already exist for Strings)
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceFirst(1, 99); // [99, 1, 2, 3]
// Can replace with multiple elements:
List<int> l2 = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceFirst(1, [99,100]); // [99, 100, 1, 2, 3]
// No replacement value means it will simply delete:
List<int> l3 = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceFirst(1); // [1, 2, 3]
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceAll(1, 99); // [99, 99, 2, 3]
List<int> l2 = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceAll(1, [99,100]); // [99, 100, 99, 100, 2, 3]
List<int> l3 = [1, 1, 2, 3].replaceAll(1); // [2, 3]
subtract, subtractAll
subtract removes elements one at a time (like Haskell's \\):
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 2, 3].subtract([1, 3]); // [1, 2, 2]
l = [1, 1, 2, 2].subtract([1, 2, 3]); // [1, 2]
// ignores 3 since it is not in original list
String s = 'hello'.subtract('eo'); // 'hll'
subtractAll removes all occurrences:
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 2].subtractAll([1]); // [2, 2]
String s = 'hello'.subtractAll('lo'); // 'he'
union, intersect
union adds elements that aren't already present.
It doesn't remove duplicates from original, but doesn't add duplicates from input.
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2].union([1, 2, 3]); // [1, 1, 2, 3]
String s = 'hello'.union(' world'); // 'hello wrd'
(Use .nub() to remove duplicates, and concatenate normally to keep duplicates.)
intersect keeps all elements from original list that are also in input.
List<int> l = [1, 1, 2, 3].intersect([1, 2]); // [1, 1, 2]
String s = 'hello'.intersect('world'); // 'llo'
// Remove duplicates with .nub()
head, tail(s), last, inits,
head returns first element.
tail returns everything but the first element.
last returns the last element (Dart has this for lists but not strings).
int? i = [1, 2, 3].head(); // 1
List<int>? l = [1, 2, 3].tail(); // [2, 3]
[1].tail() // []
[].tail() // null
'hello'.head() // 'h'
'hello'.tail() // 'ello'
'hello'.last() //'o'
inits
returns a list of lists (or strings) by adding elements from the beginning:
[1, 2, 3].inits()
// [[], [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3]]
'hi'.inits()
// ['', 'h', 'hi']
tails returns a list of lists (or strings) by removing one element at a time from the beginning:
[1, 2, 3].tails()
// [[1, 2, 3], [2, 3], [3], []]
// nums function defined in this package
List<List<int>> twelveDaysOfChristmas = nums(12, 1).tails().backwards();
// [[], [1], [2, 1], [3, 2, 1], [4, 3, 2, 1], [5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]]
'hello'.tails()
// ['hello', 'ello', 'llo', 'lo', 'o', '']
insertInOrder
Inserts a value before the first element that is >=. Does not sort.
List<double> l2 = [1.1, 2.2, 0.2].insertInOrder(1.7);
// [1.1, 1.7, 2.2, 0.2]
String s = 'ABDKEO'.insertInOrder('J'); // 'ABDJKEO'
splitAt
Split a list or string into two:
List<List<int>> l = [5, 6, 7, 8].splitAt(2); // [[5, 6], [7, 8]]
'hello'.splitAt(2) // ['he', 'llo']
interleave
Combine two lists or strings by taking turns:
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3].interleave([4, 5, 6]);
// [1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6]
'abc'.interleave('123')
// 'a1b2c3'
Extra characters get added to the end:
[1, 2, 3, 4].interleave([5])
// [1, 5, 2, 3, 4]
riffleIn, riffleOut
Riffle shuffle: splits list or string in half and interleaves them
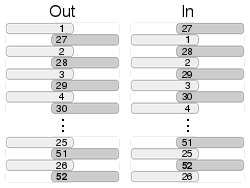
// .riffleOut interleaves first half to second.
List<int> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].riffleOut();
// [1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6]
// .riffleIn interleaves second half to first
List<int> l2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].riffleIn();
// [4, 1, 5, 2, 6, 3]
String s = 'hello'.riffleOut();
// 'hleol'
String s2 = 'hello'.riffleIn();
// 'lhleo'
group, groupBy
group combines consecutive elements together if they are equal:
List<List<int>> l = [1, 2, 3, 3, 1].group();
// [[1], [2], [3, 3], [1]]
List<String> ls = 'hello'.group();
// ['h', 'e', 'll', 'o']
groupBy combines consecutive elements if they meet criteria.
In this example, items are in the same sublist if they are less than the one after:
List<List<int>> l = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1].groupBy((a, b) => a < b);
// [[1, 2, 3], [2], [1]]
List<String> ls = 'HelLo'.groupBy((a, b) => a.isUpperCase() && b.isLowerCase());
// ['He', 'l', 'Lo']
chr, chrs
chr returns a String from a character code.
chrs returns a String from a list of codes.
97.chr() // 'a'
[97, 98].chrs() // 'ab'
// .codeUnits converts back to codes
Other methods for lists
toStringList
Convert all elements to strings:
List<String> l = [1, 2, 3].toStringList(); // ['1', '2', '3']
zip, zip2
zip takes in a list of lists, returns a list of lists where corresponding elements are paired together.
List l = zip([['one','two','three'], [1,2,3]]);
// [['one', 1], ['two', 2], ['three', 3]]
zip2 takes in a list of 2 lists and performs a function between corresponding elements (similar to Haskell's zipWith):
List l = zip2([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], (a,b) => a+b); // [5, 7, 9]
zip3 and zip4 work similarly.
Other methods for Strings
removeWhitespace
String s = ' hello \n world '.removeWhitespace(); // 'helloworld'
// Dart's .trim() only removes leading and trailing whitespace.
words, wordCount, letters, letterCount
words returns a list of words without whitespace.
wordCount takes the length of this List. Equivalent to words().length.
List<String> listOfWords = 'hello world'.words(); // ['hello', 'world']
int w = 'hello world'.wordCount(); // 2
letters returns a List of all the characters, with optional keepWhitespace parameter.
letterCount counts all characters, with optional keepWhitespace parameter.
List<String> listOfCharacters = 'hello world'.letters();
// ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']
int lc = 'hello world'.letterCount();
// 10
'hello world'.letters(keepWhitespace: true)
// ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', ' ', 'o', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']
'hello world'.letterCount(keepWhitespace: true)
// 11 (same as .length)
unwords
Combine a list of strings into one, with spaces in between:
String s = ['hello', 'world'].unwords(); // 'hello world'
String s2 = 'hello world'.letters().unwords(); 'h e l l o w o r l d'
isUpperCase, isLowerCase
Checks if all characters are upper or lower case, with optional ignoreSymbols parameter.
bool b = 'hello world'.isLowerCase(); // true
bool b2 = 'hello world'.isLowerCase(ignoreSymbols: false); // false (because of space)
bool b3 = 'Hello'.isUpperCase(); // false
bool b4 = 'Hello'.isLowerCase(); // false
bool b5 = 'á'.isLowerCase(ignoreSymbols: false); // true
// accented letters don't count as symbols
Other features
nums
Generate a list of integers:
List<int> l = nums(5); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
nums(-5) // [-4, -3, -2, -1, 0]
nums(0) // []
Two values generates an inclusive range:
nums(1, 5) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
nums(1, -5) // [1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5]
Three values adds a step count. Step count must be positive:
nums(1, 5, 2) // [1, 3, 5]
nums(1, -5, 2) // [1, -1, -3, -5]
deepEquals
deepEquals can check equality for nested lists, sets, and maps:
By default, Dart doesn't compare elements in a list for equality.
[1, 2] == [1, 2] // false
Use deepEquals for this and other iterables:
bool a = deepEquals([1, 2], [1, 2]); // true
bool b = deepEquals(
{1: 2, 3: [4,5]},
{3: nums(4, 5), 1: 2}
); // true
bool c = deepEquals(1, 1); // true
deepContains
deepContains uses deepEquals to check if an iterable contains an element:
List l = [[1, 2], {3: 4}];
Map m = {3: 4};
// By default:
bool b = l.contains(m); // false
bool b2 = l.deepContains(m); // true
Operators for strings and lists
>, >=, <, <=
Compare elements in two lists, starting at the beginning:
[1, 2, 3] > [1, 1, 3] // true
Compare strings according to their character codes:
'b' > 'a' // true
'hello' < 'hi' // true
['a', 1] >= ['b', 1] // false
(If elements cannot be compared, both >= and <= will return false.)
^
Get next String by character codes:
String s = 'a' ^ 1; // 'b'
'b' ^ (-1) // 'a'
'abc' ^ 1 // 'bcd
*
Repeat elements of a list with *
List<int> l = [1, 2] * 3; // [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2]
// Dart has this for Strings
String s = 'hello' * 3; // 'hellohellohello'
Libraries
- heart
- Extension methods, with extra functions at the bottom
- helper/helper
- Helper functions used for extension methods. See heart.dart for more extensive documentation.