geoflutterfire_plus 🌍
geoflutterfire_plus allows your Flutter apps to query geographic data saved in Cloud Firestore.
This package is forked from GeoFlutterFire and whole codes are redesigned with some new features, and will be maintained to work with latest Flutter SDK, Dart SDK, and other dependency packages.

Getting started
Prerequisites are following.
Dart: '>=2.17.0 <3.0.0'
Flutter: '>=2.10.0'
Run this command in your project.
flutter pub add geoflutterfire_plus
Or, add dependency to your pubspec.yaml.
dependencies:
geoflutterfire_plus: <latest-version>
Geohash and geo queries
Refer to Firebase official document Geo queries to understand what Geohash is, why you need to save geo location as Geohash, and how to query them. It will also help you understand limitations of using Geohashes for querying locations.
Save geo data
In order to save geo data as documents of Cloud Firestore, use GeoFirePoint. GeoFirePoint.data gives geopoint (GeoPoint type defined in cloud_firestore package) and Geohash string.
// Define GeoFirePoint by instantiating GeoFirePoint with latitude and longitude.
final GeoFirePoint geoFirePoint = GeoFirePoint(GeoPoint(35.681236, 139.767125));
// Gets GeoPoint instance and Geohash string as Map<String, dynamic>.
final Map<String, dynamic> data = geoFirePoint.data;
// {geopoint: Instance of 'GeoPoint', geohash: xn76urx66}
print(data);
GeoCollectionReference instance provides add method to create a new document in the collection (internally, just calling add method of cloud_firestore).
// Adds new documents to locations collection.
GeoCollectionReference<Map<String, dynamic>>(
FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations'),
).add(<String, dynamic>{
'geo': geoFirePoint.data,
'name': name,
'isVisible': true,
});
Or, you can just call add or set method of cloud_firestore to save the data. For example,
// Adds new documents to locations collection.
FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations').add(
<String, dynamic>{
'geo': geoFirePoint.data,
'name': 'Tokyo Station',
'isVisible': true,
},
);
The created document would be like the screenshot below. Geohash string (geohash) and Cloud Firestore GeoPoint data (geopoint) is saved in geo field as map type.
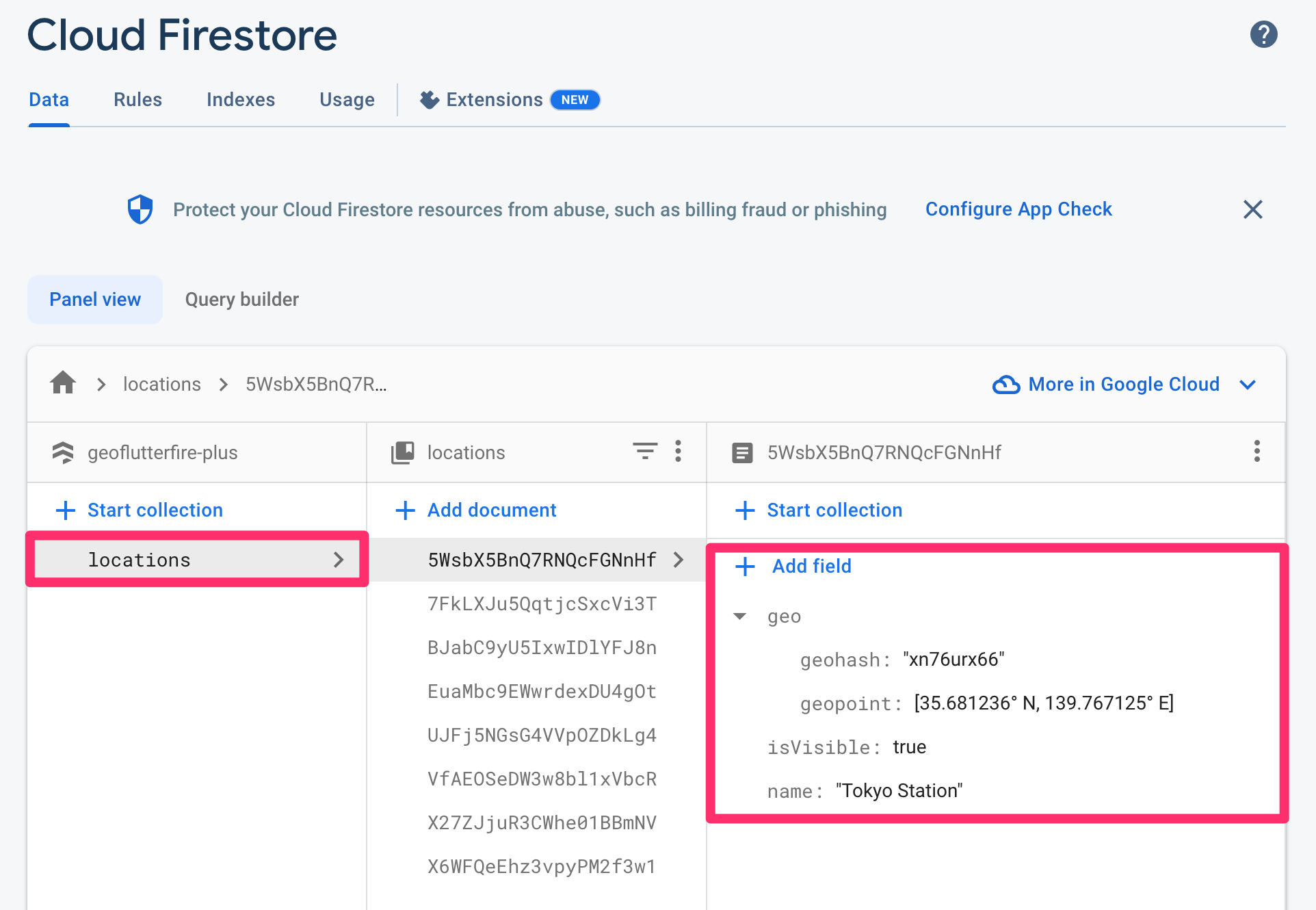
In order to set or update the pair of latitude and longitude as cloud_firestore GeoPoint and also Geohash string on the specified document's given field, GeoCollectionReference.set or GeoCollectionReference.updatePoint methods are available.
// Sets a new document by giving geoFirePoint.data to 'geo' field.
GeoCollectionReference(FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations'))
.set(
id: 'your-document-id',
data: {
'geo': geoFirePoint.data,
'foo': 'foo',
'bar': 'bar',
},
options: SetOptions(merge: true),
);
// Updates an existing document's 'geo' field by giving GeoPoint instance.
GeoCollectionReference(FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations'))
.updatePoint(
id: 'your-document-id',
field: 'geo',
geopoint: GeoPoint(35.681236, 139.767125),
);
Query geo data
In order to query location documents within a 50 km radius of a given point, you will write query like the following:
Basic query
// cloud_firestore [GeoPoint] of Tokyo Station.
const GeoPoint tokyoStation = GeoPoint(35.681236, 139.767125);
// Center of the geo query.
final GeoFirePoint center = GeoFirePoint(tokyoStation);
// Detection range from the center point.
const double radiusInKm = 50;
// Field name of Cloud Firestore documents where the geohash is saved.
const String field = 'geo';
// Reference to locations collection.
final CollectionReference<Map<String, dynamic>> collectionReference =
FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations');
// Function to get GeoPoint instance from Cloud Firestore document data.
GeoPoint geopointFrom(Map<String, dynamic> data) =>
(data['geo'] as Map<String, dynamic>)['geopoint'] as GeoPoint;
// Streamed document snapshots of geo query under given conditions.
final Stream<List<DocumentSnapshot<Map<String, dynamic>>>> stream =
GeoCollectionReference<Map<String, dynamic>>(collectionReference)
.subscribeWithin(
center: center,
radiusInKm: radiusInKm,
field: field,
geopointFrom: geopointFrom,
);
Using withConverter
If you would like to use withConverter to type-safely write query, first, you need to define its entity class and factory constructors.
/// An entity of Cloud Firestore location document.
class Location {
Location({
required this.geo,
required this.name,
required this.isVisible,
});
factory Location.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => Location(
geo: Geo.fromJson(json['geo'] as Map<String, dynamic>),
name: json['name'] as String,
isVisible: (json['isVisible'] ?? false) as bool,
);
factory Location.fromDocumentSnapshot(DocumentSnapshot documentSnapshot) =>
Location.fromJson(documentSnapshot.data()! as Map<String, dynamic>);
final Geo geo;
final String name;
final bool isVisible;
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => <String, dynamic>{
'geo': geo.toJson(),
'name': name,
'isVisible': isVisible,
};
}
/// An entity of `geo` field of Cloud Firestore location document.
class Geo {
Geo({
required this.geohash,
required this.geopoint,
});
factory Geo.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => Geo(
geohash: json['geohash'] as String,
geopoint: json['geopoint'] as GeoPoint,
);
final String geohash;
final GeoPoint geopoint;
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => <String, dynamic>{
'geohash': geohash,
'geopoint': geopoint,
};
}
Then, define typed collection reference.
/// Reference to the collection where the location data is stored.
final typedCollectionReference =
FirebaseFirestore.instance.collection('locations').withConverter<Location>(
fromFirestore: (ds, _) => Location.fromDocumentSnapshot(ds),
toFirestore: (obj, _) => obj.toJson(),
);
// Function to get GeoPoint instance from Location instance.
GeoPoint geopointFrom: (Location location) => location.geo.geopoint;
You can write query in the same way as the first example.
// Streamed typed document snapshots of geo query under given conditions.
final Stream<List<DocumentSnapshot<Location>>> stream =
GeoCollectionReference<Location>(typedCollectionReference).subscribeWithin(
center: center,
radiusInKm: radiusInKm,
field: field,
geopointFrom: geopointFrom,
);
Custom query conditions
If you would like to add custom query conditions, queryBuilder parameter of fetchWithin (fetchWithinWithDistance) / subscribeWithin (subscribeWithinWithDistance) method is available.
For example, when you filter only isVisible field is true documents, your queryBuilder would be like this:
// Custom query condition.
Query<Location> queryBuilder(Query<Location> query) =>
query.where('isVisible', isEqualTo: true);
Then, just give the queryBuilder to the parameter of fetchWithin (fetchWithinWithDistance) / subscribeWithin (subscribeWithinWithDistance) method.
🚨 Note: Custom query condition may require a composite index. If the index is not created, you will see the "cloud_firestore/failed-precondition The query requires an index..." error from Firestore on the debug console. You can create the index by clicking the link in the error message.
// Streamed typed document snapshots of geo query under custom query conditions.
final Stream<List<DocumentSnapshot<Map<String, dynamic>>>> stream =
GeoCollectionReference<Map<String, dynamic>>(typedCollectionReference)
.subscribeWithin(
center: center,
radiusInKm: radiusInKm,
field: field,
geopointFrom: geopointFrom,
// Specify queryBuilder parameter here.
queryBuilder: queryBuilder,
);
🚨 Limitation: currently limit and orderBy queries are not supported because of the geo hash query algorithm and Cloud Firestore query limitations. Alternatively documents can be sorted on client side after getting the data (documents).
Examples
If you would like to try out the features, refer to the example project.


