Formx
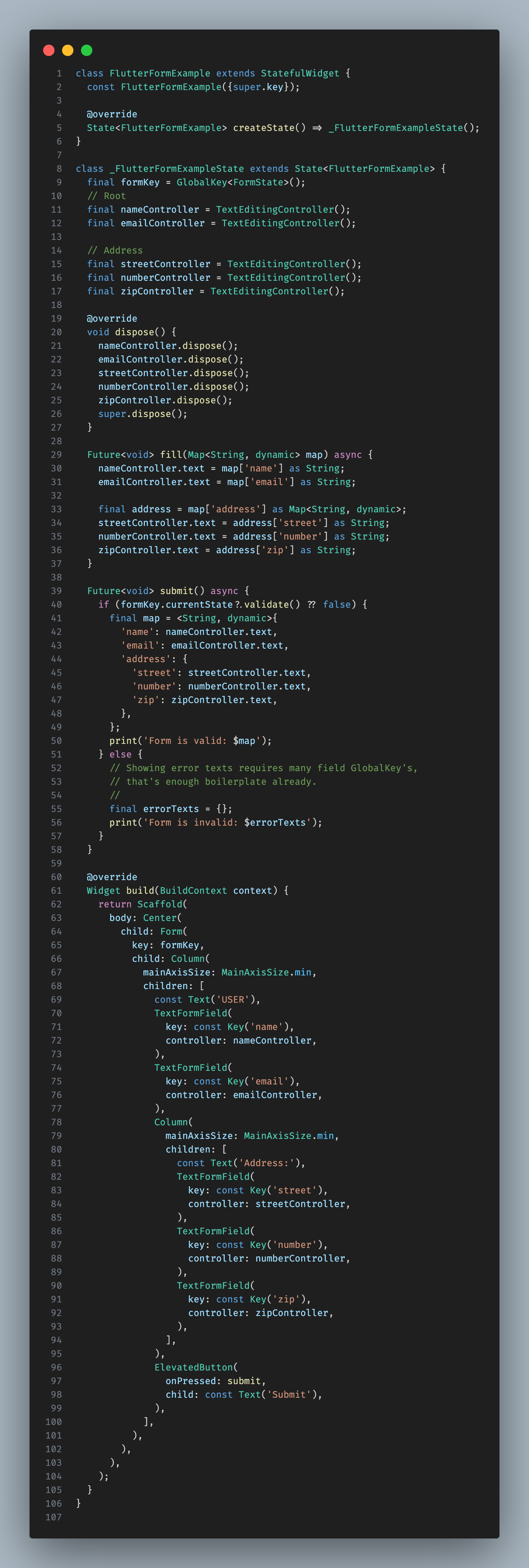
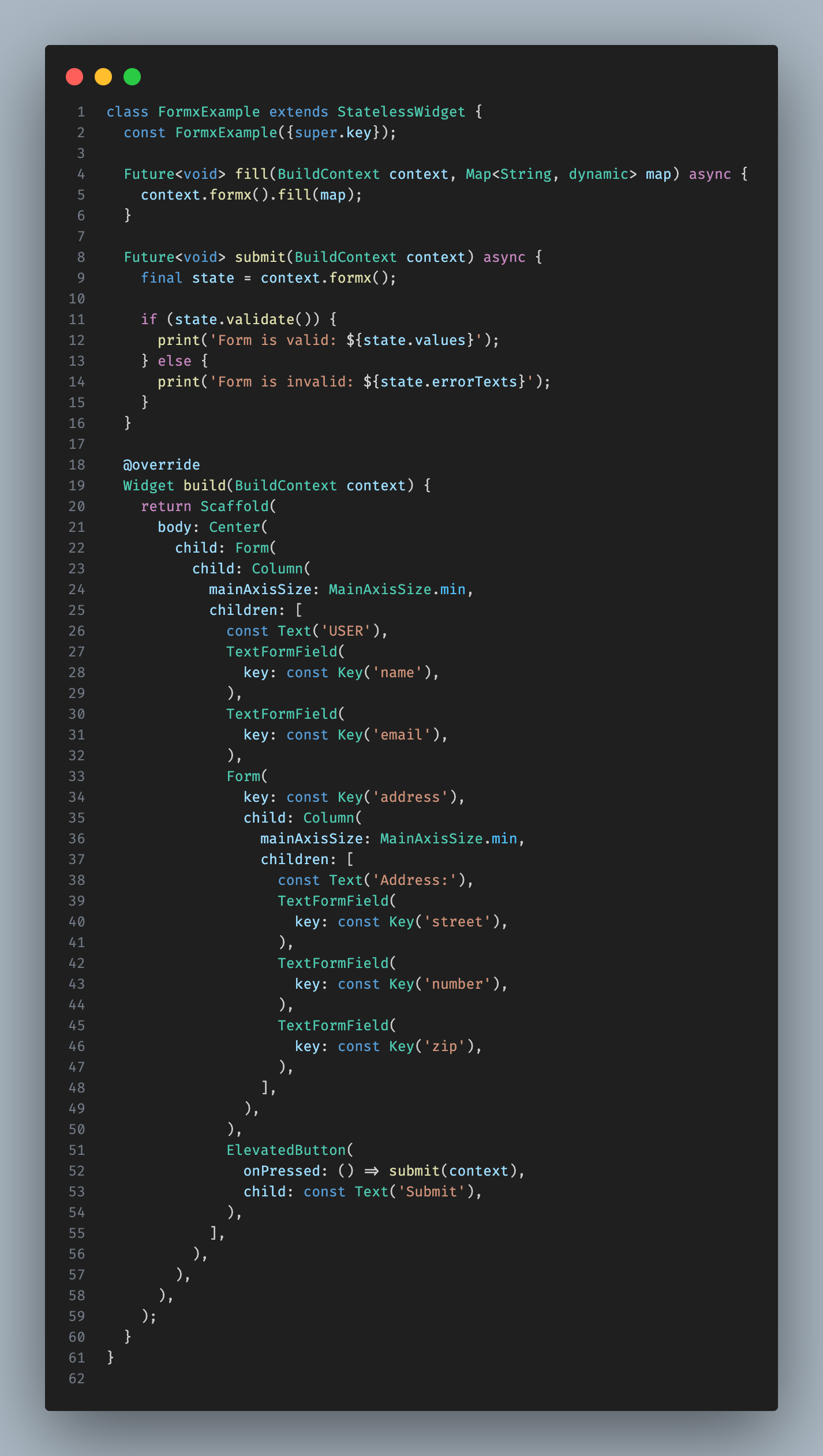
Acessing the state
BuildContext.formx([String? key]) automatically retrieves the appropriate FormState for you, though you can specify a key if necessary.
final state = context.formx();
final addressState = context.formx('address');
final email = context.field('email').value;
Alternatively, use
Formx.of(context)for a traditional approach without visitors, which also rebuilds the widget on form state changes, similar toForm.of(context).
FormState extensions
.value<T>(String key), gets the FormFieldState.value of a specific field..values, a structuredMapwith all the values of the form..initialValues, a structuredMapwith all the initial values of the form..hasInteractedByUser, whether any nested FormFieldState.hasInteractedByUser..hasError, whether any nested FormFieldState.hasError..isValid, whether all nested FormFieldState.isValid..errorTexts, a flatMapwith all nested FormFieldState.errorText.operator [key], operator to get a specific FormFieldState by it's key value.operator [key] = value, operator to set any nested form/field value(s) directly.
FormxState extension type
FormxState is an inline-class that redeclares some of the FormState methods:
.validate([List<String>? keys]).save([List<String>? keys]).reset([List<String>? keys])
These methods function identically to their original counterparts but extend their effects to nested forms. Using FormState.validate only validates the top-level form, whereas FormxState.validate also validates any nested forms.
You have the option to specify a list of keys with these methods to target specific forms or fields for validation, saving, or resetting.
You can redeclare any FormState to a FormxState by using FormxState(formState) type extension.
FormFieldState extensions
.setErrorText(String? errorText), sets the field errorText programmatically. RequiresValidator.
Validator class
Looking for a way to create validators declaratively? The Validator class provides a readable and declarative approach to defining validation rules for your Dart applications.
TextFormField(
validator: Validator<String>(
isRequired: true,
test: (value) => value.isEmail,
),
),
For the one-liners, the modifiers allows you to chain your validators.
TextFormField(
validator: Validator().required().email(),
),
You can also easily create custom validators:
extension CustomValidators on Validator<T> {
Validator<T> myValidator([String? requiredText]) {
return test((value) => /* your logic here */, requiredText);
}
}
Customizing
// You can set a default `requiredText`/`invalidText` for all validators:
Validator.defaultRequiredText = 'This field is required';
Validator.defaultInvalidText = 'This field is invalid';
// You can also modify the errorText of a validator:
Validator.modifier = (validator, errorText) => errorText; // good for translations
// And disable them all:
Validator.disableOnDebug = true; // only works on debug mode
Modifiers
.test(bool Function(T value) test).number(bool Function(num value) test).datetime(bool Function(DateTime value) test).required.email.url.phone.creditCard.cpf.cnpj.date.alpha.numeric.alphanumeric.hasAlpha.hasNumeric.hasAlphanumeric.hasUppercase.hasLowercase.hasSpecialCharacter.minLength(int length).maxLength(int length).minWords(int words).maxWords(int words).minNumber(num number).maxNumber(num number).isAfter(DateTime date).isBefore(DateTime date)
Validators, Sanitizers & Helpers extensions
Formx comes bundled with a set of built-in validators and sanitizers, which you can use to validate and sanitize your form fields.
String
.isEmail.isPhone.isUrl.isDate.isCreditCard.isCpf.isCnpj.isNumeric.isAlpha.isAlphanumeric.hasAlpha.hasNumeric.hasAlphanumeric.hasUppercase.hasLowercase.hasSpecialCharacters.equalsIgnoreCase(String).onlyNumeric(removes all non-numeric characters).onlyAlpha(removes all non-alphabetic characters).onlyAlphanumeric(removes all non-alphanumeric characters)
Map
.indentedfor a map view that indents when printed..indentedTextfor getting an indented text..deepMapfor mapping nested maps..cleanfor values that arenullor empty string/iterable/map..cleanedfor a new map with allnullor empty values removed.
Deeply recases all your map keys:
.camelCase"camelCase".constantCase"CONSTANT_CASE".sentenceCase"Sentence case".snakeCase"snake_case".dotCase"dot.case".paramCase"param-case".pathCase"path/case".pascalCase"PascalCase".headerCase"Header-Case".titleCase"Title Case"
List<Widget>
.keepAliveusually needed for building forms withPageView.children..expandedusually needed for building forms with Column.children or Row.children.
Contributing
Contributions to formx are welcome! Whether it's bug reports, feature requests, or pull requests, all "forms" of collaboration can help make formx better for everyone.
Libraries
- formx
- Build, validate and fill forms easily with extended Form and TextFormField.