
Flutter Control is complex library to maintain App and State management.
Library merges multiple functionality under one hood. This approach helps to tidily bound separated logic into complex solution.
import 'package:flutter_control/control.dart';
- App State Management - Managing application state, localization, theme and other global App changes.
- Widget State Management - UI / Logic separation. Controlling State and UI updates.
- Dependency Injection - Factory, Singleton, Lazy initialization and Service Locator.
- Navigation and Routing - Routes, transitions and passing arguments to other pages and Models.
- Localization - Json based localization with basic formatting.
- Event System - Global event/data stream to easily notify app events.
Flutter Control Core
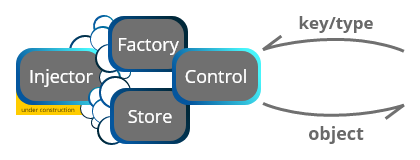
ControlMain static class. InitializesControlFactorythat serves as Service Locator with Factory and object initialization.ControlFactoryIs responsible for creating and storing givenfactoriesandentries. Then locating this services and retrieving on demand.
Factory has own Storage. Objects in this storage are accessible via custom key or Type. Best practice is to use Type as a key.ControlModuleholds all resources for custom extension. Factory will load thesemodulesand stores dependencies.
Control.initControl(
entries: {
CounterListControl: CounterListControl(),
},
initializers: {
CounterModel: (_) => CounterModel(),
CounterDetailControl: (args) => CounterDetailControl(model: Parse.getArg<CounterModel>(args)),
},
modules: [
LocalinoModule(LocalinoLive.options()),
],
initAsync: () async {
loadAppConfig();
},
);
ControlRootWraps basic app flow and global state management - Theme, Locale, Home Widget. It's just shortcut to start with Flutter Control.
ControlRoot(
theme: MaterialThemeConfig(
themes: {
Brightness.light: () => ThemeData.light(),
Brightness.dark: () => ThemeData.dark(),
}
),
states: [
AppState.init.build(builder: (_) => LoadingPage()),
AppState.main.build(
builder: (_) => DashboardPage(),
transition: TransitionToDashboard(),
),
],
builders: [
Localino,
],
app: (context, home) => MaterialApp(
title: setup.title('app_name', 'Example App'),
theme: context.themeConfig?.value,
home: home,
locale: LocalinoProvider.instance.currentLocale,
supportedLocales: setup.supportedLocales,
localizationsDelegates: [
...
],
),
);
-
ControlWidgetis base abstract class (StatefulWidget) to maintain larger UI parts of App (Pages and complex Widgets). Widget is created with defaultControlStateto correctly reflect lifecycle of Widget to Models. So there is no need to create custom State.
Widget will init all containing Models and pass arguments to them.
ControlWidgethas mutable State to control state management. -
SingleControlWidgetis focused to single ControlModel. But still can handle multiple Controls. -
ControllableWidget- Subscribes to one or moreObservable- ObservableComponent, ActionControl, FieldControl, Stream, Future, Listenable
Whenever state of ControlObservable is changed, this Widget is rebuild. -
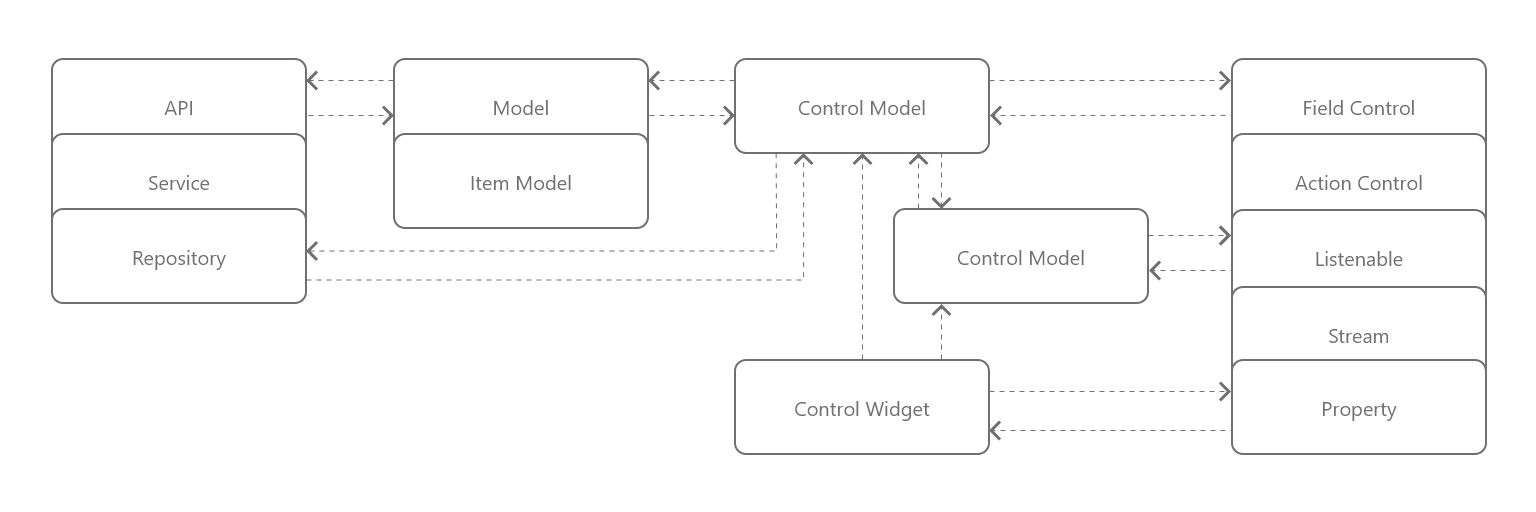
ControlModelis base class to maintain Business Logic parts.
BaseControlis extended version of ControlModel with more functionality. Mainly used for robust Logic parts.
BaseModelis extended but lightweight version of ControlModel. Mainly used to control smaller logic parts.\
-
ControlObservableandControlSubscriptionare core underlying observable system and abstract base for other concrete robust implementations - mainly ActionControl and FieldControl.
WithControlBuilderandControlBuilderGroupon the Widget side. These universal builder widgets can handle all possible types of Notifiers. -
ActionControlis one type of Observable used in this Library. It's quite lightweight and is used to notify listeners about value changes.
Has tree main variants - Single (just one listener), Broadcast (multiple listeners) and Empty (null).
4th variant is provider that subscribe to global BroadcastProvider.
On the Widget side isControlBuilderto dynamically build Widgets. It's also possible to useControlBuilderGroupto group values of multiple Observables.
Upon dismiss of ActionControl, everyControlSubscriptionis closed.
final counter = ActionControl.broadcast<int>(0);
ControlBuilder<int>(
control: counter,
builder: (context, value) => Text('$value'),
);
FieldControlis more robust Observable solution aroundStreamandStreamController. Primarily is used to notify Widgets and to provide events about value changes.
Can listenStream,Futureor subscribe to another FieldControl with possibility to filter and convert values.
FieldControl comes with pre-build primitive variants asStringControl,NumberControl, etc., where is possible to use validation, regex or value clamping. And alsoListControlto work with Iterables.
On the Widget side isFieldBuilderandControlBuilderto dynamically build Widgets. AlsoControlBuilderGroupfor use with multiple Observables. It's also possible to use standardStreamBuilder.
FieldSinkorFieldSinkConverterprovides Sink of FieldControl.
Upon dismiss of FieldControl, everyFieldSubscriptionis closed.
final counter = FieldControl<int>(0);
FieldBuilder<int>(
control: counter,
builder: (context, value) => Text(value.toString()),
);
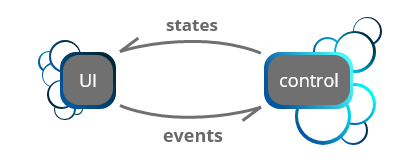
Structure below shows how data and events flows between UI and Controls. ControlWidget can use multiple ControlModels with multiple Models, Streams and Observables..
Localization
- Moved to Localino package.
Global Event System
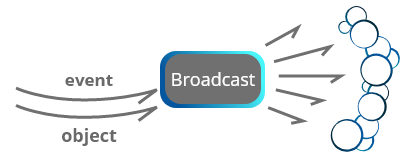
ControlBroadcastEvent stream across whole App. Default broadcaster is part ofControlFactoryand is stored there.
Every subscription is bound to it'skeyand/orTypeso notification to Listeners arrives only for expected data.
WithBroadcastProvideris possible to subscribe to any stream and send data or events from one end of App to the another, even to Widgets and their States. Also custom broadcaster can be created to separate events from default stream.
BroadcastProvider.subscribe<int>('on_count_changed', (value) => updateCount(value));
BraodcastProvider.broadcast('on_count_changed', 10);
Navigation and Routing
ControlRouteSpecifiesRoutewithTransitionand WidgetBuilder forRouteHandler. Handler then solves navigation and passes args to Widgets and Models.
UseDependencymixin to enable this argument injection into ControlWidget.- Routes are stored in
RouteStore.
Control.initControl(
modules: [
RoutingModule(
[
ControlRoute.build<DetailPage>(builder: (_) => DetailPage()),
ControlRoute.build(key: 'detail_super', builder: (_) => DetailPage()).path('super').viaTransition(_transitionBuilder),
]
);
],
);
class ListPage extends ControlWidget with RouteControl {
Widget build(CoreContext context){
...
onPressed: () => context.routeOf<DetailPage>().openRoute();
onPressed: () => context.routeOf<DetailPage>().viaTransition(_transitionBuilder).openRoute();
onPressed: () => context.routeOf(key: 'detail_super').openRoute();
...
};
}
- Initial app routing is handled with
RoutingProvider, that stores initial route for later use (after app is initialized, auth confirmed, etc.).
ControlRoot(
builder(context, home) => MaterialApp(
onGenerateRoute: (settings) => context.generateRoute(settings, root: () => MaterialPageRoute(builder: (_) => home)),
)
);
class HomePage extends ControlWidget {
void onInit(CoreContext context, Map args){
//Restores initial route navigation from from onGenerateRoute
context.root.restoreNavigation();
}
}
Other classes
DisposeHandler- mixin for any class, helps with object disposing.PrefsProvider- mixin for any class, helps to store user preferences - based on shared_preferences.ParseHelps to parse json primitives and Iterables. Also helps to look up Lists and Maps for objects.FutureBlockRetriggerable delay.DelayBlockDelay to wrap a block of code to prevent 'super fast' completion and UI jiggles.
Check set of Flutter Control Examples at Git repository for more complex solutions and how to use this library. More examples comes in future..