Dart package for Azure AD Sign In
You can support me by purchasing a coffee if this package has been helpful to you.
Table of content
- 1 Platform Support
- 2 Features
- 3 Authentication Flow
- 4 Getting started
- 5 Usage
- 6 Where to go from here
- 7 Bugs and issues
1 Platform Support
| Dart | Flutter | Dart - Tested on | Flutter - Tested on | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Android | :heavy_multiplication_x: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | Tested on Pixel 4 (Emulator) and Xiaomi 9T. |
| iOS | :heavy_multiplication_x: | :heavy_minus_sign: | - | Not yet tested, but should work. |
| Linux | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | Tested on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. | Tested on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. |
| MacOS | :heavy_minus_sign: | :heavy_minus_sign: | Not yet tested, but should work. | Not yet tested, but should work. |
| Web | :heavy_multiplication_x: | :heavy_multiplication_x: | Uses dart.io for the HttpServer, will not work. | Uses dart.io for the HttpServer, will not work. |
| Windows | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | Tested on Windows 11. | Tested on Windows 11. |
2 Features
dart_azure_ad_sign_in allows Flutter and Dart apps to obtain authentication tokens for authorized access to protected resources like Azure web APIs. The package can simply be used without any configuration to gain the same access you would have with the az cli, or it can be configurated to modify the access.
Check out the Dart and Flutter example app to have a quick view of how this package could be used. dart_azure_ad_sign_in_poc
3 Authentication Flow
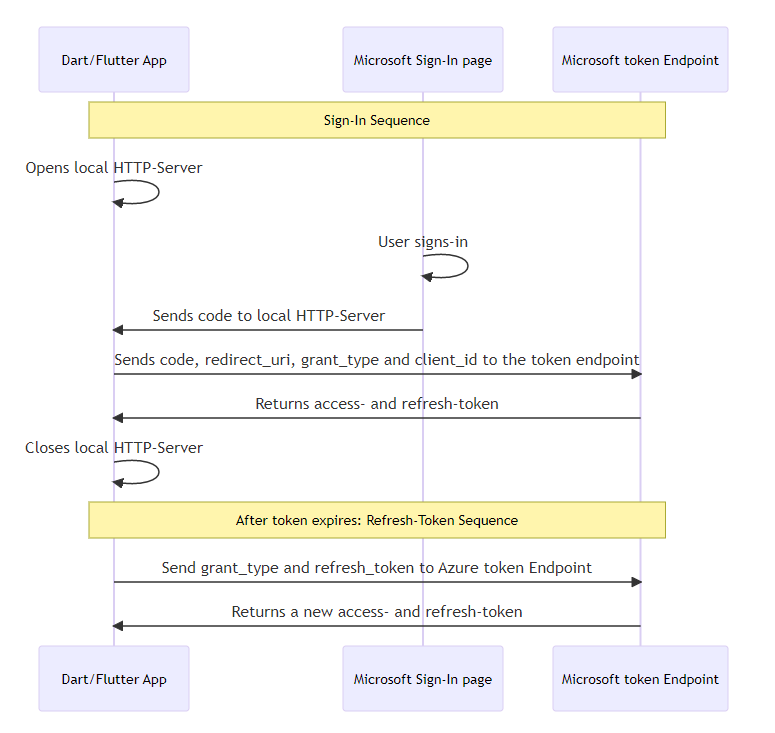
4 Getting started
4.1 Installation
Go to Installing to get the newest version.
4.2 Import
Import the package:
import 'package:dart_azure_ad_sign_in/dart_azure_ad_sign_in.dart';
4.3 Android Settings
4.3.1 Networking
As this app uses the internet, networking needs to be enabled in the AndroidManifest.xml.
<manifest xmlns:android...>
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application ...
</manifest>
4.3.2 Cleartext traffic
This app will open a local HTTP Server, which accepts cleartext traffic, allowing an insecure connection to only the localhost by creating res/xml/network_security_config.xml and configuring it as follows.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<network-security-config>
<domain-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="true">
<domain includeSubdomains="true">localhost</domain>
</domain-config>
</network-security-config>
Then load the file into your AndroidManifest.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest ...>
<application
...
android:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"
...>
...
</application>
</manifest>
4.4 iOS Settings
4.4.1 Networking
Not necessary for iOS.
4.4.2 Cleartext traffic
This app will open a local HTTP Server, which accepts cleartext traffic, allowing an insecure connection to only the localhost by creating a specific rule as following info.plist.
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<false/>
<key>NSExceptionDomains</key>
<dict>
<key>localhost</key>
<dict>
<key>NSIncludesSubdomains</key>
<true/>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionAllowsInsecureHTTPLoads</key>
<true/>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionMinimumTLSVersion</key>
<string>TLSv1.1</string>
</dict>
</dict>
</dict>
4.5 macOS Settings
4.5.1 Networking
As this app uses the internet, networking needs to be enabled in the .entitlements.
<key>com.apple.security.network.client</key>
<true/>
4.5.2 Cleartext traffic
This app will open a local HTTP Server, which accepts cleartext traffic, allowing an insecure connection to only the localhost by creating a specific rule as following info.plist.
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<false/>
<key>NSExceptionDomains</key>
<dict>
<key>localhost</key>
<dict>
<key>NSIncludesSubdomains</key>
<true/>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionAllowsInsecureHTTPLoads</key>
<true/>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionMinimumTLSVersion</key>
<string>TLSv1.1</string>
</dict>
</dict>
</dict>
4.6 Windows Settings
No further settings are required.
4.7 Linux Settings
No further settings are required.
5 Usage
5.1 AzureSignIn instance creation and configuration
The class itself is very flexible, no parameters need to be set and it will use the az cli configuration. For information on all available variables in this class, refer to 5.5 AzureSignIn Variables
5.1.1 Creating an instance without parameters (using az cli default settings)
final azureSignIn = AzureSignIn();
5.1.2 Creating an instance with parameters
Parameters for the Authentication and local Http-Server can be set if needed.
final azureSignIn = AzureSignIn(
// The Application (client) ID that the Azure portal – App registrations page assigned to your app.
// Optional, uses the az cli client id: '04b07795-8ddb-461a-bbee-02f9e1bf7b46'
clientId: '04b07795-8ddb-461a-bbee-02f9e1bf7b46',
// A list of scopes that you want the user to consent to.
// Optional, uses the az cli scope: ['https://management.core.windows.net//.default', 'offline_access', 'openid', 'profile']
scope: [
'https://management.core.windows.net//.default',
'offline_access',
'openid',
'profile',
],
// Port of the Local HttpServer which will receive the code after sign in.
// Optional, uses the port 5000
port: 5000,
// Response of the Local HttpServer, which the user will see in the browser after successful sign in.
// Optional, uses 'Sign In successful. This window can now be closed.'
serverSuccessResponse: '<h1>Sign In successful.</h1><p>This window can now be closed.</p>',
// Response of the Local HttpServer, which the user will see in the browser after sign in failure.
// Optional, uses 'Sign In failed. Close this window and try again.'
serverErrorResponse: '<h1>Sign In failed.</h1><p>Close this window and try again.</p>',
// Duration on how long the local HttpServer waits, for the user to sign in before creating a cancelled-token and closing.
// Optional, uses Duration(minutes: 5)
signInTimeoutDuration: Duration(minutes: 5),
);
5.2 Sign In
5.2.1 Get the Microsoft Sign-In page URL
The user needs to sign-in to the Browser, to do so the Sign In URL can be received. If Flutter is being used, this URL could be opened with the url_launcher
// Print the SignIn URL, the user has to open in the browser.
print(azureSignIn.signInUri);
5.2.2 Start the Sign In process
The sign-in will return a new Token.
In the background an HttpServer is started and waits for the code to be received after the sign-in in the Browser,
then the Microsoft token Endpoint will be called with the code and a token is returned.
The Token will always be created, but depending on success or error, different values will be set, see the variable token.status in 5.6. The Token-Entity.
Token token = await azureSignIn.signIn();
5.3 Cancel the Sign In process
The Sign In Process itself has the defined timeout set in the variable azureSignIn.signInTimeoutDuration, but with the following function the user could cancel the Sign in if needed.
The azureSignIn.signIn() will then receive a Token with the information of cancellation in the variable token.status (See more: 5.6. The Token-Entity).
// Cancels the sign-in process.
async azureSignIn.cancelSignIn();
5.4 Refresh a Token
Once the token expires it can be either refreshed by giving it the existing Token or just giving it a refresh-token String.
One of the Values needs to be sent, else a Token with an error status will be returned, see token.status in 5.6. The Token-Entity.
5.4.1 Refresh Token with an existing Token
The Token can be refreshed by using the existing Token
// refresh a token by giving the previous aquired token object.
token = await azureSignIn.refreshToken(token: token);
5.4.2 Refresh Token with the Refresh-Token String
Or if the Token is not available anymore the refresh token can be sent as a String.
// refresh a token by giving the refresh-token as a string.
token = await azureSignIn.refreshToken(refreshToken: refreshTokenString);
5.5 AzureSignIn Variables
Some class variables can be modified while running, some others are read-only.
| Name | Type | Default value | Can be modified | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
azureSignIn.clientId |
String | 04b07795-8ddb-461a-bbee-02f9e1bf7b46 | ✓ | The Application (client) ID that the Azure portal – App registrations page assigned to your app. Uses the az cli client ID by default, no app registration is necessary. |
azureSignIn.scope |
List<String> | [ 'https://management.core.windows.net//.default', 'offline_access', 'openid', 'profile' ] |
✓ | A space-separated list of scopes that you want the user to consent to. For the /authorize leg of the request, this parameter can cover multiple resources. This value allows your app to get consent for multiple web APIs you want to call. Uses the az cli Scopes by default |
azureSignIn.grantType |
String | authorization_code | ✗ | Grant Type for the authorization flow. Must be authorization_code for the authorization code flow. |
azureSignIn.port |
int | 5000 | ✓ | Port of the Local HttpServer which will receive the code after sign-in via a web browser. |
azureSignIn.signInTimeoutDuration |
Duration() | Duration(minutes: 5) |
✓ | Duration on how long the local HttpServer waits, for the user to sign in, before closing. |
azureSignIn.serverSuccessResponse |
String | Sign In successful. This window can now be closed. | ✓ | Response of the Local HttpServer, which the user will see after successfully logging in, can be simple Text or HTML. |
azureSignIn.serverErrorResponse |
String | Sign In failed. Close this window and try again. | ✓ | Response of the Local HttpServer, which the user will see after sign-in failure, can be simple Text or HTML. |
azureSignIn.signInUri |
String | https://login.microsoftonline.com/organizations/oauth2/v2.0/authorize ?client_id=[CLIENT_ID] &response_type=code &redirect_uri=http://localhost:[PORT] &scope=[SCOPE] &response_mode=form_post |
✗ | Getter for the Microsoft Sign-In URL used to Sign In via Browser. Combines azureSignIn.clientId, azureSignIn.port and azureSignIn.scope, which can not be directly modified. |
azureSignIn.signOutUri |
String | https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/v2.0/logout | ✗ | Azure Auth URL used to Sign out from the Browser. |
5.6. The Token-Entity
The Token has multiple fields, some are set in case of success, some in case of failure.
| Name | Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
token.tokenType |
String | Bearer | Indicates the token type value. The only type that Azure AD supports is Bearer |
token.scope |
String | user_impersonation | The scopes that the access_token is valid for. Optional. This parameter is non-standard and, if omitted, the token is for the scopes requested on the initial leg of the flow. |
token.expiresIn |
String | 5084 | How long the access token is valid, in seconds. |
token.extExpiresIn |
String | 5084 | Used to indicate an extended lifetime for the access token and to support resiliency when the token issuance service is not responding. |
token.expiresOn |
String | 1674580651 | Timestamp when the token expires. |
token.notBefore |
String | 1674575266 | The time at which the token becomes valid, represented in epoch time. This time is usually the same as the time the token was issued. Azure AD B2C validates this value and rejects the token if the token lifetime is not valid. |
token.resource |
String | https://management.core.windows.net/ | Resource the token has access to. |
token.accessToken |
String | eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJS... | The requested access token. The app can use this token to authenticate to the secured resource, such as a web API. |
token.refreshToken |
String | 0.AQUAjHBCWE0CK06v4qgD88sl3Z... | An OAuth 2.0 refresh token. The app can use this token to acquire other access tokens after the current access token expires. Refresh tokens are long-lived. They can maintain access to resources for extended periods. |
token.idToken |
String | eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIs... | A JSON Web Token. The app can decode the segments of this token to request information about the user who signed in. The app can cache the values and display them, and confidential clients can use this token for authorization. |
token.foci |
String | 1 | Access to Microsoft Office apps while they have a session on a mobile device using FOCI (Family of Client IDs). |
token.status |
int | 0: Success 1: Azure API error 2: HttpServer error 3: Sign In canceled |
Status of the Token authorization code flow result, can be used for error-handling or giving the user some further information. |
token.error |
String | invalid_grant | An error code string that can be used to classify types of errors, and to react to errors. |
token.errorDescription |
String | AADSTS900144: The request body must contain the following parameter: 'code'... | A specific error message that can help a developer identify the root cause of an authentication error. |
token.errorCodes |
List<dynamic> | [900144] | A list of STS-specific error codes that can help in diagnostics. |
token.errorUri |
String | https://login.microsoftonline.com/error?code=900144 | URL to a Microsoft documentation, concerning the emerged error. |
6 Where to go from here
With the token.accessToken you now have access to the Microsoft APIs.
Read more on the Azure Rest API reference, or check out the Application IDs of commonly used Microsoft applications to add some pre-existing azureSignIn.clientId.
7 Bugs and issues
Please file feature requests and bugs at the issue tracker



