Brick Offline First
Offline First combines SQLite and a remote provider into one unified repository. And, optionally, a memory cache layer as the entry point. The remote provider could query Firebase or REST, hydrate the results to SQLite, and then deliver those SQLite results back to the app. In this way, the app functions identically when it's online or offline:

Models
@ConnectOfflineFirstWithRest decorates the model that can be serialized by one or more providers. Offline First does not have configuration at the class level and only extends configuration held by its providers:
@ConnectOfflineFirstWithRest(
restConfig: RestSerializable(),
sqliteConfig: SqliteSerializable(),
)
class MyModel extends OfflineFirstModel {}
Fields
@OfflineFirst(where:)
Using unique identifiers, where: can connect multiple providers. It is declared using a map between a local provider (key) and a remote provider (value). This is useful when a remote provider only includes unique identifiers (such as "id": 1) of associations, the OfflineFirstRepository can lookup that instance from another source and deserialize into a complete model.
:warning: This is a rare instance where the serializer property name is used instead of the field name, such as last_name instead of lastName.
For a concrete example, SQLite is the local data source and REST is the remote data source:
Given the API:
{ "assoc": {
// These don't have to map to SQLite columns.
// They can also be String uuids that SQLite considers unique
"id": 12345,
"ids": [12345, 6789]
}}
The association can be automatically mapped to SQLite (note the inclusion of data; this will always be "data" as it specifies the in-progress deserialization):
@OfflineFirst(where: {'id' : "data['assoc']['id']"})
final Assoc assoc;
@OfflineFirst(where: {'id' : "data['assoc']['ids']"})
final List<Assoc> assoc;
@OfflineFirst(where:) only applies to associations or iterable associations. If @OfflineFirst(where:) is not defined, the model will attempt to be instantiated by the REST key that maps to the field.
:warning: When @OfflineFirst(where:) is defined, the @Rest(toGenerator:) generator will not feature the field unless a toRest custom generator is defined OR only one pair is defined in the map.
OfflineFirstSerdes
When storing raw data is more optimal than storing it as an association, an OfflineFirstSerdes can be used. For example, a child model has only a few properties but hosts a significant number of computed members and methods:
import 'dart:convert';
class Weight extends OfflineFirstSerdes<Map<int, String>, String> {
final int size;
final String unit;
Weight(this.size, this.unit);
// A fromRest factory must be defined
factory Weight.fromRest(Map<String, dynamic> data) {
if (data == null || data.isEmpty) return null;
final size = double.parse(data.keys.first.toString() ?? '0');
return Weight(size, data.values.first);
}
// A fromSqlite factory must be defined
factory Weight.fromSqlite(String data) => Weight.fromRest(jsonDecode(data));
toRest() => {size: unit};
toSqlite() => jsonEncode(toRest());
}
OfflineFirstSerdes should not be used when the managed data must be queried. Plainly, Brick does not support JSON searches.
Mixins
Some regularly requested functionality doesn't exist in out-of-the-box Brick. This functionality does not exist in the core because it is dependent on remote data formatting outside the scope of Brick or it's non-essential. However, for convenience, these features are available in a mix-and-match support library. As this is not officially supported, please use caution determining if these mixins are applicable to your implementation.
| Mixin | Description |
|---|---|
DeleteAllMixin |
Adds methods #deleteAll and #deleteAllExcept |
DestructiveLocalSyncFromRemoteMixin |
Extends get requests to force resync the remoteProvider to the local providers (also covered by new method #destructiveLocalSyncFromRemote) |
General Usage
import 'package:brick_offline_first/mixins.dart';
class MyRepository extends OfflineFirstRepository with DeleteAllMixin {}
Offline First With Rest Repository
OfflineFirstWithRestRepository streamlines the REST integration with an OfflineFirstRepository. A serial queue is included to track REST requests in a separate SQLite database, only removing requests when a response is returned from the host (i.e. the device has lost internet connectivity). See OfflineFirstWithRest#reattemptForStatusCodes.
The OfflineFirstWithRest domain uses all the same configurations and annotations as OfflineFirst.
Generating Models from a REST Endpoint
A utility class is provided to make model generation from a JSON API a snap. Given an endpoint, the converter will infer the type of a field and scaffold a class. For example, the following would be saved to the lib directory of your project and run $ dart lib/converter_script.dart:
// lib/converter_script.dart
import 'package:brick_offline_first/rest_to_offline_first_converter.dart';
const BASE = "http://0.0.0.0:3000";
const endpoint = "$BASE/users";
final converter = RestToOfflineFirstConverter(
endpoint: endpoint,
);
void main() {
converter.saveToFile();
}
// => dart lib/converter_script.dart
After the model is generated, double check for List<dynamic> and null types. While the converter is smart, it's not smarter than you.
OfflineQueueHttpClient
All requests to the REST provider in the repository first pass through a queue that tracks unsuccessful requests in a SQLite database separate from the one that maintains application models. Should the application ever lose connectivity, the queue will resend all upserted requests that occurred while the app was offline. All requests are forwarded to an inner client.
The queue is automatically added to all OfflineFirstWithRestRepositorys. This means that a queue should not be used as the RestProvider's client, however, the queue should use the RestProvider's client as its inner client:
final client = OfflineQueueHttpClient(
restProvider.client, // or http.Client()
"OfflineQueue",
);
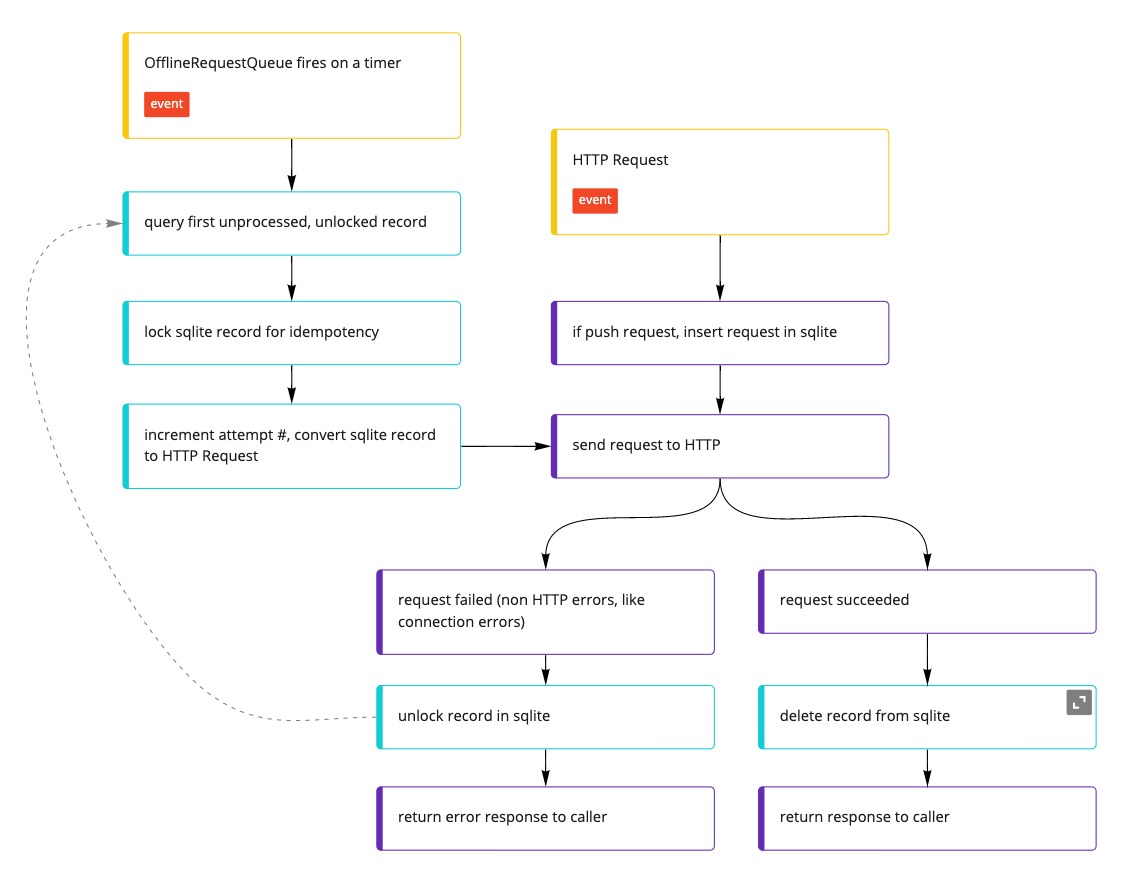
:warning: The queue ignores requests that are not DELETE, PATCH, POST, and PUT. get requests are not worth tracking as the caller may have been disposed by the time the app regains connectivity.
Testing
Responses can be stubbed to and from an OfflineFirstWithRest repository. For convenience, file data can be used to stub JSON responses from an API:
// test/models/api/user.json
{
"user": { "name" : "Thomas" }
}
// test/models/user_test.dart
import 'package:brick_sqlite/testing.dart';
import 'package:my_app/app/repository.dart';
void main() {
group("MySqliteProvider", () {
late MyRepository repository;
setUpAll(() async {
repository = MyRepository(
restProvider: RestProvider(
client: StubOfflineFirstWithRest.fromFiles('http://0.0.0.0:3000', {
'users': 'api/user.json'
}).client,
)
);
await repository.initialize()
});
});
}
By default, the same response is returned for both upsert and get methods, with the only variation being in status code. However, responses can be configured for different methods:
StubOfflineFirstWithRest(
baseEndpoint: 'http://0.0.0.0:3000',
responses: [
StubOfflineFirstRestResponse.fromFile('users', 'api/user.json', StubHttpMethod.get),
StubOfflineFirstRestResponse.fromFile('users', 'api/user-post.json', StubHttpMethod.post),
],
)
Stubbing Without Files
While storing the responses in a file can be convenient and reduce code clutter, responses can be defined inline:
StubOfflineFirstWithRest(
baseEndpoint: 'http://0.0.0.0:3000',
responses: [
StubOfflineFirstRestResponse('users', '{"name":"Bob"'),
StubOfflineFirstRestResponse('users', '{"name":"Alice"'),
],
)
Handling Endpoint Variations
Variants in the endpoint must be explicitly declared. For example, /user, /users, /users?by_first_name=Guy are all different. When instantiating, specify any expected variants:
StubOfflineFirstRestResponse<User>(
endpoints: ["user", "users", "users?by_first_name=Guy"]
)
Stubbing Multiple Models
Rarely will only one model need to be stubbed. All classes in an app can be stubbed efficiently using StubOfflineFirstWithRest:
setUpAll() async {
final config = {
User: ['user', 'users'],
// Even individual member endpoints must be declared for association fetching
// REST endpoints are manually configured, so the content may vary
Hat: ['hat/1', 'hat/2', 'hats'],
}
final responses = config.entries.map((modelConfig) {
return modelConfig.value.map((endpoint) {
return StubOfflineFirstRestResponse.fromFile(
'api/${modelConfig.key.toString().toLowerCase()}.json',
endpoint: endpoint,
);
});
}).expand((e) => e);
final client = StubOfflineFirstWithRest(
baseEndpoint: 'http://0.0.0.0:3000',
responses: responses,
).client;
}
FAQ
Why can't I declare a model argument?
Due to an open analyzer bug, a custom model cannot be passed to the repository as a type argument.
Unsupported Field Types
- Any unsupported field types from
RestProviderandSqliteProvider - Future iterables of future models (i.e.
Future<List<Future<Model>>>.